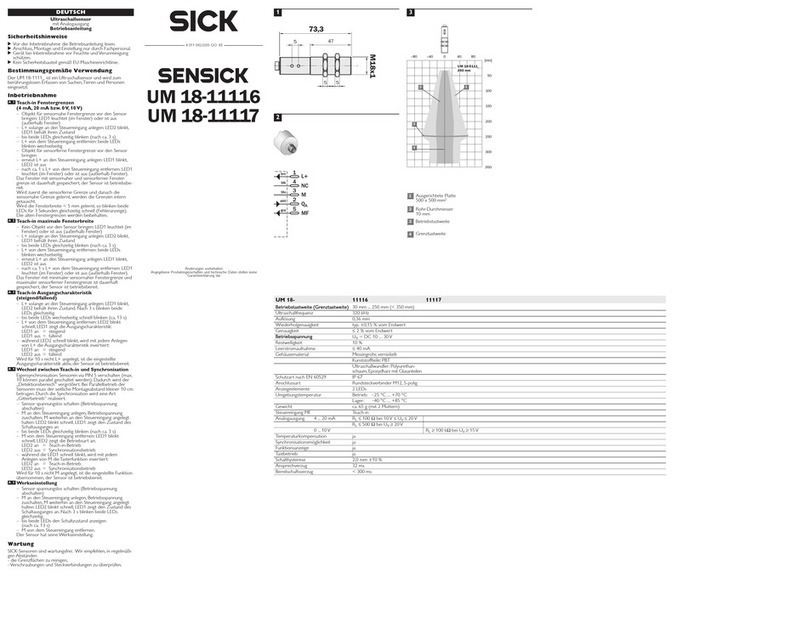
4.4.3 OSSDs....................................................................................... 40
4.4.4 Control inputs........................................................................... 41
4.4.5 Universal inputs, universal outputs, universal I/Os.............. 44
4.4.6 Restart interlock...................................................................... 44
4.4.7 External device monitoring (EDM).......................................... 44
4.5 Integration into the network..................................................................... 45
4.5.1 Network topology..................................................................... 45
4.5.2 Network services and ports.................................................... 45
4.6 Testing plan............................................................................................... 45
4.6.1 Planning the thorough check during commissioning and in
certain situations..................................................................... 46
4.6.2 Planning the regular thorough check..................................... 47
4.6.3 Notes on the tests................................................................... 47
5 Mounting............................................................................................. 51
5.1 Mounting the heat sink............................................................................ 51
5.2 Mounting the device................................................................................. 51
6 Electrical installation........................................................................ 53
6.1 Connecting................................................................................................ 53
6.1.1 System connection.................................................................. 53
6.1.2 Ethernet connection................................................................ 54
7 Configuration..................................................................................... 55
7.1 Delivery state............................................................................................ 55
7.2 Safety Designer configuration software.................................................. 55
7.2.1 Installing Safety Designer....................................................... 55
7.2.2 Creating a project..................................................................... 55
7.2.3 User interface.......................................................................... 56
7.2.4 Configuring devices online...................................................... 56
7.2.5 Configuring devices offline...................................................... 57
7.2.6 User groups.............................................................................. 57
7.3 Add device tile........................................................................................... 58
7.4 Open the device window – configure devices......................................... 58
7.5 Overview.................................................................................................... 59
7.6 Network settings....................................................................................... 60
7.6.1 Ethernet.................................................................................... 60
7.7 Reading configuration.............................................................................. 60
7.8 Identification............................................................................................. 60
7.9 Monitoring settings................................................................................... 61
7.10 3D editor.................................................................................................... 63
7.10.1 Adjusting the mounting settings............................................. 65
7.10.2 Calibration data and Contours................................................ 66
7.10.3 Fields and ROI.......................................................................... 67
7.11 Inputs and outputs, local......................................................................... 70
7.11.1 Output signals.......................................................................... 70
CONTENTS
4O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | safeVisionary2 8025919/1I9E/2023-01-09 | SICK
Subject to change without notice