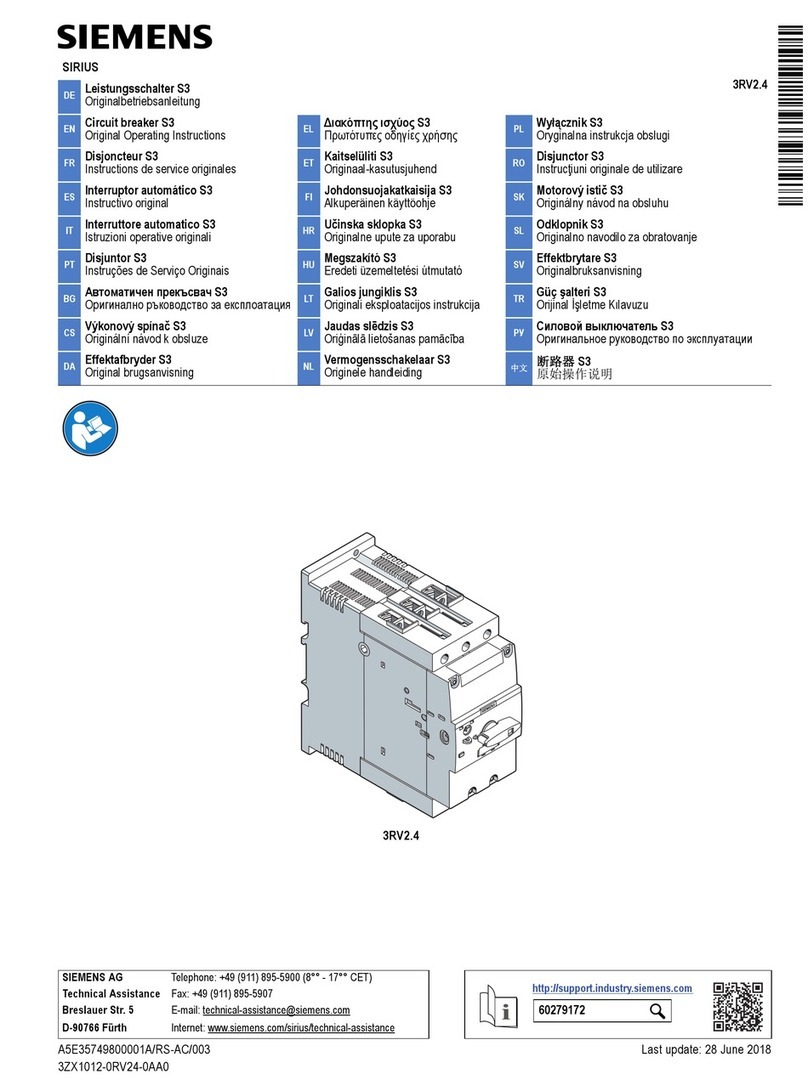
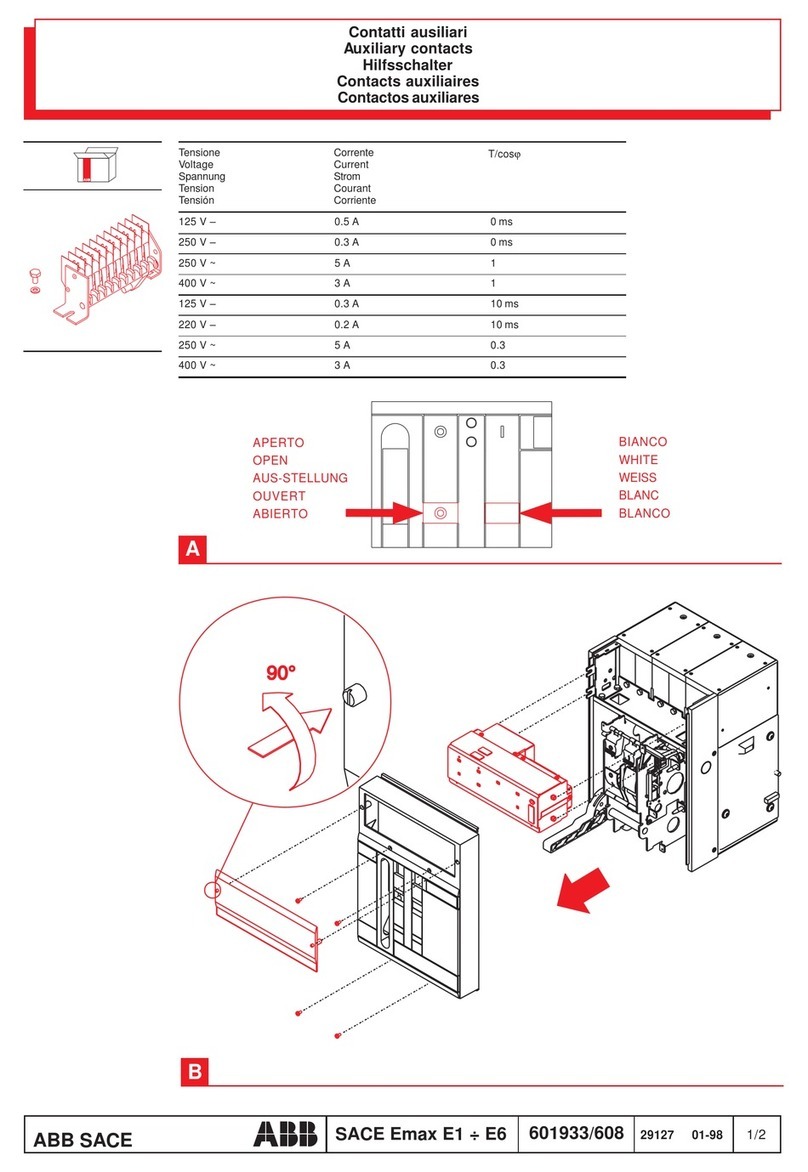
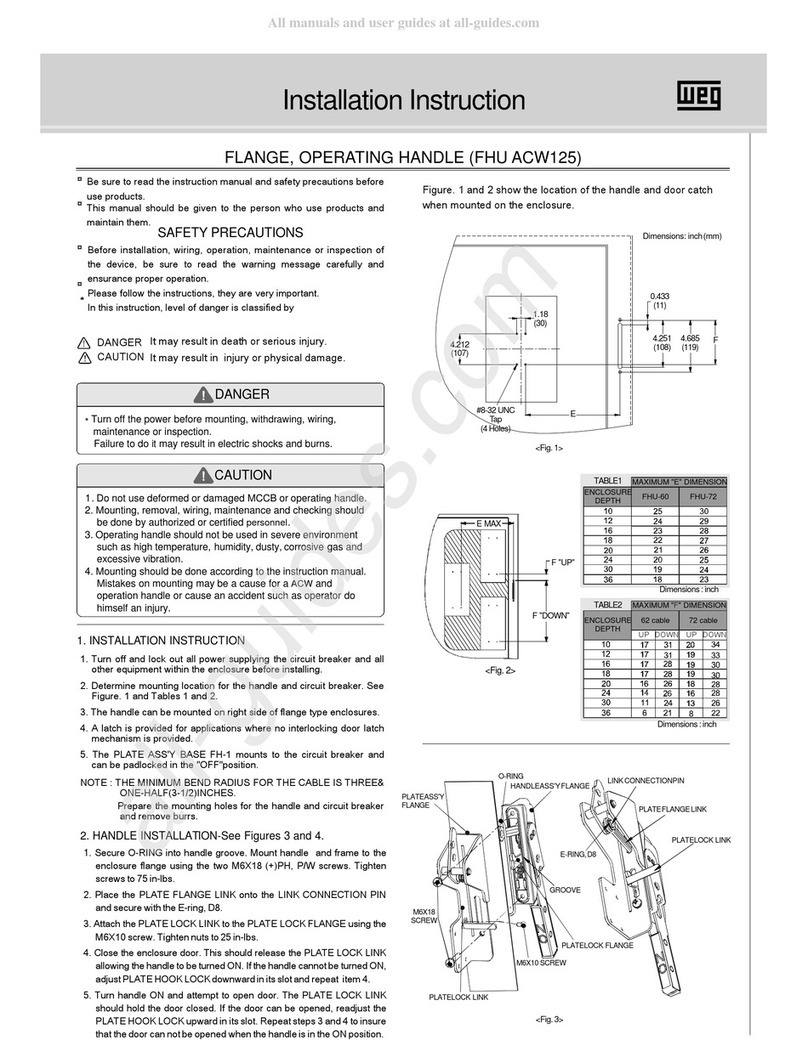
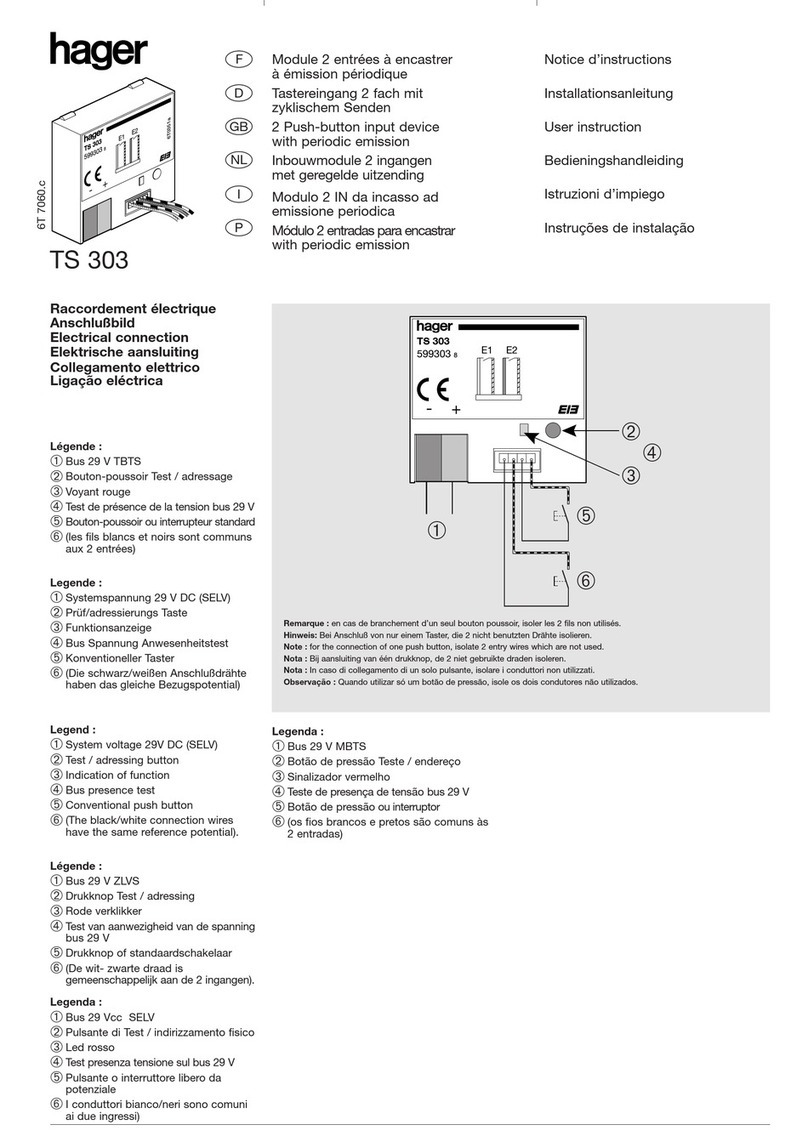
