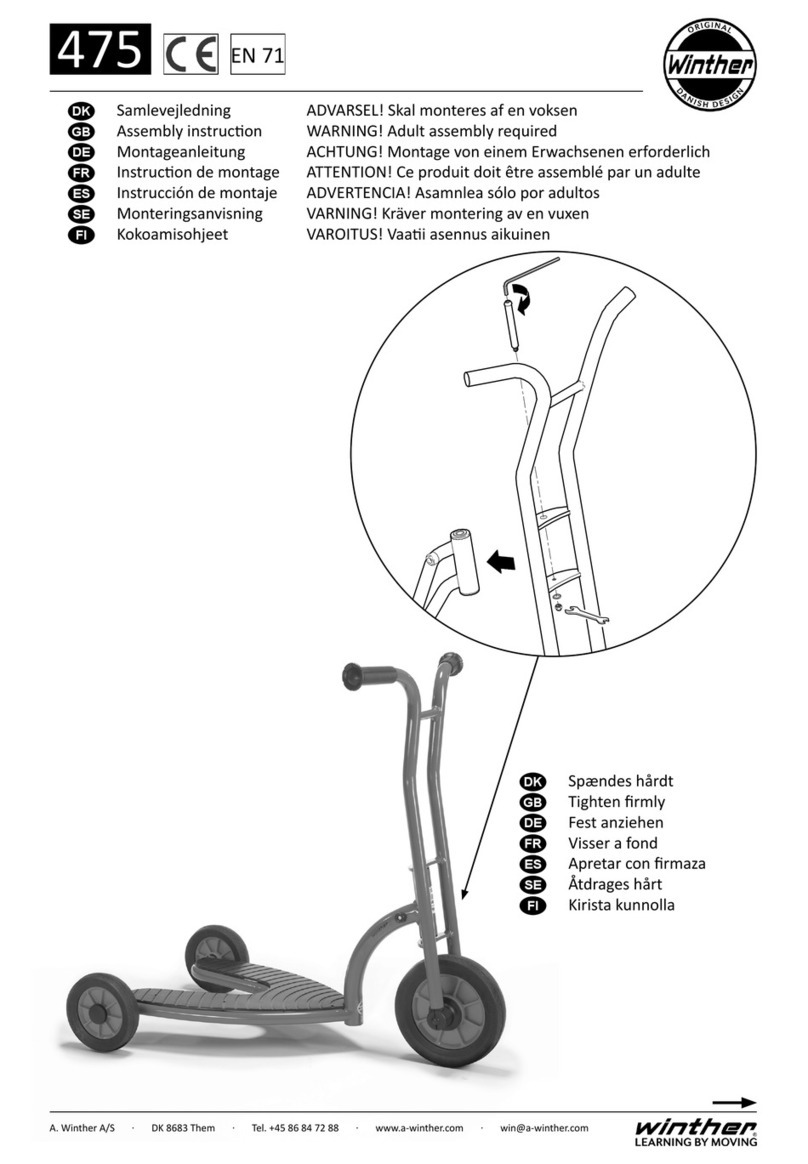
1. General Information/Trouble Diagnosis
1-2
General safety
Carbon monoxide
If you must run your engine, ensure the place is
well ventilated. Never run your engine in a
closed area. Run your engine in an open area, if
you have to run your engine in a closed area, be
sure to use an extractor.
Caution
Gasoline
Gasoline is a low ignition point and explosive
material. Work in a well-ventilated place, no
flame or spark should be allowed in the work
place or where gasoline is being stored.
Caution
Used engine oil
Caution
Hot components
Caution
Battery
Caution
Brake shoe
Do not use an compressed air or a dry brush to
clean components of the brake system, use a
vacuum cleaner or the equivalent to avoid
asbestos dust flying.
Caution
Brake fluid
Caution
Exhaust contains toxic gas which may cause
one to lose consciousness and even result in
death.
•Battery emits explosive gases; flame is
strictly prohibited. Keep the place well
ventilated when charging the battery.
•Battery contains sulfuric acid (electrolyte)
which can cause serious burns so be
careful do not be spray on your eyes or
skin. If you get battery acid on your skin,
flush it off immediately with water. If you
get battery acid in your eyes, flush it off
immediately with water, then go to hospital
to see an ophthalmologist.
•If you swallow it by mistake, drink a lot of
water or milk, and take some laxative such
as castor oil or vegetable oil, and then go
to see a doctor.
•Keep electrolyte beyond reach of children.
Gasoline is highly flammable, and may
explode under some conditions, keep it away
from children.
Prolonged contact with used engine oil (or
transmission oil) may cause skin cancer
although it might not be verdict.
We recommend that you wash your hands
with soap and water right after contacting.
Keep the used oil beyond reach of children.
Inhaling asbestos dust may cause disorders
and cancer of the breathing system.
Spilling brake fluid on painted, plastic, or
rubber parts may cause damage to the
parts. Place a clean towel on the
above-mentioned parts for protection when
servicing the brake system. Keep brake fluid
beyond reach of children.
Components of the engine and exhaust
system can become extremely hot after
engine running. They remain very hot even
after the engine has been stopped for some
time. When performing service work on these
parts, wear insulated gloves and wait until
cooling off.
This chapter Contents