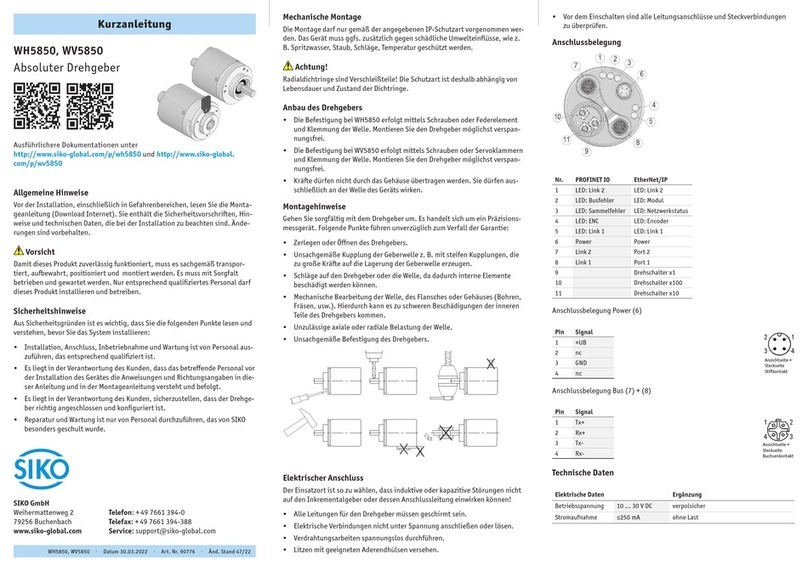
Siko SG5 User manual

SG5 Datum 25.08.2010 Art.Nr. 83679 Änd. Stand 281/10 1
Kabelschuh
Messbereich
max. Auszugslänge
Abb. 2: Prüfung Auszugslänge
Abb. 1: Montage
DEUTSCH
1. Gewährleistungshinweise
Lesen Sie vor der Montage und der Inbetriebnahme
dieses Dokument sorgfältig durch. Beachten Sie zu
Ihrer eigenen Sicherheit und der Betriebssicherheit
alle Warnungen und Hinweise.
Ihr Produkt hat unser Werk in geprüftem und be-
triebsbereitem Zustand verlassen. Für den Betrieb
gelten die angegeben Spezifikationen und die
Angaben auf dem Typenschild als Bedingung.
Garantieansprüche gelten nur für Produkte der
Firma SIKO GmbH. Bei dem Einsatz in Verbindung
mit Fremdprodukten besteht für das Gesamtsystem
kein Garantieanspruch.
Reparaturen dürfen nur im Werk vorgenommen
werden. Für weitere Fragen steht Ihnen die Firma
SIKO GmbH gerne zur Verfügung.
2. Identifikation
Das Typenschild zeigt den Gerätetyp mit Varianten-
nummer. Die Lieferpapiere ordnen jeder Varianten-
nummer eine detaillierte Bestellbezeichnung zu.
z.B. SG5-0023
Varianten-Nr.
Geräte-Typ
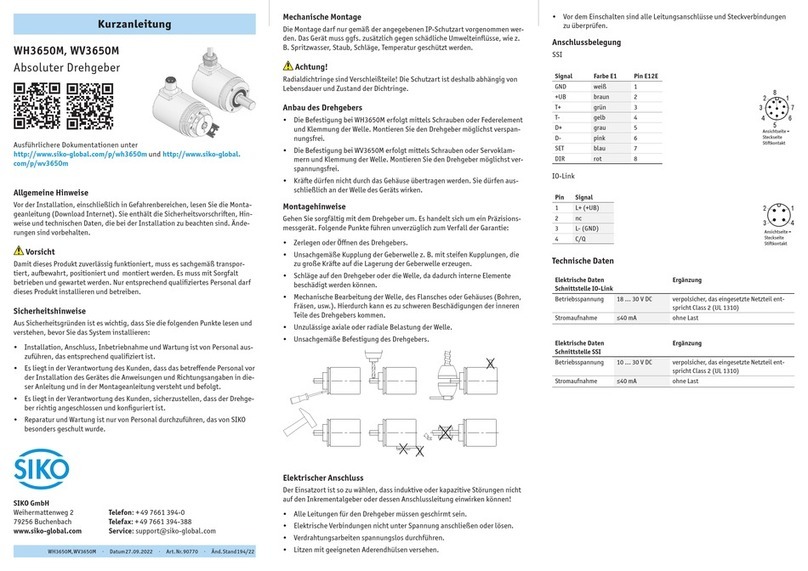
3. Mechanische Montage
Die Montage darf nur gemäß der angegebenen IP-
Schutzart vorgenommen werden. Das System muss
ggfs. zusätzlich gegen schädliche Umwelteinflüs-
•
•
•
•
se, wie z.B. Spritzwasser, Staub, Schläge, Tempe-
ratur geschützt werden.
