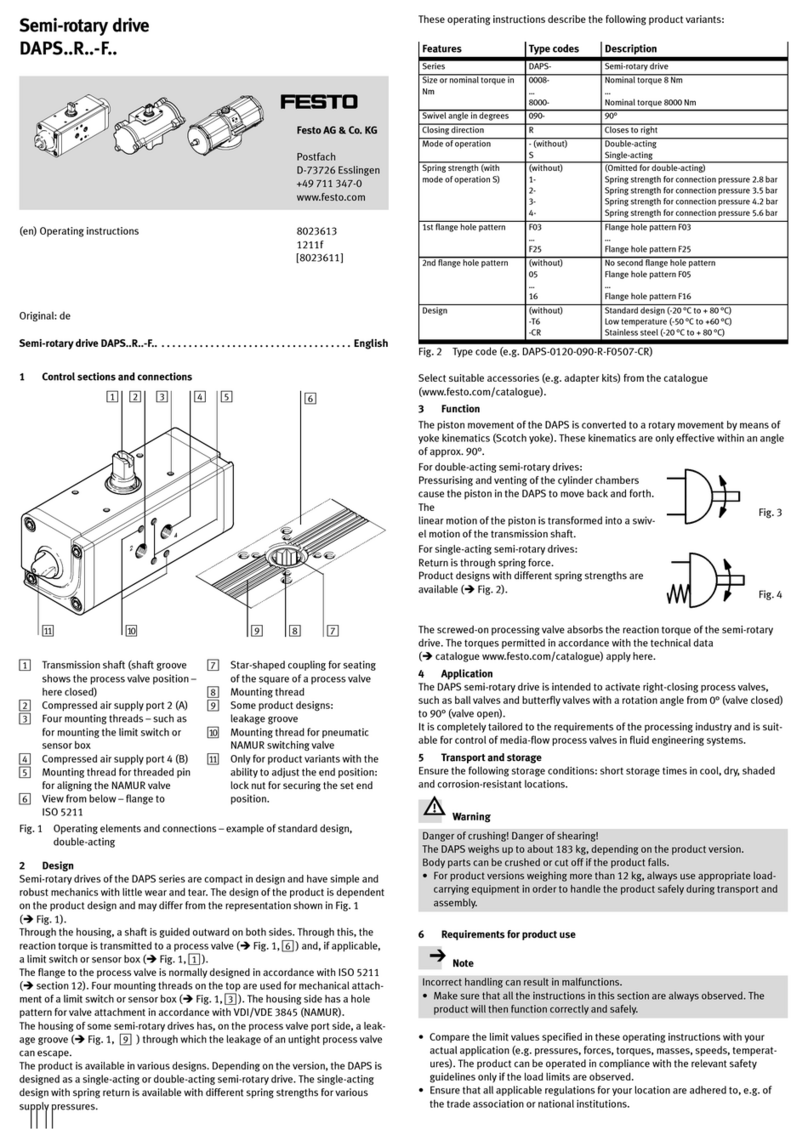
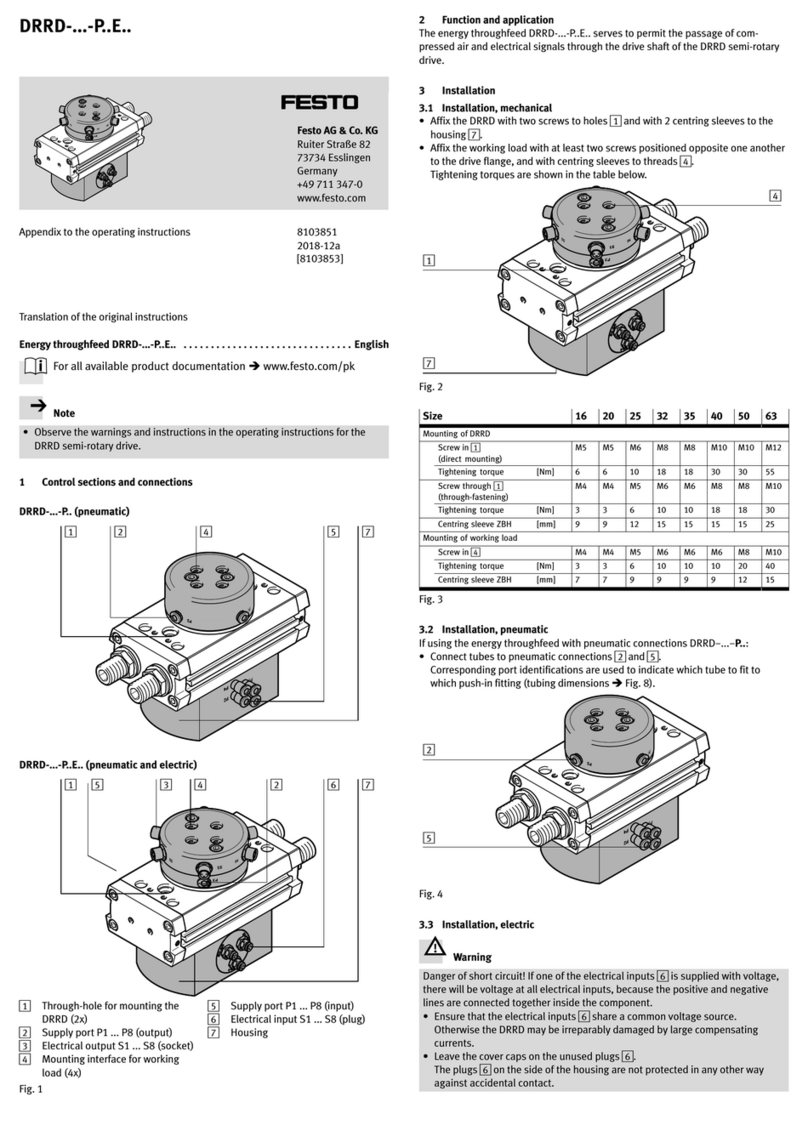
When using additional proximity
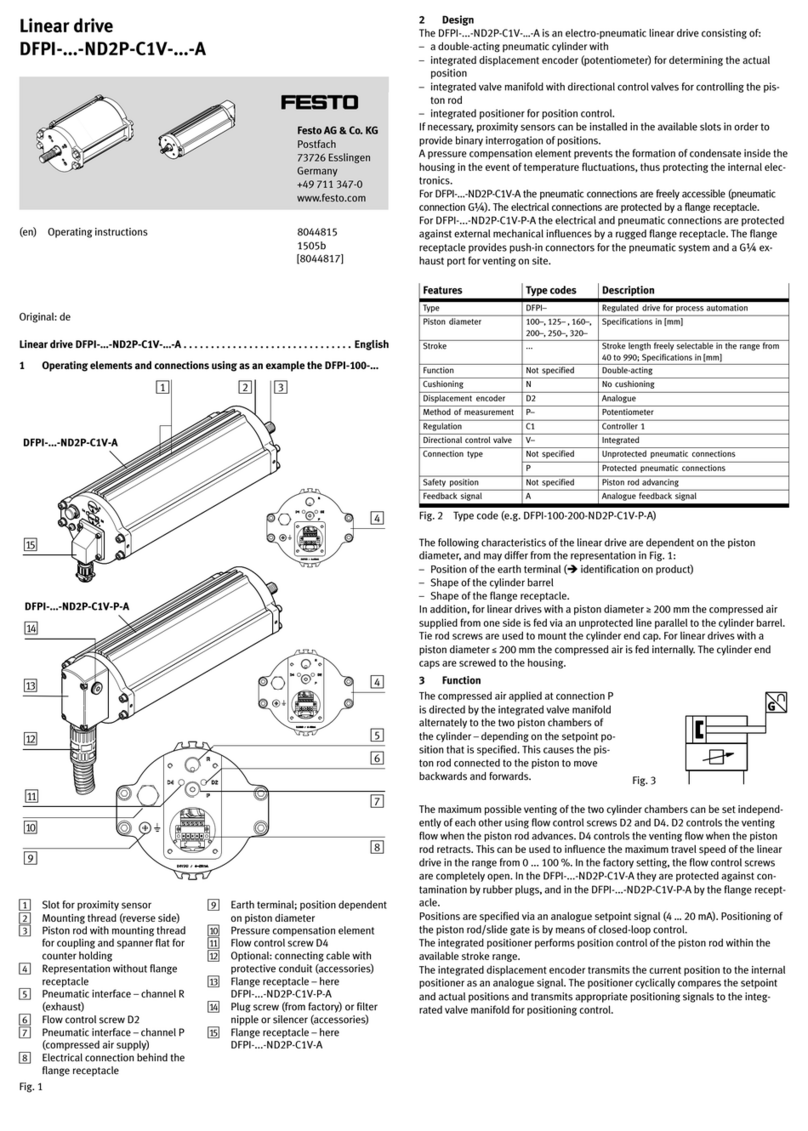
switches:
· Place the proximity switches in the
corresponding grooves. Cover rails
over the grooves fasten the cables
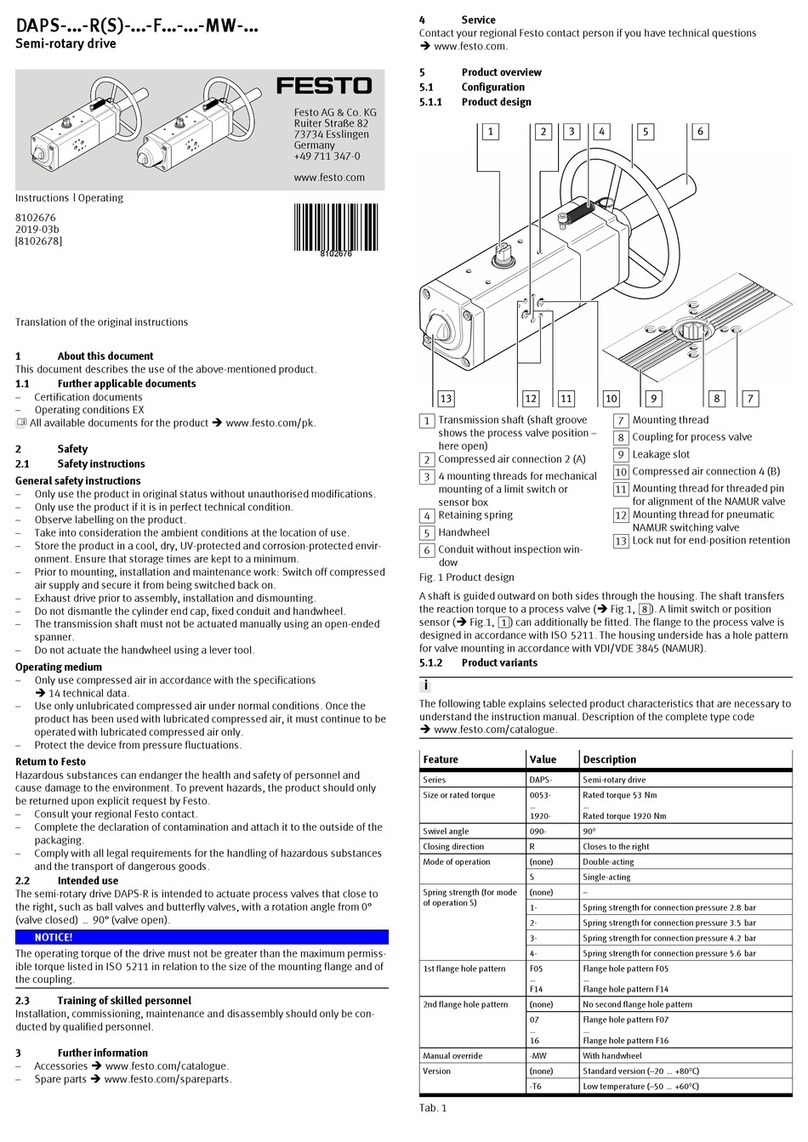
and protect them against dirt.
· Duringassembly, maintain the
required minimum distances from
ferrous materials.
Fig.6
7.2 Electrical installation
Warning
· Use only power units which guarantee reliable electrical isolation of the
operating voltage as per IEC/DIN EN 60204−1.
Take into account also the general requirements for PELV circuits as per
IEC/DIN EN 60204−1.
Please note
Installation errors can damage the electronics or cause faults.
· Make sure that the length of the displacement encoder cable does not exceed
the permissible length of 30 m.
· Connect the earth terminal (Fig.1 7) with the earth potential with low resis
tance (short cable with large cross−section) tightening torque 5 Nm ±10 %.
