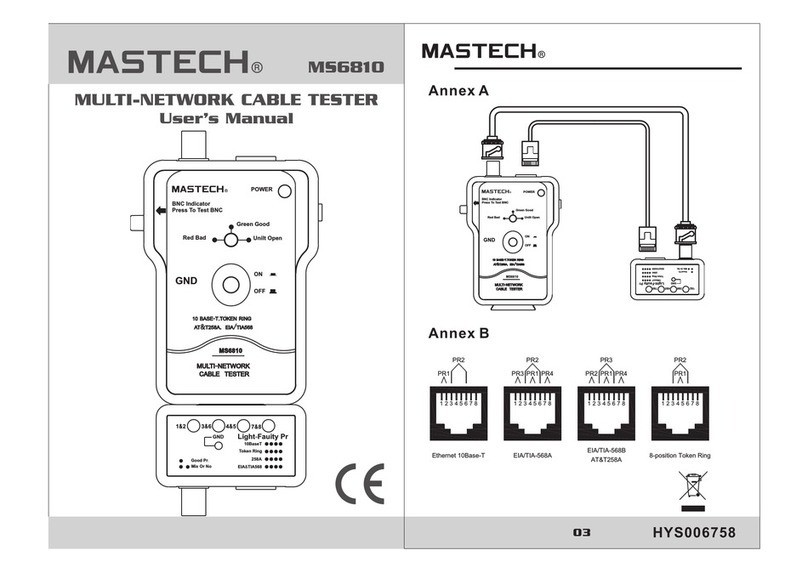
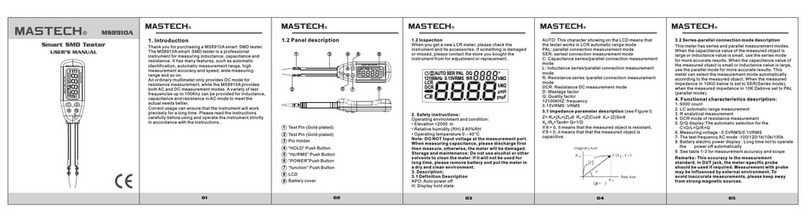
15 16
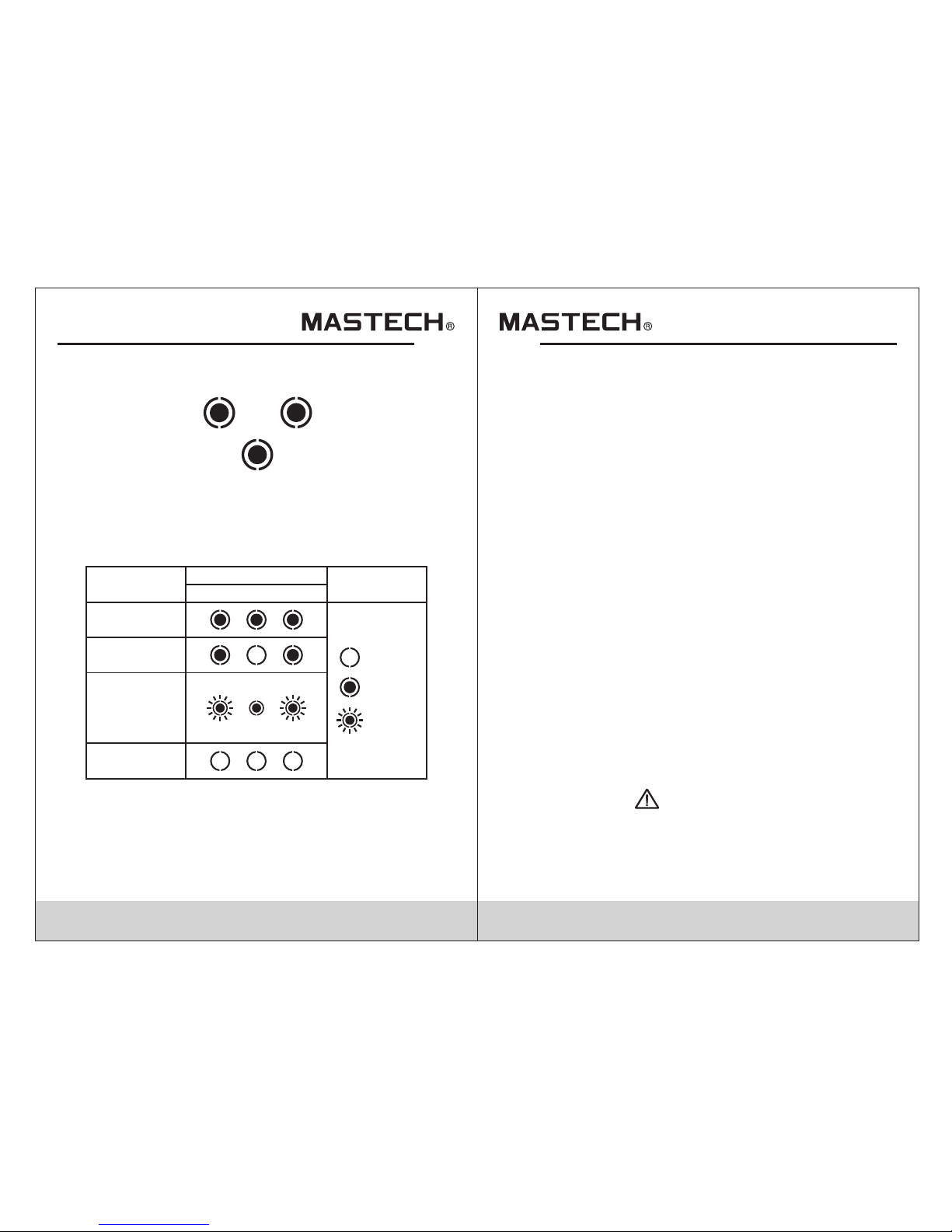
Voltage drop (V ) measurement
Dummy load shall be used in the circuit to
measure the load phase voltage and then calculate
the voltage drop. The voltage drop and load phase
voltage will be displayed when the load reaches
12A, 15A and 20A.
In terms of qualified circuit, when measurement
is made in the most remote socket from the
switchboard, the voltage drop shall be less than 5%.
During the measurement of the remaining sockets
of the same area, the farthest socket from the
switchboard shall be measured first and then other
measurements shall be made from the distant to
the near. The reading of the voltage drop shall be
shown on the downward trend.
If the voltage drop exceeds 5% and no obvious
drop of reading is found during the measurement
made near the switchboard, it indicates that the
first connection point goes wrong. In this case,
perform a visual inspection of the wire connection
among the first connection point, equipment and
switchboard and the connection of breaker
(air-break switch). Usually, a high impedance point
generates heat. To locate this problem, infrared
radiation thermometer can be used. In addition, we
can directly measure the voltage on both sides of
the breaker (air-break switch) to locate the point of
failure.
d If the voltage drop exceeds 5%, and during the
measurement made near the switchboard, the
reading drops constantly and no obvious change
is found between the two sockets, it indicates that
the lead wire diameter is too small compared with
the transmission distance, the transmission
distance is too long or the circuit is overloaded.
Under such circumstances, check the cable to see
if the lead wire diameter complies with the required
standard, and measure the lead wire current to see
if it is overloaded.
If the voltage drop exceeds 5% and there is an
obvious change of voltage drop reading between
the two sockets, it indicates that a high impedance
point exists between the two sockets. Usually,
problems are found at the contact, such as poor
connection, loose connector, or socket problem.