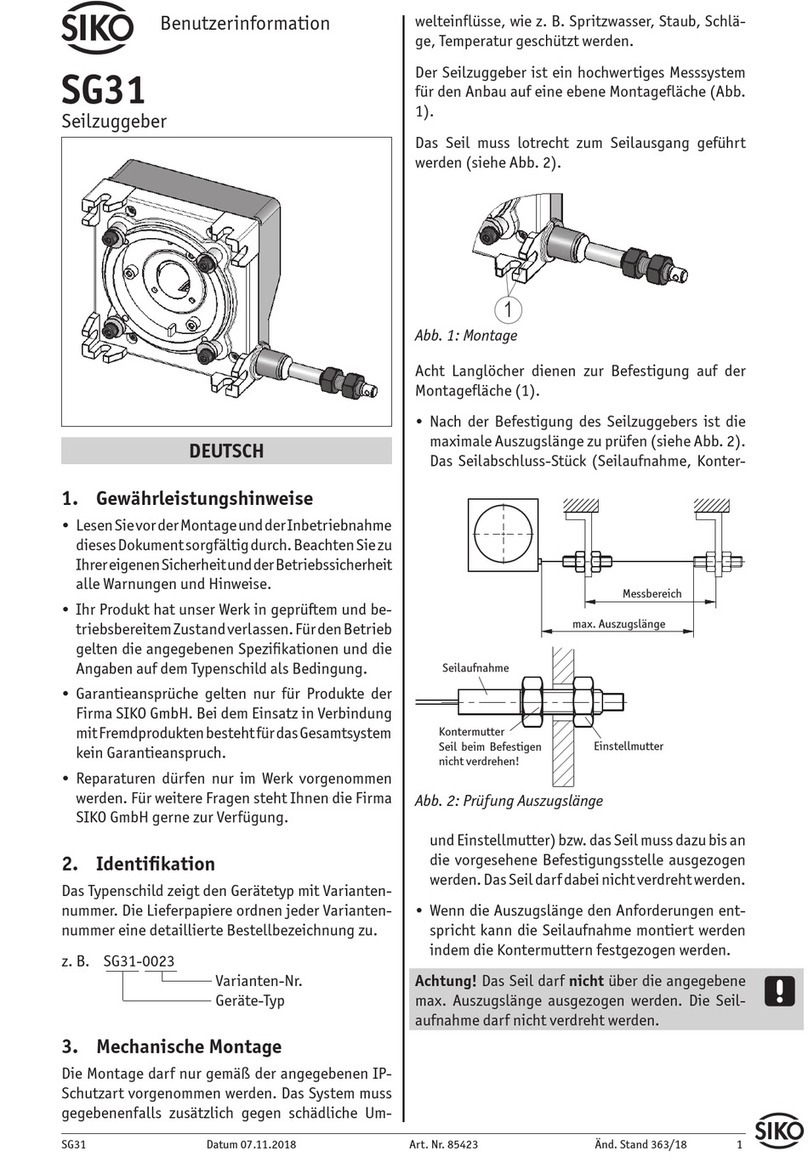
Der Seilzuggeber ist ein hochwertiges Messsystem
für den Anbau auf eine ebene Montagefläche (Abb.
1).
Zwei M3-Gewinde an der Unterseite (max.
