Contents UM2231
2/26 UM2231 Rev 6
Contents
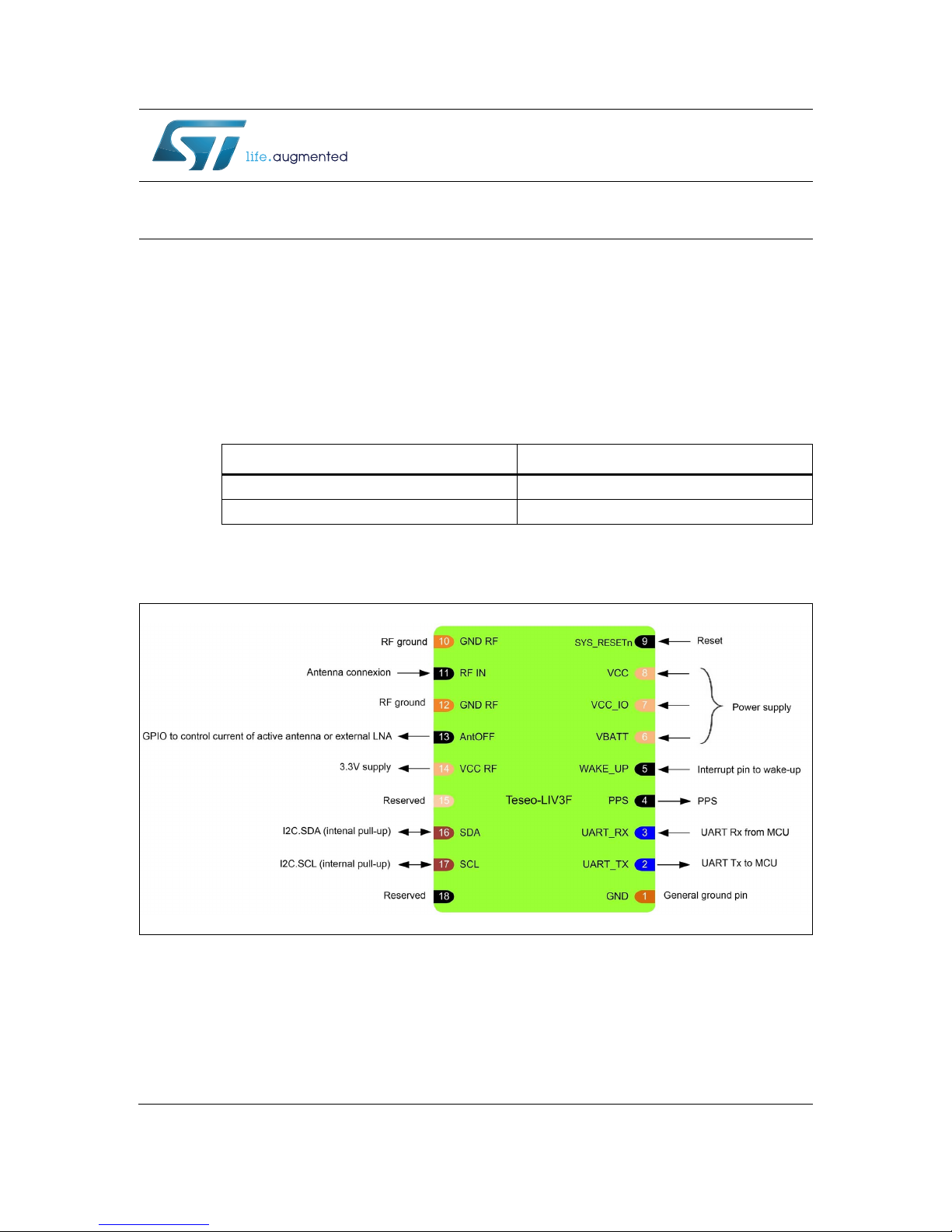
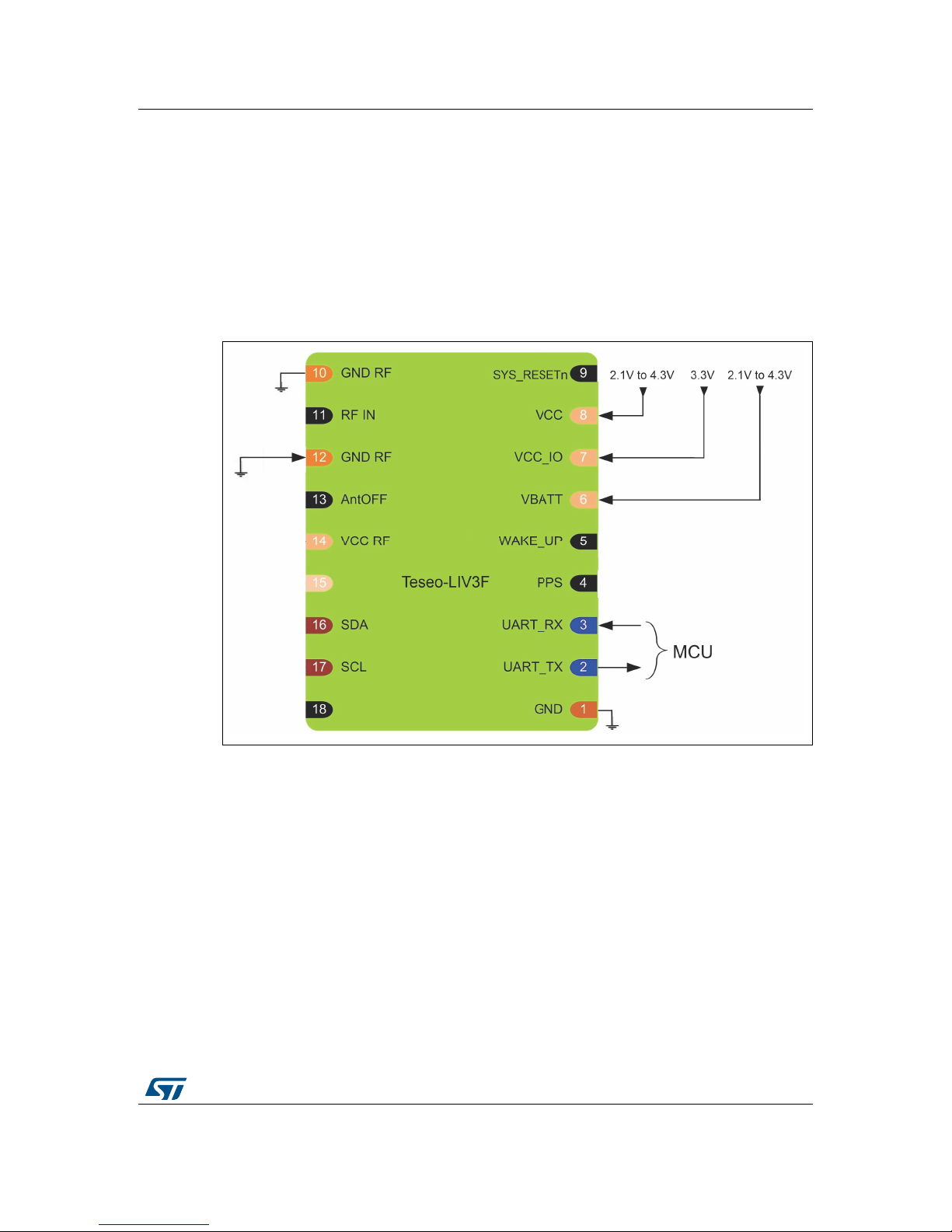
1 Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.1 VCC (pin8) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.2 VBAT (pin6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.3 VCC_IO (pin7) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1.4 VCC_RF (pin14) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1.5 Power supply design reference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.6 Current consumption optimization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2 Reserved (pin15, 18) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3 Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3.1 I2C (pin16, 17) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
3.2 UART (pin2, 3) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
4 I/O pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.1 PPS (pin4) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.2 Wake_Up (pin5) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.3 SYS_RESETn (pin9) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.4 RF_IN (pin10) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.5 AntOFF (pin13) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
5 Standby modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
5.1 Software standby . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
5.2 Hardware standby . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
6 Front ends management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
6.1 External LNA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
6.2 Active antenna . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
7 Reference schematic and BOM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
7.1 Schematic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
7.1.1 Bill of material . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17