Kramer TP-410 User manual
Other Kramer Transmitter manuals

Kramer
Kramer WP-110xl User manual

Kramer
Kramer Cobra TS2 User manual

Kramer
Kramer TA User manual

Kramer
Kramer 675T User manual

Kramer
Kramer 691 User manual

Kramer
Kramer 691 User manual

Kramer
Kramer SID-X1N User manual
Kramer
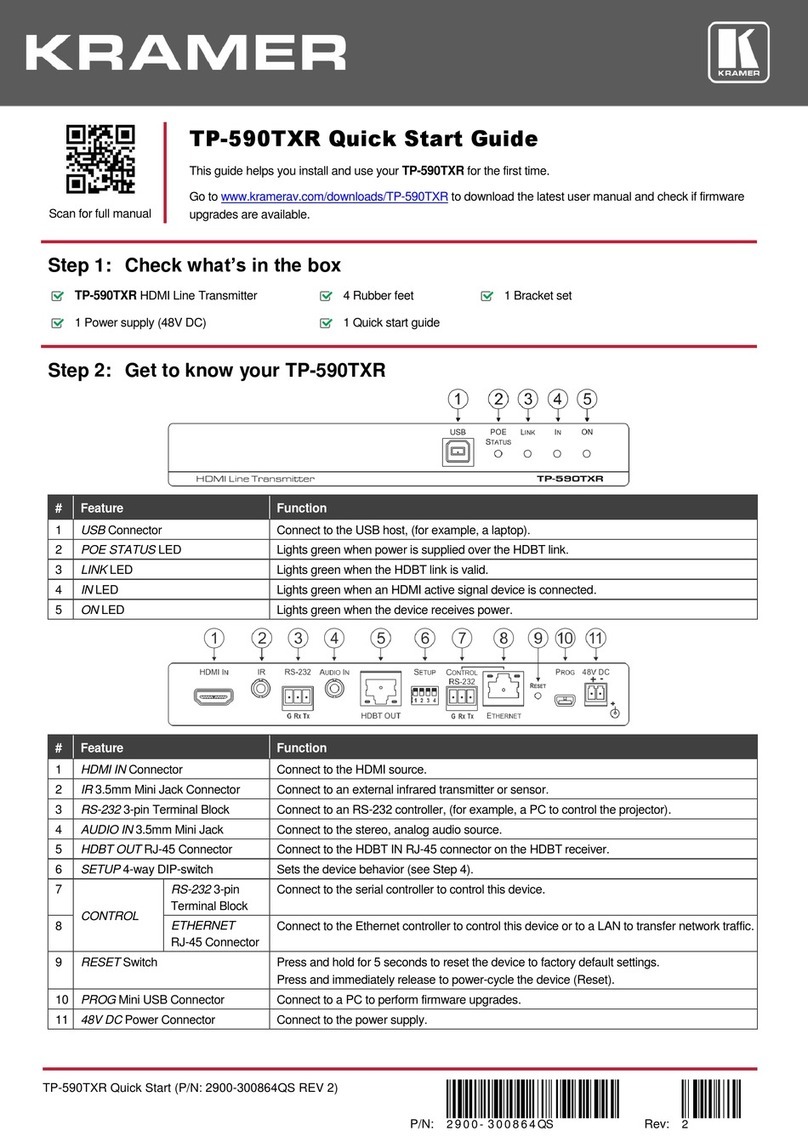
Kramer TP-590Txr User manual

Kramer
Kramer TOOLS TP-104 User manual

Kramer
Kramer WP-871xr User manual

Kramer
Kramer TP-121EDID User manual

Kramer
Kramer 610T User manual

Kramer
Kramer TP-551N User manual

Kramer
Kramer PT-572HDCP+ User manual
Kramer
Kramer SID-VGA User manual

Kramer
Kramer TP-121EDID User manual

Kramer
Kramer TP-210 User manual

Kramer
Kramer TP-45EDID User manual

Kramer
Kramer TP-205A User manual

Kramer
Kramer 614T User manual
Popular Transmitter manuals by other brands

Dejero
Dejero EnGo 3x manual

Rosemount
Rosemount 4600 Reference manual

Speaka Professional
Speaka Professional 2342740 operating instructions

trubomat
trubomat GAB 1000 instruction manual

Teledyne Analytical Instruments
Teledyne Analytical Instruments LXT-380 instructions
Rondish
Rondish UT-11 quick start guide