Einschraubtiefe 6mm) dienen zur Befestigung
des Gebers.
•
Benutzerinformation
SG5
Seilzuggeber
Prüfen Sie nach der Befestigung des Seilzuggebers,
die maximale Auszugslänge (Abb. 2). Der Kabel-
schuh bzw. das Seil muss bis an die vorgesehene
Befestigungsstelle ausgezogen werden. Das Seil
darf dabei nicht verdreht werden.
•
Achtung! Das Seil darf nicht über die angegebene
max. Auszugslänge ausgezogen werden. Die Seil-
aufnahme darf nicht verdreht werden.
Handhabung des Seils
Das Seil muss lotrecht zum Seilausgang geführt
werden (Abb. 2).
Das Seil darf nicht lose zurückschnellen. Es muss
in jeder Situation und Bewegung, durch die Feder-
kraft der Seiltrommel, gespannt sein.
Für eine korrekte Funktion darf das Seil nicht ge-
quetscht oder geknickt werden.
Kein Garantieanspruch bei falscher Seilmontage/
Verlegung.

2 SG5 Datum 25.08.2010 Art.Nr. 83679 Änd. Stand 281/10
Abb. 3: Umlenkrolle
Seilzuggeber
Umlenkrolle
Messbereich
Abb. 5: Anschluss / Schaltbild Potentiometer
Abb. 4: Öffnen
Umlenkrolle (Zubehör)
Wenn das Seil nicht lotrecht zum Seilausgang he-
rausgeführt werden kann, ermöglicht der Einsatz
von Umlenkrollen den Auszug in jede beliebige
Richtung.
vorzusehen. Leitungsführungen parallel zu Ener-
gieleitungen vermeiden.
4.1 Öffnen und Schließen des Gerätes
Öffnen (Abb. 4):
Schnappung der Haube (1) mittels Schraubendre-
her beidseitig sehr vorsichtig (Bruchgefahr) immer
weiter öffnen bis die Haube abnehmbar ist!
•
Die Umlenkrolle muss parallel zum Seil montiert
werden.
Starke Schmutzbildung ist im Bereich der Um-
lenkrolle zu vermeiden. Die Funktion muss in
regelmäßigen Abständen kontrolliert werden.
4. Elektrischer Anschluss
Anschlussverbindungen dürfen nicht unter
Spannung geschlossen oder gelöst werden!!
Verdrahtungsarbeiten dürfen nur spannungslos
erfolgen.
Vor dem Einschalten sind alle Leitungsanschlüsse
und Steckverbindungen zu überprüfen.
Hinweise zur Störsicherheit
Der Einsatzort ist so zu wählen, dass induktive
oder kapazitive Störungen nicht auf den Geber
oder deren Anschlussleitungen einwirken kön-
nen! Durch geeignete Kabelführung und Verdrah-
tung können Störeinflüsse (z.B. von Schaltnetztei-
len, Motoren, getakteten Reglern oder Schützen)
vermindert werden.
Erforderliche Maßnahmen:
Nur geschirmtes Kabel verwenden. Den Kabelschirm
Steuerungsseitig auflegen. Litzenquerschnitt der
Leitungen min. 0,14mm², max. 0,25mm².
Die Verdrahtung von Abschirmung und Masse (0V)
muss sternförmig und großflächig erfolgen. Der An-
schluss der Abschirmung an den Potentialausgleich
muss großflächig (niederimpedant) erfolgen.
Das System muss in möglichst großem Abstand von
Leitungen eingebaut werden, die mit Störungen
belastet sind; ggfs. sind zusätzliche Maßnahmen
wie Schirmbleche oder metallisierte Gehäuse
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Schließen (Abb. 4):
Haube (1) aufschieben, bis beide Schnappungen
eingerastet sind.
4.2 Potentiometer ohne Messwandler
Bei Montage eines eigenen Kabels, Gerät entspr.
Kap. 4.1 öffnen (max. Kabel-ø3,5+0,3). Potentiome-
teranschlüsse sind nun zugänglich (Abb. 5).