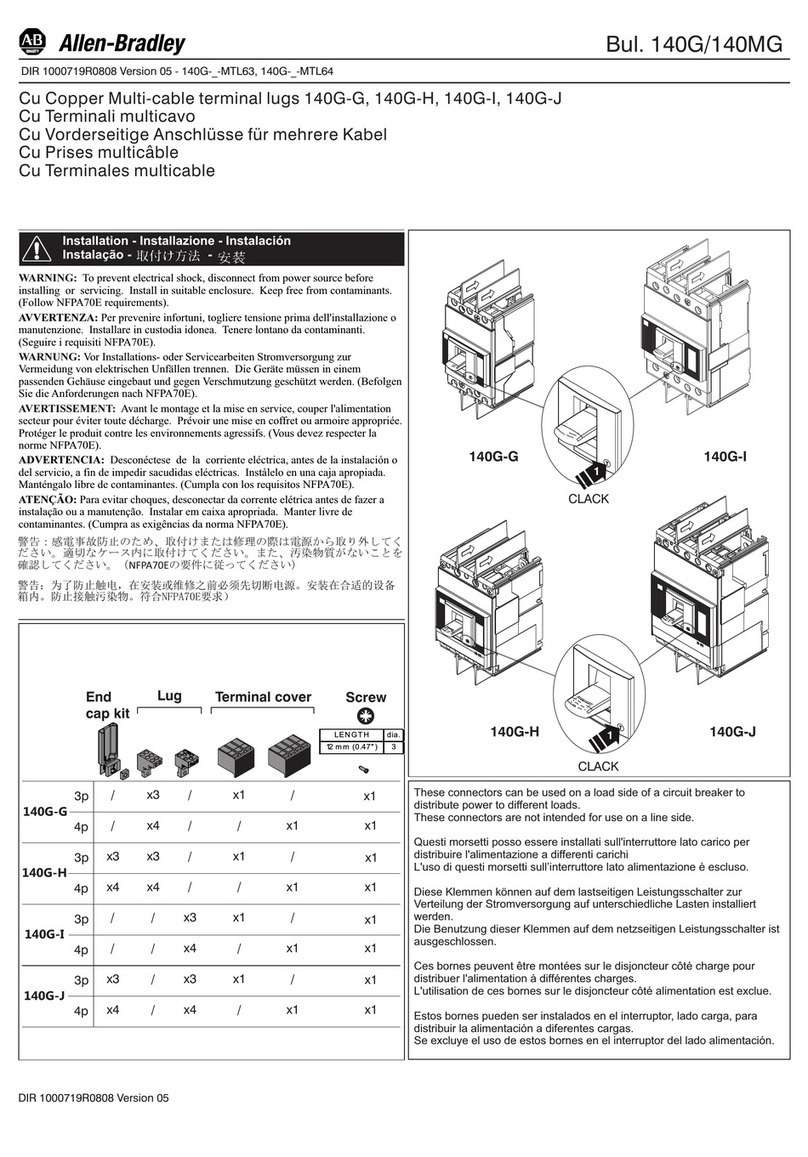
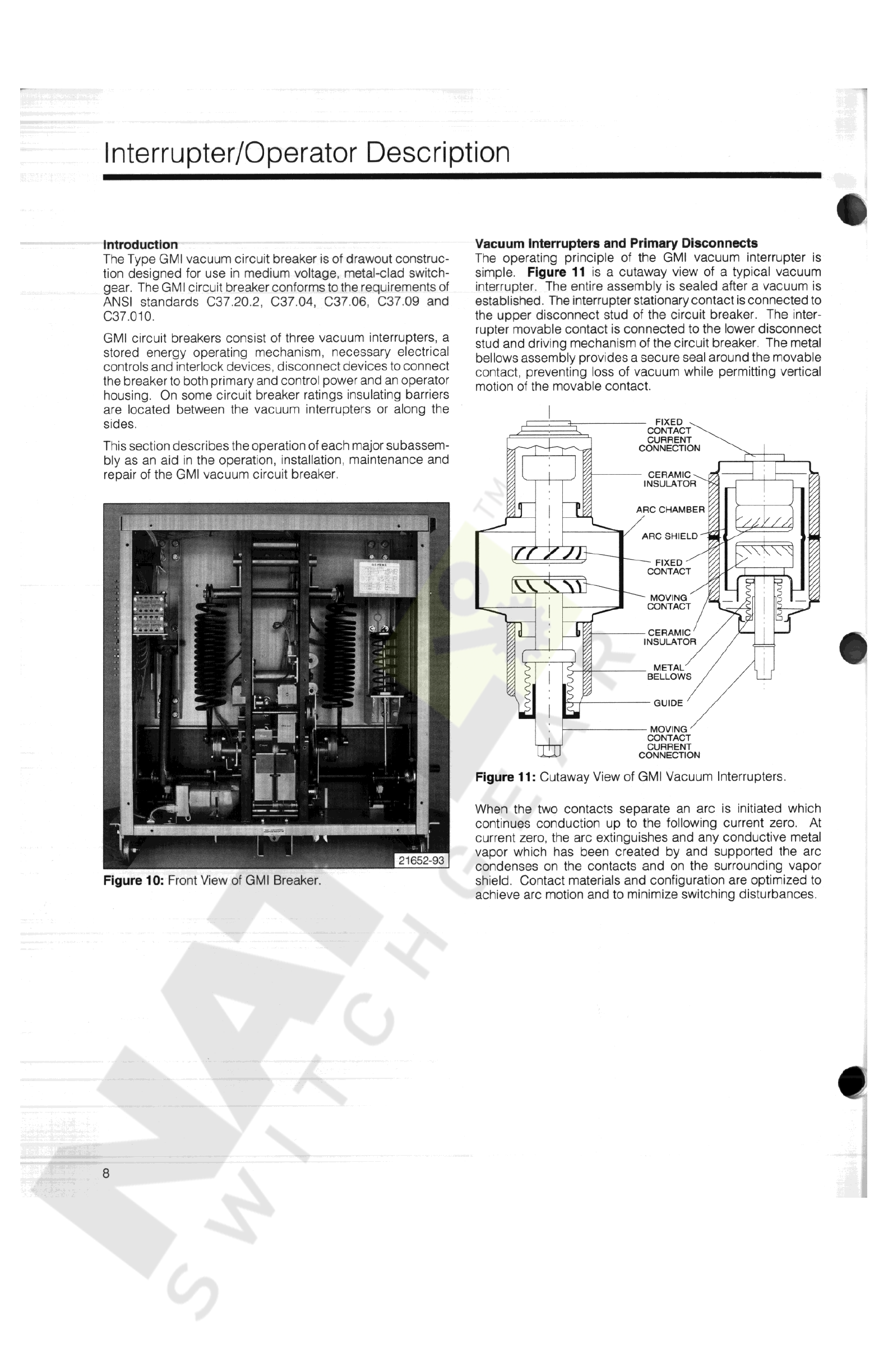
Siemens GMI Series Owner's manual
Other Siemens Circuit Breaker manuals

Siemens
Siemens 3VF9423–1Q 0 Series User manual
