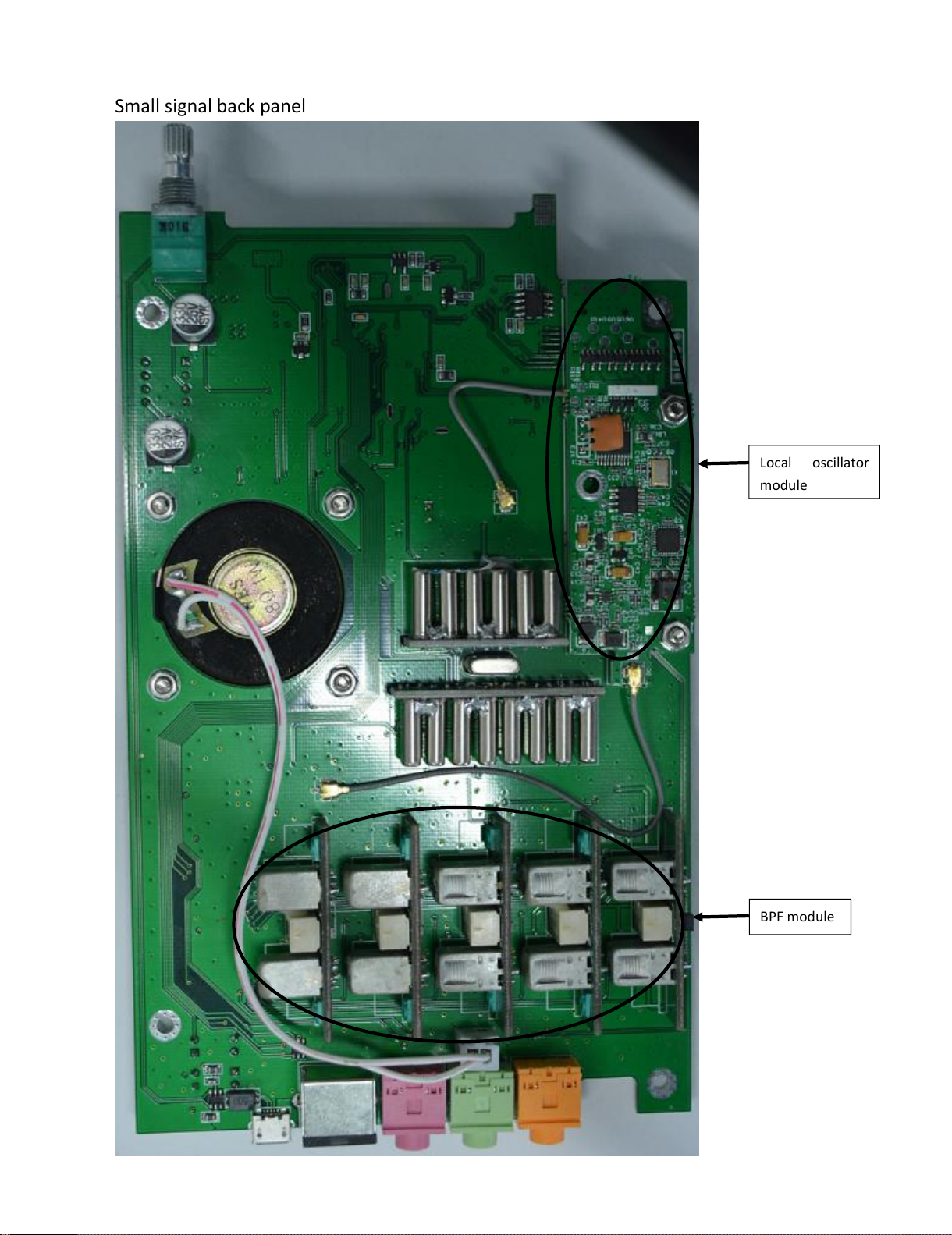
3.1.1 RF front-end circuit
The RF front-end circuit of 0.5--30MH is composed of a
Receiving band-pass filter, receiving preamplifier, pre
Band-pass filter consists of 5 modules (XGM1--XGM5),
it can make 10 amateur bands. U20, U21 are band
switching controller,connect the input band switching
signal to LPF unit switching relay of power amplifier
Preamplifier is composed of Q7 and its periphery
circuit. Preattenuator is πType attenuator, which is
composed of R57、
R64、
R65. U4、
U12、
U15、
U18 are
RF switching trigger, to control the RX Signal trend.
PRE_EN and ATT_EN are control signals ,by these 2
control signals to control the signal to be passthrough
mode, amplifier mode, attenuator mode,
amplifier+attenuator mode.Q8 、Q9 are switching
U5
(ADE-1)
is receiving mixer,
inside is diode balanced
mixing structure. The RX receiving signal is mixing 1st
LO here, to bring 10.7MHz IF signal.
D15 is LO input switch, it’s in forward conduction
status when receiving, the LO enters the mixer. D15 is
closed when transmitting.
After mixing, it brings a receiving 1st IF signal. This
signal enters IF preamplifier Q21 via transformer T7 to
finish the first IF amplify. This amplified IF signal
outputs to intermediate frequency crystal filter(IFCF)
by T5. Q6 is NB control switch which controls the
The radio is builted-in with 3 sets of IFCF, they are SSB -
2.2k (XMD1), CW - 500Hz (XMD2), and AM - 7.5K (XF1).
Q1, Q11 and Q12 control the access of this three IFCF
3.1.5 IF Two stage amplifier circuit
The IF two stage amplifier circuit is composed of Q13
and Q15, the IF signal which be input by T4 makes the
final IF amplification here then sent to the automatic
gain control unit and the demodulation unit.
The automatic gain control unit is composed of Q4, D1,
U1 and its peripheral devices. The automatic gain
control voltage is sent to the G2 pole of the two stage
IF amplifier respectively to receive automatic gain
control. The starting speed is switched by U1 and Q23,
and the switching signal is AGC-S.
The automatic gain control voltage outputs S table
signal after buffering and amplifying by U2.
3.1.6 Demodulator circuit
The demodulation of single sideband signal SSB and
continuous wave signal CW is accomplished by a
product detector which is composed of U6 (SA602).
The BFO signal is input through by the 6 pins to the
demodulator, and the demodulated audio signal is
output by 5 pins. By controlling the frequency of the
injected BFO signal, the demodulation of SSB and CW
All manuals and user guides at all-guides.com
all-guides.com