Farbe Belegung Potentiometer
braun Po Anfangsstellung CCW (1)
grün S Schleifer S (2)
weiß Pe Endstellung CW (3)
•
4.3 Potentiometer mit R/I-Wandler (MWI)
Bei Montage eines eigenen Kabels, Gerät entspr.
Kap. 4.1 öffnen (max. Kabel-ø3,5+0,3). Potentiome-
teranschlüsse sind nun zugänglich (Abb. 6).

SG5 Datum 25.08.2010 Art.Nr. 83679 Änd. Stand 281/10 3
Abb. 8: Einstellen Trimmpotentiometer
Folgeelektronik
Folgeelektronik
Abb. 6: Anschluss Potentiometer MWI
Abb. 7: Anschluss Potentiometer MWU
Der Messwandler liefert einen Schleifenstrom von
4...20mA.
Farbe Belegung
braun I+
weiß I-
5. Einstellung und Abgleich
5.1 Einrichtung Potentiometer
Nach ordnungsgemäßem Anschluss gibt der Seil-
zuggeber bei Einschalten der Betriebsspannung
den aktuellen Widerstandswert aus.
Der Messbereich des Potentiometers erstreckt sich
über die gesamte Auszugslänge des Seils. Bei Aus-
zugslänge 0mm (vollständig eingezogen) liegt der
Widerstandswert des Potentiometers bei etwa 3%.
5.2 Abgleich des R/I-Wandlers (MWI)
Ist das Gerät mit einem Widerstands-Stromwand-
ler ausgestattet, wird der Potentiometer-Wider-
stand in einen Strom von 4...20mA umgewandelt.
Es handelt sich um eine Zweileitertechnik. Der
Messstrom dient gleichzeitig zur Versorgung des
Wandlers.
Der Messwandler ist bei Auslieferung auf Stan-
dardwerte, 4mA für die Anfangsstellung (Po),
entspricht Auszugslänge 0mm (vollständig einge-
zogen), und 20mA für die Endstellung (Pe), ent-
spricht Auszugslänge max. mm (vollständig aus-
gezogen), des Potentiometers abgeglichen. Durch
zwei Trimmpotentiometer Po und Pe (siehe
Abb. 8) können diese Werte an die tatsächli-
chen Anfangs- und Endstellungen der Anwen-
dung angepaßt werden.
Einstellen des Messwandlers
Nach Lösen der Haubenschnappung (siehe Kapitel
4.1) sind die Trimmpotentiometer zugänglich.
Anschluss Messwandler (MWI) Bürde gegen Masse:
Anschluss Messwandler (MWI) Bürde gegen +UB:
4.4 Potentiometer mit R/U-Wandler (MWU)
Bei Montage eines eigenen Kabels, Gerät entspr.
Kap. 4.1 öffnen (max. Kabel-ø3,5+0,3). Potentiome-
teranschlüsse sind nun zugänglich (Abb. 7).
Der Messwandler liefert eine Ausgangsspannung
von 0 ... 10VDC.
Farbe Belegung
braun +24VDC
weiß GND
grün Uout
Mit Trimmpotentiometer Po kann ein Strom von 4
mA bei Potentiometerwerten von 0 bis 15% des
Gesamtwertes eingestellt werden.
Mit Trimmpotentiometer Pe kann ein Strom von
20 mA bei Potentiometerwerten von 90 bis 100%
des Gesamtwertes eingestellt werden.
Der kleinste nutzbare Bereich des Potentiome-
ters, in dem 4...20mA abgegeben werden, beträgt
demnach 15% bis 90% des Potentiometer-Wider-
•
•

4 SG5 Datum 25.08.2010 Art.Nr. 83679 Änd. Stand 281/10
Abb. 10: Einstellen Trimmpotentiometer
Abb. 9: Abgleich
Strom
Messweg
20mA
4mA (Po)
(Pe)
0
standsbereichs.
Abgleich
Masch. auf Anfangsstellung fahren
Potentiometer (Po) drehen, bis Anfangswert
(4mA) gemessen wird.
Masch. auf Endstellung fahren
Potentiometer (Pe) drehen, bis Endwert (20mA)
gemessen wird.