Siemens
Siemens 3VA911-0KB01 Series User manual
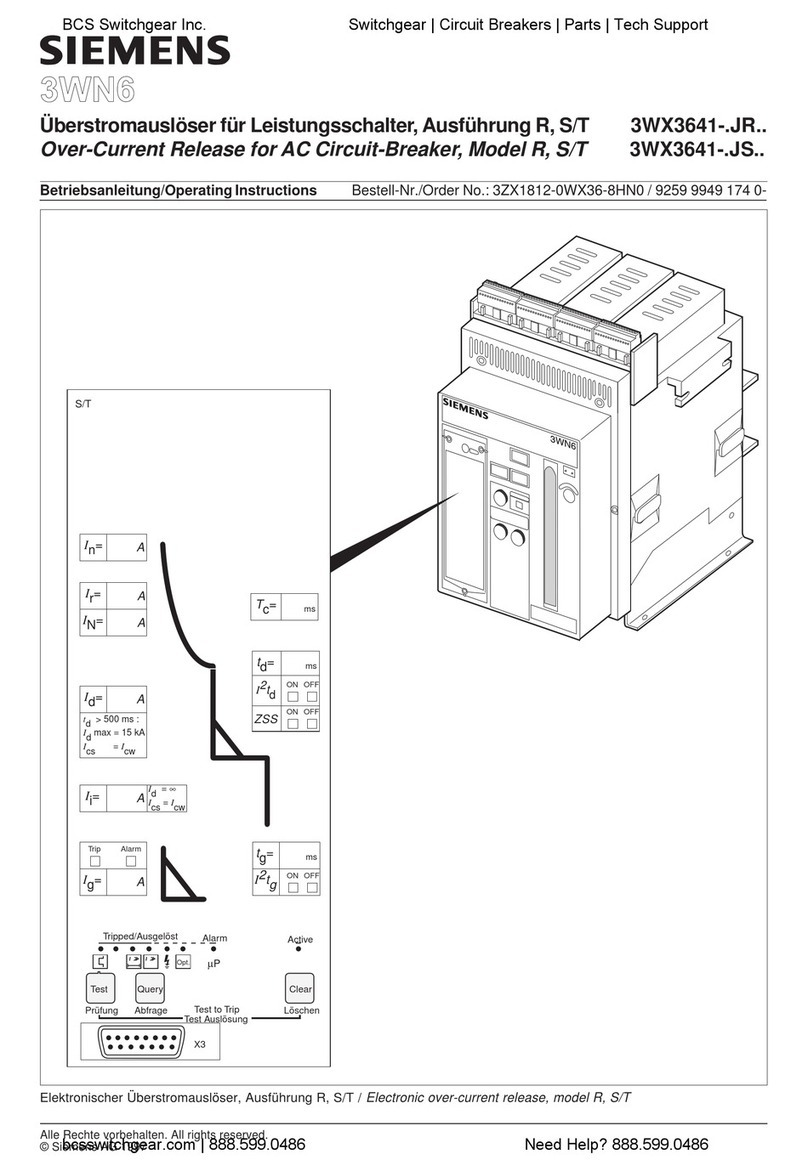
Siemens
Siemens 3WX3641-JR Series User manual

Siemens
Siemens MEMOSKOP 2 SUB Operating instructions