·Totransmit analogue signals, use only screened cables with twisted pairs.
Attach the cable screening at one end to the higher−level system.
· Use an electrical connecting cable with a nominal outside diameter of 8 mm.
· Observe the pin assignment (èFig.8). The displacement encoder may only
be used as a voltage divider not as a variable resistor.
The electrical connection is covered by the flange receptacle (èFig.1). To perform
electrical installation you will have to dismantle the flange receptacle.
The structure of the flange receptacle and the cable conduit fitting are shown in
the following illustration:
1Mounting screws
tightening torque èFig.9
2Seals (O−rings)
3Protective conduit
can be pulled on using
assembly tool
4Cable conduit fitting
tightening torque 15 Nm
5Seal insert
6Threaded connector
tightening torque 15 Nm
Fig.7
1
2
3
4
5
6
1. Loosen the mounting screws of the flange receptacle (èFig.7 1) and carefully
remove the flange receptacle.
2. Loosen the cable conduit fitting (èFig.7 4).
3. Stick the electrical connecting cable through the passage of the seal insert of
the flange receptacle (èFig.10 3).
4. If necessary, loosen the socket strip of the electrical connection, which is
fastened with two screws.
5. Use the wire end sleeves suitable for the connection and wire the socket strip
according to the pin assignment (èFig.8) tightening torque 0.2 Nm +20 %.
The 3−pole connection is used to supply power to the integrated displacement
encoder and to make the sensor signal available.
Pin Assignment 1) Connection
1 Power supply 3
1
2 Actual value, signal
3 Power supply +
1) Maximum permissible supply voltage ètechnical specifications in chapter 13
Fig.8
6. Carefully plug the wired−up socket strip onto the connector.
7. Refasten the socket strip with the two screws
tightening torque: 0.5 Nm ±10 %.
8. Reinstall the flange receptacle. When doing so, make sure that the seals and
O−rings are correctly seated.
9. When tightening the mounting screws of the flange receptacle, observe the
tightening torque (èFig.9).
Tightening torque of the mounting screws of the flange receptacle
Version DFPI−100−...−E−P to
DFPI−160−...−E−P
DFPI−200−...−E−P to
DFPI−320−...−E−P
Tightening torque [Nm] 2.7 ±10 % 6 ±10 %
Fig.9
7.3 Installing the pneumatic system
· Use standard O.D. pneumatic connecting tubes with an outside diameter of
8 mm. The pneumatic tube PNU−8x1,25 from Festo is suitable, for example.
· Check to see if closed−loop controlled non−return valves type HGL−... are
necessary.
This way you can prevent the moveable mass sliding down if there is a drop in
pressure when the product is fitted in a vertical or sloping position.
Connection is via the flange receptacle (èFig.10). This providespush−in
connectors for the pneumatic system and a through−hole for the electric cable.
Connect the tubing of the DFPI as follows:
1. If necessary, loosen the cable conduit fitting (èFig.7 4).
2. Connect the tubing of the DFPI to the compressed air connections (èFig.10).
To do this, stick the individual tubes into the corresponding holes in the seal
insert as far as they will go (èincluding Fig.7 5and Fig.10).
1Dowel pin
2Pneumatic connection 2:
retract piston rod
3Passage for electric cables
4Pneumatic connection 4:
advance piston rod
Fig.10
1
2
3
4
Air supply at connection 2 (èFig.10 2): piston rod retracts
(open processing valve)
Air supply at connection 4 (èFig.10 4): piston rod advances
(close processing valve)
3. Retighten the cable conduit fitting (èFig.74 ) on the flange receptacle
tightening torque èFig.7 4.
8 Commissioning
The product is ready for operation as soon as it is fitted and electrically and
pneumatically connected.
· Make sure that the operating conditions lie within the permitted ranges
(Technical specifications èchapter 13).
· Make sure that a slide plate (processing valve) mounted on the linear drive can
be positioned without hindrance.
·Ifnecessary, adjust the linear drive adapter fitted on the piston rod. This setting
serves for optimising the opening or closing reaction of the connected
processing valve or penstock shut−off valve.
· Slowly pressurise the linear drive.
For slow start−up pressurisation use soft−start valve type HEL.
·Atfirst, select a slow positioning speed.