Die Schritte 1 bis 4 sind solange zu wiederholen,
bis die Werte austariert sind (iterativer Abgleich).
1.
2.
3.
4.
Abgleich
Masch. auf Endstellung fahren
Potentiometer (Pe) drehen, bis eine Ausgangs-
spannung (10V) gemessen wird.
1.
2.
5.3 Abgleich des R/U-Wandlers (MWU)
Ist das Gerät mit einem Widerstands-Spannungs-
wandler ausgestattet, wird der Potentiometer-
Widerstand in eine Spannung von 0...10VDC
umgewandelt. Der Anschluss erfolgt über eine
Dreileitertechnik.
Der Messwandler ist bei Auslieferung auf den An-
fangswert 0V Ausgangsspannung (Po), bei 0mm
Auszugslänge und den Endwert 10V Ausgangs-
spannung (Pe), bei max. Auszugslänge des Ge-
bers, abgeglichen. Der Ausgang des Messwandlers
sollte mit einem Widerstand 2...10KΩ gegen GND
beschaltet werden, damit sich der Anfangswert
0V einstellt. Die Ausgangslast sollte jedoch so di-
mensioniert sein, dass in der Endstellung (10V)
ein Ausgangsstrom von 10mA nicht überschritten
wird. Mit dem Trimmpotentiometer Pe (siehe
Abb. 10) kann der Endwert an die tatsächliche
Endstellung der Anwendung angepaßt werden.
Einstellen des Messwandlers
Nach Lösen der Haubenschnappung (siehe Kapitel
4.1) ist das Trimmpotentiometer Pe zugänglich.
Da es sich um SMD Bauweise handelt, sollte es
dementsprechend behutsam eingestellt werden. Es
läßt sich eine Ausgangsspannung von 10V bei ei-
ner Auszugsstellung von 60...100% der insgesamt
möglichen Auszugslänge des Gebers einstellen.
5.4 Was tun wenn... (Messwandler)
... sich die Anfangs- und Endwerte des Strom-
wandlers nicht auf 4 bzw. 20 mA bringen las-
sen?
Dann ist vermutlich der Verstellbereich des
Potentiometers zu klein (Schleifer bewegt sich
innerhalb des minimalen Bereichs von 15...90%
und überstreicht einen zu kleinen Widerstands-
bereich).
... ein undefinierter Wert angezeigt wird?
Es muss ein Neuabgleich oder Feinabgleich vor-
genommen werden. Mögliche Ursache kann auch
eine Leitungsunterbrechung sein.
6. Inbetriebnahme
Bitte beachten Sie die Hinweise auf ordnungsge-
mäßen mechanischen und elektrischen Anschluss
in Kapiteln 4 und 5. Nur dann sind die Vorausset-
zungen für eine problemlose Inbetriebnahme und
einwandfreien Betrieb gegeben.
Prüfen Sie vor der Inbetriebnahme nochmals auf:
korrekte Polung der Betriebsspannung
korrekten Anschluss der Kabel
einwandfreie Montage des Geräts
•
•
•
•
•

SG5 Datum 25.08.2010 Art.Nr. 83679 Änd. Stand 281/10 5
Measuring range
max. extension length
Cable lug
Fig. 2: Extension length check
Fig. 1: Mounting
ENGLISH
1. Warranty information
In order to carry out installation correctly, we
strongly recommend this document is read very
carefully. This will ensure your own safety and
the operating reliability of the device.
Your device has been quality controlled, tested
and is ready for use. Please observe all warnings
and information which are marked either directly
on the device or specified in this document.
Warranty can only be claimed for components
supplied by SIKO GmbH. If the system is used
together with other products, there is no warranty
for the complete system.
Repairs should be carried out only at our works.
If any information is missing or unclear, please
contact the SIKO sales staff.
2. Identification
Please check the particular type of unit and type
number from the identification plate. Type number
and the corresponding version are indicated in the
delivery documentation.
e.g. SG5-0023
version number
type of unit
3. Installation
For mounting, the degree of protection specified
must be observed. If necessary, protect the unit
•
•
•
•
against environmental influences such as sprayed
water, dust, knocks, extreme temperatures.