Siemens
Siemens 3RV1.2 User manual
Siemens
Siemens SIRIUS 3RV2.1 User manual

Siemens
Siemens 5SP3 Series User manual

Siemens
Siemens 5SY17 Series User manual

Siemens
Siemens 3VA20 H Series User manual
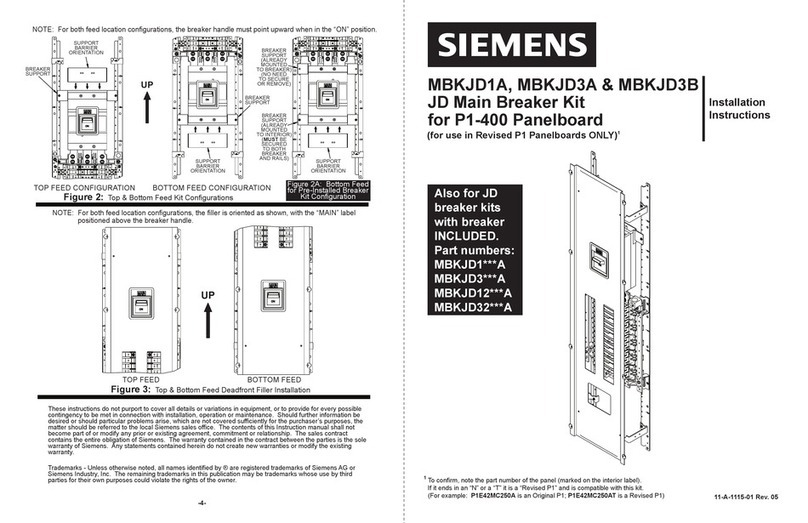
Siemens
Siemens MBKJD1A User manual

Siemens
Siemens SENTRON 3WL10 User manual
