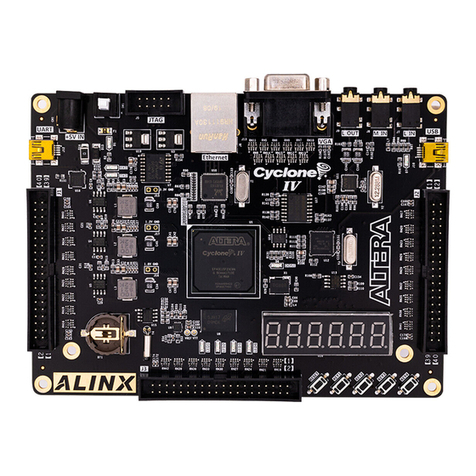
Alinx ACU15EG User manual
Other Alinx Motherboard manuals

Alinx
Alinx ZYNQ UltraScale+ AXU9EGB User manual

Alinx
Alinx ZYNQ7000 FPGA User manual

Alinx
Alinx ARTIX-7FPGA User manual
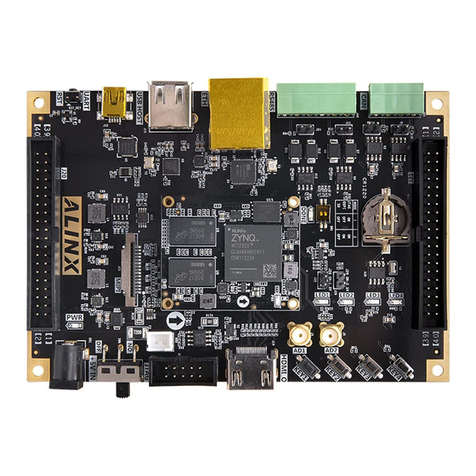
Alinx
Alinx ZYNQ7000 FPGA User manual

Alinx
Alinx ZYNQ UltraScale+ AXU2CG-E User manual
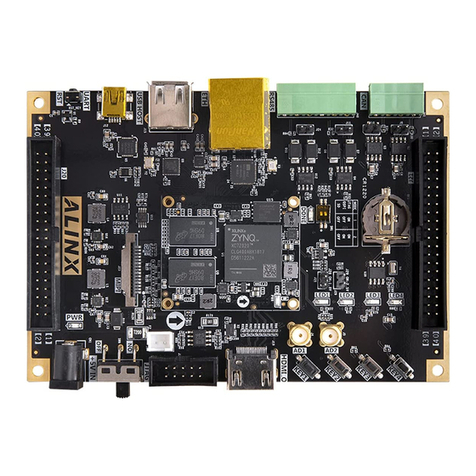
Alinx
Alinx ZYNQ7000 FPGA User manual
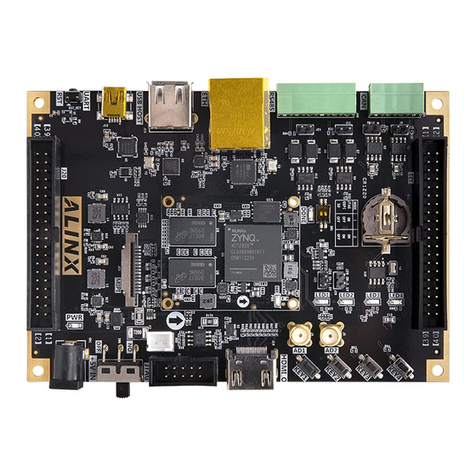
Alinx
Alinx ZYNQ7000 FPGA User manual

Alinx
Alinx AXKU041 User manual
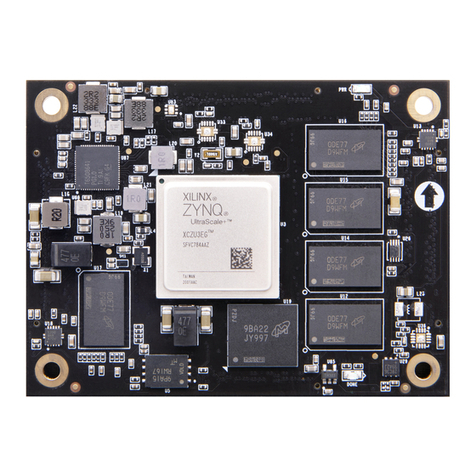
Alinx
Alinx ACU3EG User manual

Alinx
Alinx AX7021 User manual

Alinx
Alinx AX7103 User manual

Alinx
Alinx ARTIX-7 FPGA User manual

Alinx
Alinx AXU4EVB-E User manual
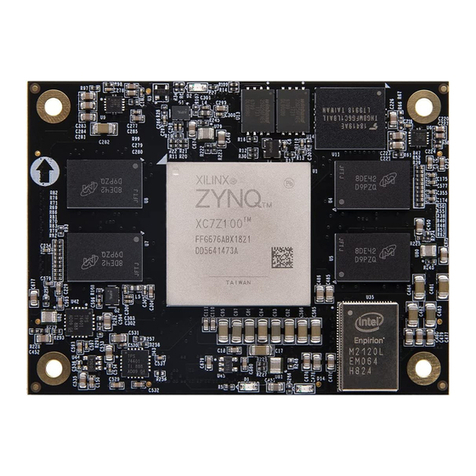
Alinx
Alinx AC7Z100 User manual

Alinx
Alinx AXU7EV User manual

Alinx
Alinx ZYNQUltraScale+ AXU3EGB User manual
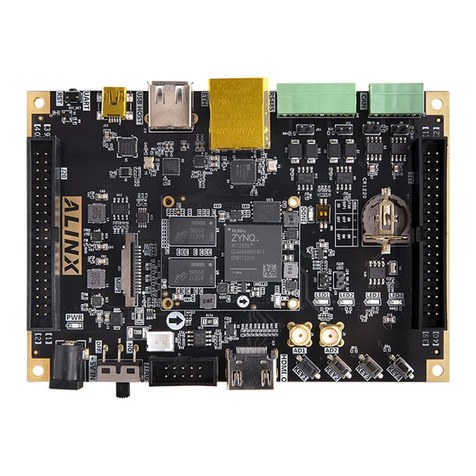
Alinx
Alinx ZYNQ7000 FPGA User manual

Alinx
Alinx AC7010C User manual

Alinx
Alinx ZYNQ UltraScale+ User manual
Alinx
Alinx AV4040 User manual