The wire actuated transmitter is a high quality
measuring device and should be mounted to a flat
surface (fig. 1).
Two M3 threads on the lower surface (max. screw-in
depth 6mm) serve to fasten the encoder.
•
User Information
SG5
Wire Actuated
After mounting, check that the maximum exten-
sion length complies with the application (fig.
2). The cable lug or rope must be drawn out to
the intended fastening position. The rope must
not be twisted.
•
Attention! Do not extend the wire beyond the
max. allowable extension length and do not twist
wire insert.
Wire handling
Pull out the wire perpendicular to the wire outlet
(fig. 2).
Do not let the wire go; in every position and du-
ring every move the wire must be stretched by the
cable drum's spring force.
For correction function the wire must remain wit-
hout kinks or flattening.
No warranty claim in the case of faulty mounting
/ laying of the wire.

6 SG5 Datum 25.08.2010 Art.Nr. 83679 Änd. Stand 281/10
Fig. 3: Guide roller
Wire actuated transducer
Guide rollers
Measuring range
Fig. 5: Potentiometer connection / circuit diagram
Fig. 4: Opening
Guide rollers (accessory)
If the wire cannot be led perpendicularly to the
wire outlet, then guide rollers make it possible to
pull out the wire in any direction.
4.1 How to open and close the device
For opening (fig. 4):
Use a screwdriver for opening snap-in cap (1)
on both sides very carefully and slowly (risk of
breakage) until the cap can be removed!
•
Guide rollers must be mounted in line with the
wire.
Maintain cleanliness of guide rollers at all
times.
4. Electrical connection
Switch power off before any plug is inserted
or removed!!
Wiring must only be carried out with power off.
Check all lines and connections before switching
on the equipment.
Interference and distortion
The location should be selected to ensure that
no capacitive or inductive interferences can
affect the encoder or the connection lines!
Suitable wiring layout and choice of cable can
minimise the effects of interference (eg. interfe-
rence caused by SMPS, motors, cyclic controls and
contactors).
Necessary measures:
Only screened cable should be used. Put on the
cable screen on the control side. Wire cross section
is to be at least 0,14mm², max. 0,5mm².
Wiring to screen and to ground (0V) must be via
a good earth point having a large surface area
for minimum impedance.
The unit should be positioned well away from
cables with interference; if necessary a protective
screen or metal housing must be provided. The
running of wiring parallel to the mains supply
should be avoided.
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
For closing (fig. 4):
Put cap (1) back and make sure that both snap
connections catch.
4.2 Potentiometer without instrument transformer
If you want to mount your own cable, please open
the unit as described in chapter 4.1 (max. cable-
ø3,5+0,3). Potentiomter connections will then be
accessible (fig. 5).
Color Designation Potentiometer
brown Po Start point CCW
green S Moving contact S
white Pe End point CW
•
4.3 Potentiometer with R/I transformer (MWI)
If you want to mount your own cable, please open
the unit as described in chapter 4.1 (max. cable-
ø3,5+0,3). Potentiomter connections will then be
accessible (fig. 6).
The instrument transformer provides a loop current
of 4 to 20mA.

SG5 Datum 25.08.2010 Art.Nr. 83679 Änd. Stand 281/10 7
Fig. 8: Setting the trimming potentiometers
follower electronics
Fig. 7: Potentiometer connection MWU
Fig. 6: Potentiometer connection MWI
follower electronics
Color Designation
brown I+
white I-
5. Adjustment and Alignment
5.1 Potentiometer setting
Following correct connection, the wire-actuated
encoder outputs the actual resistance value after
switching on the operational voltage.
The measuring range of the potentiometer is mat-
ched to the total pull-out length of the wire. At
pull-out length 0mm (completely pulled-in), the
resistance value of the potentiometers is approx.
3%.
5.2 Alignment of the R/I transformer (MWI)
If the device is equipped with a resistance-current
converter, then the potentiometer resistance is
converted into a current of 4 to 20mA. The measu-
ring current is also used for feeding the instru-
ment transformer.