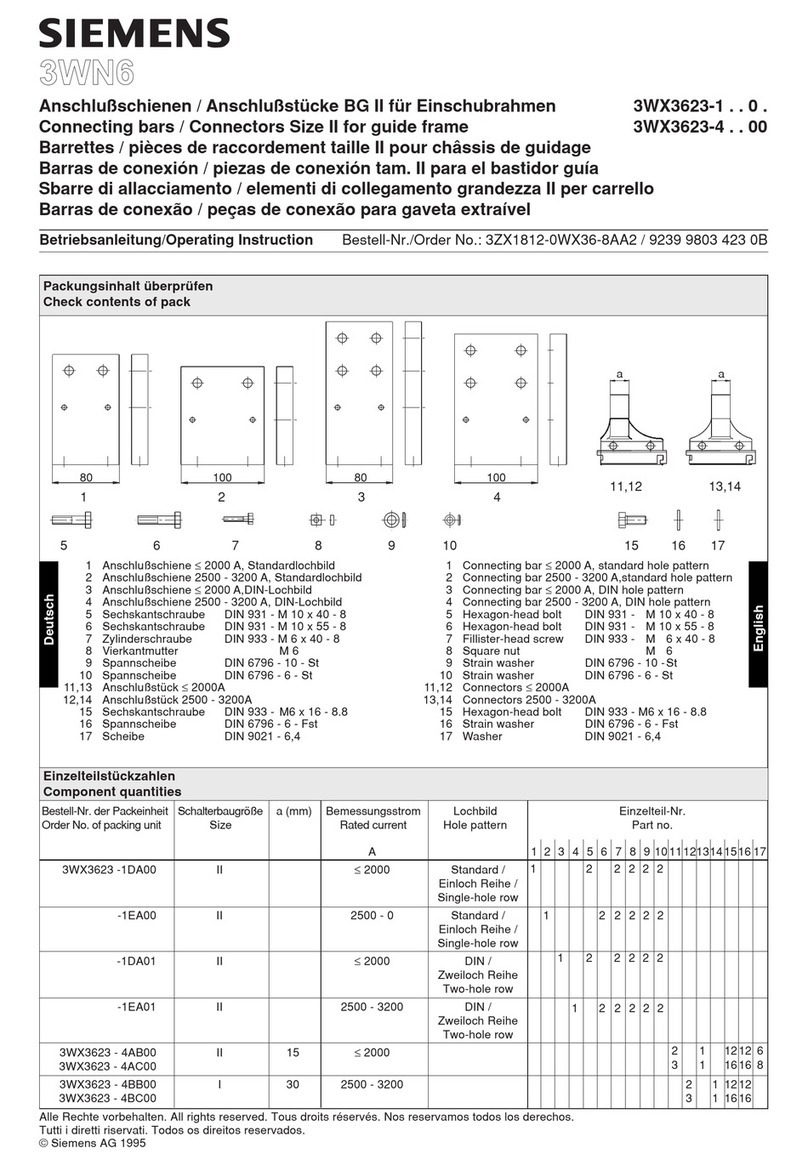
Siemens
Siemens 3WN6 User manual

Siemens
Siemens SIRIUS 3RV1.4 User manual

Siemens
Siemens 3WX3641-0JB00 User manual
Siemens
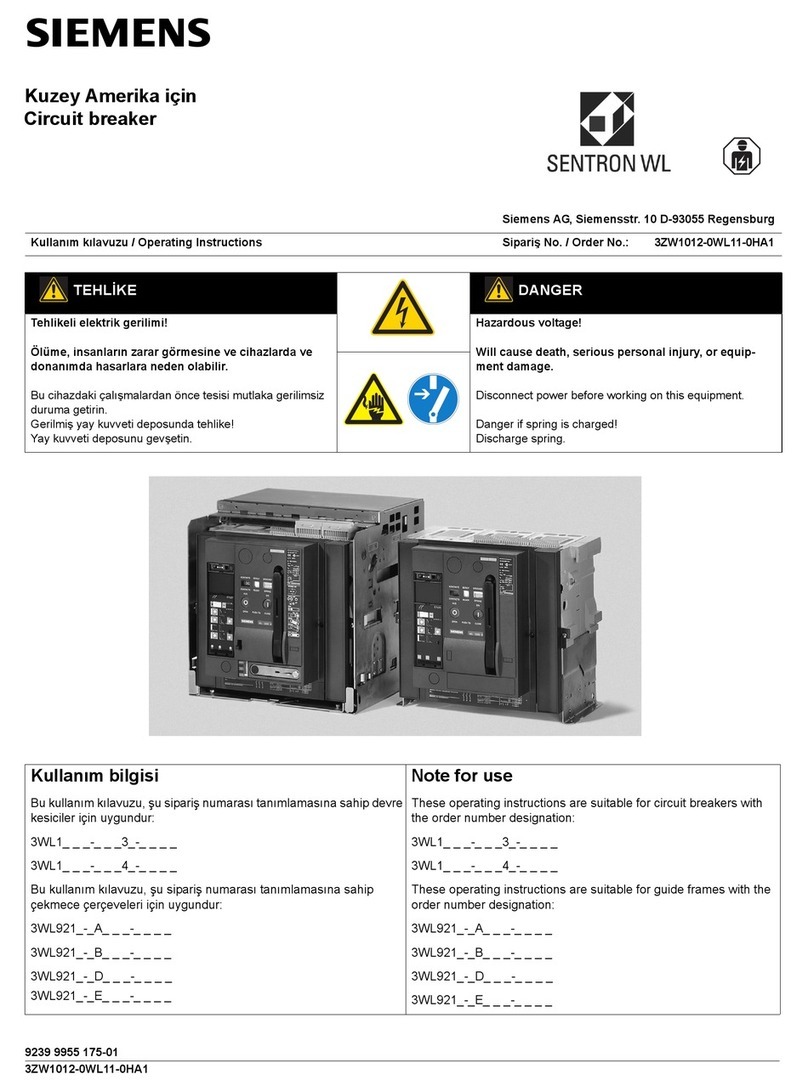
Siemens 3ZW1012-0WL11-0HA1 User manual

Siemens
Siemens 3WN6 3WX3651-1J.00 User manual

Siemens
Siemens 3WN6 User manual
Siemens
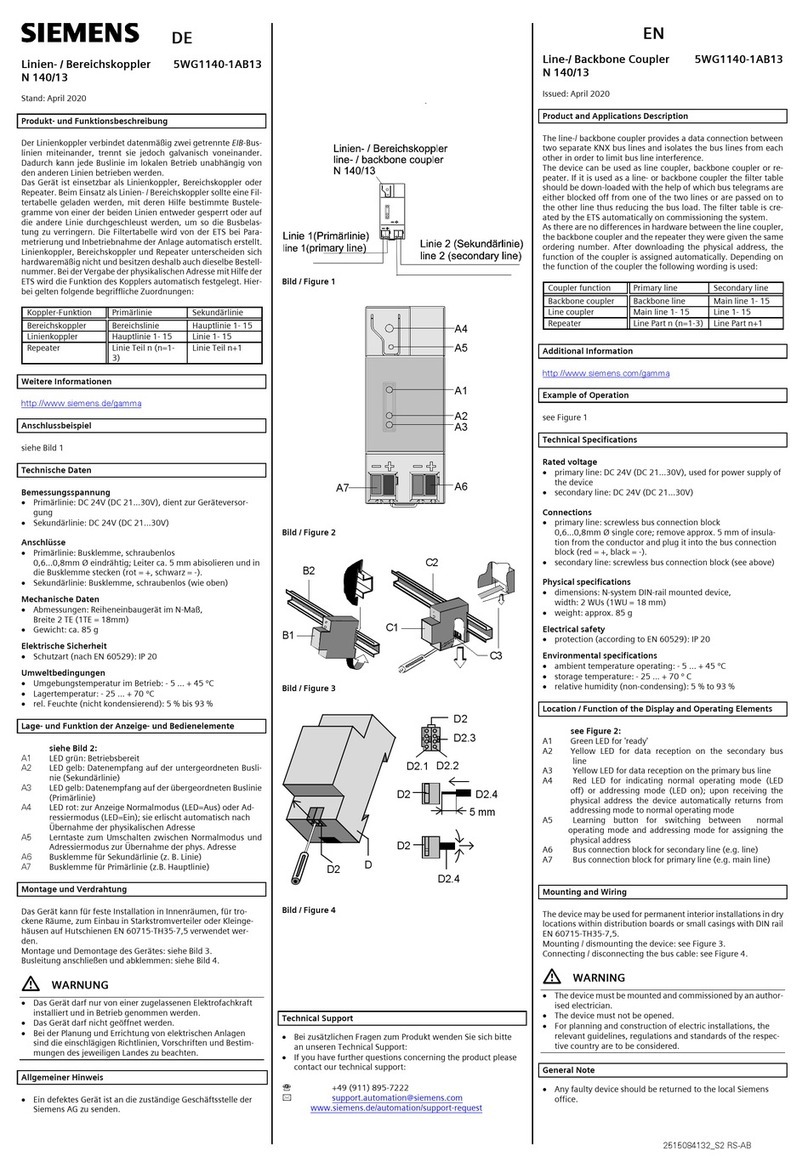