Ex works, the instrument transformer is aligned to
default values: 4mA for the start position (Po),
corresponding to the pull-out length of 0 mm
(completely pulled in), and 20mA for the end po-
sition (Pe), corresponding to the max. mm pull-
out length (completely pulled out) of the poten-
tiometer. Via two trimmpotentiometer's Po and
Pe (see fig. 8) these values can be adjusted to
the application's actual start and end position.
Setting the instrument transformer
After releasing the hood snap (see capter 4.1), the
trimming potentiometers can be accessed.
Connection instrument transformer (MWI) load
against mass:
Connection instrument transformer (MWI) load
against +UB:
4.4 Potentiometer with R/U transformer (MWU)
If you want to mount your own cable, please open
the unit as described in chapter 4.1 (max. cable-
ø3,5+0,3). Potentiomter connections will then be
accessible (fig. 7).
The instrument transformer provides an output
voltage of 0 to 10VDC.
Color Designation
brown +24VDC
white GND
green Uout
Trimmpotentiometer's Po is used to adjust a
current of 4 mA to potentiometer values of 0 to
15% of the total range.
Trimmpotentiometer's Pe is used to adjust a
current of 20 mA to potentiometer values of 90
to 100% of the total range.
The smallest available potentiometer range, in
which 4 to 20 mA are delivered, is hence 15% to
90% of the potentiometer's resistance range.
•
•

8 SG5 Datum 25.08.2010 Art.Nr. 83679 Änd. Stand 281/10
Fig. 9: Aligment
Current
Distance
20mA
4mA (Po)
(Pe)
0
Fig. 10: Setting the trimming potentiometers
Alignment
Move axis to start position.
Turn potentiometer (Po) until start value (4mA)
is measured.
Move axis to end position.
Turn potentiometer (Pe) until end value (20mA)
is measured.
The steps 1 to 4 are to be repeated until the va-
lues are counterbalanced.
1.
2.
3.
4.
Turn potentiometer (Pe) until an output voltage
of (10V) is measured.
2.
SIKO GmbH
Werk / Factory:
Weihermattenweg 2
79256 Buchenbach-Unteribental
Postanschrift / Postal address:
Postfach 1106
79195 Kirchzarten
Telefon/Phone +49 7661 394-0
Telefax/Fax +49 7661 394-388
E-Mail info@siko.de
Internet www.siko.de
Service [email protected]e
5.3 Alignment of the R/U transformer (MWU)
If the device is equipped with a resistance-volta-
ge converter, then the potentiometer resistance is
converted into a voltage of 0 to 10VDC. Connec-
tion is via three-wire technology.
Ex works, the instrument transformer is aligned
to the initial value of 0V output voltage (Po), at
an extension length of 0mm and a final value of
10V output voltage (Pe), at a maximum extension
length of the encoder. The output of the instru-
ment transformer should be wired against GND
with a resistor 2 to 10KΩ to enable the initial
value of 0V to be set. However, the output load
should be dimensioned so that an output current
of 10mA won't be exceeded in the end position
(10V). By means of the trimming potentiometer
Pe (see fig. 10), the final value can be adjusted
to the actual final position of the application.
Setting the instrument transformer
After releasing the hood snap, the trimming po-
tentiometer Pe can be accessed. Since it is SMD
designed, it should be set up cautiously. An out-
put voltage of 10V with an extension position of
60 to 100% of the maximum encoder extension
length can be set.
Alignment
Move axis to final position1.
5.4 What to do if... (Instrument transformer)
... if the instrument transformer's start / end
value cannot be set to 4 / 20 mA?
the potentiometer's setting range is perhaps
to small.
... an undefined value is displayed?
Carry out re-alignment or precise alignment. Un-
defined values can be caused by cable breaks.
6. Starting
Please ensure that the instructions given in chap-
ter 4 and 5 regarding mechanical and electrical
connection are followed. This will ensure correct
installation and the operating reliability of the
device.
Before starting check again:
correct polarity of the supply voltage
correct cable connection
correct mounting of the device
•
•
•
•
•
Table of contents
Languages:
Other Siko Media Converter manuals