Siemens 5WG1140-1AB13 User manual

Siemens
Siemens 3VF4/5 User manual
Siemens
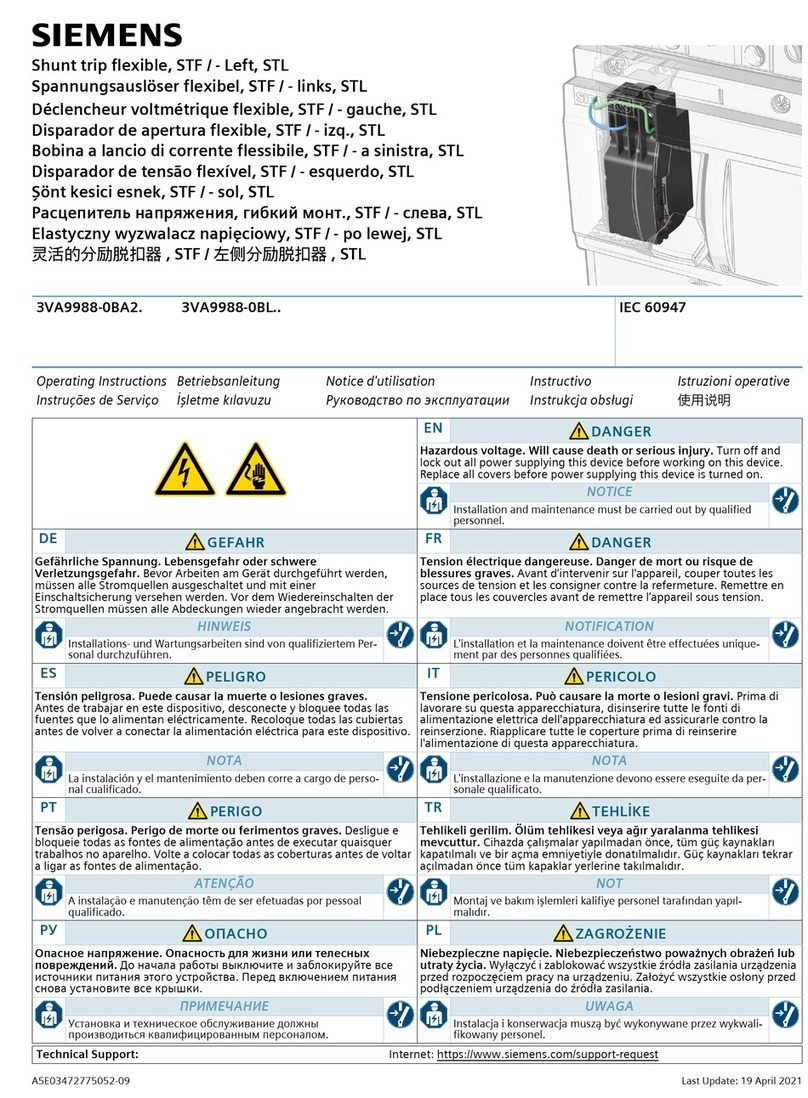
Siemens Sentron 3VA9988-0BA2 Series User manual