2Design and specifications are subject to change without notice S47183-e 01/2008
INDEX
1. WARNINGS AND SAFETY HINTS..............................3
1.1 Warnings. ...........................................................................3
1.2 Safety hints.........................................................................4
1.2.1 Securing against falling parts........................................4
1.2.2 Maintenance with zero voltage release.........................4
2. GENERAL USAGE CONDITIONS...............................4
2.1 Transportation...................................................................4
2.2 Installation..........................................................................5
2.2.1 Operational environment..............................................5
2.2.2 Installation and interfaces.............................................5
2.3 Usage...................................................................................5
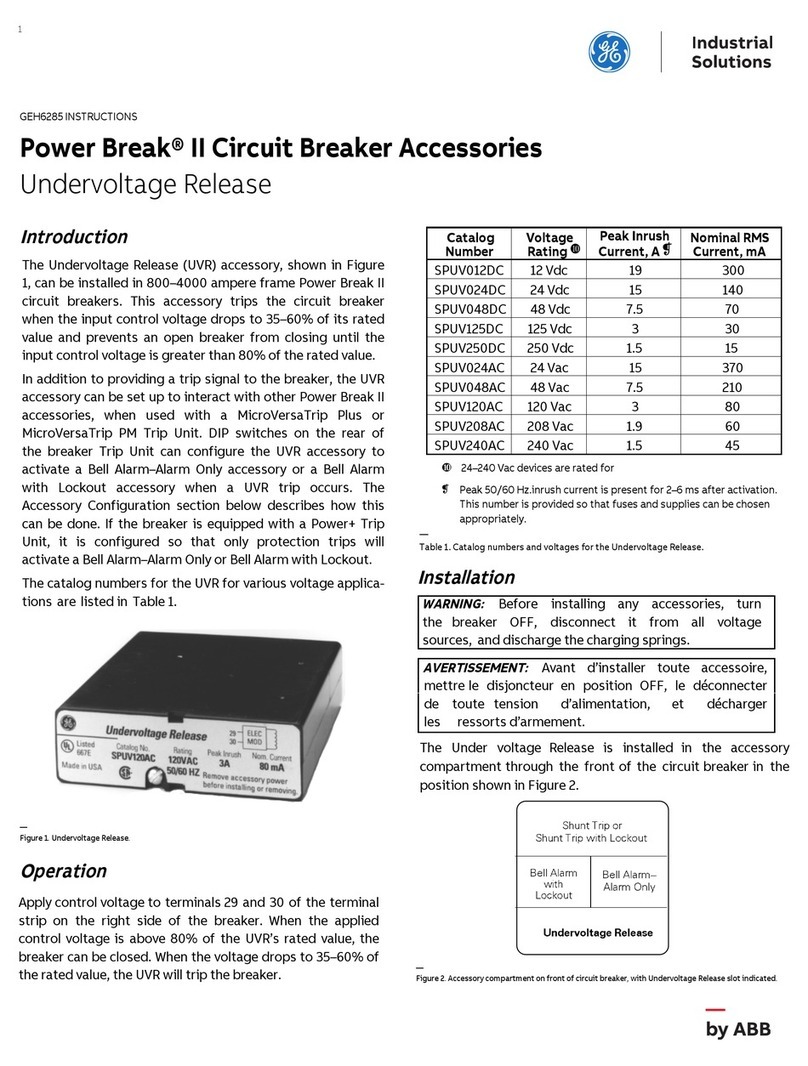
2.3.1 Supply and load. ...........................................................5
2.3.2 Adjusting the OCT........................................................5
3. TECHNICAL INFORMATIONS....................................6
3.1 Introduction. ......................................................................6
3.2 Components and accessories.............................................6
3.2.1 Contact system..............................................................6
3.2.2 Arc chute (code nr: 2)...................................................6
3.2.3 Mechanism....................................................................7
3.2.4 Over-Current Tripping device (code nr: 7)...................7
3.2.5 Electro-Dynamic tripping device (code nr: 12). ...........8
3.2.6 Auxiliary tripping devices (code nr: 11).......................8
3.2.7 Forced tripping release (code nr: 13)............................8
3.2.8 Hand lever (code nr: 16)...............................................9
3.2.9 Auxiliary switches (code nr: 9).....................................9
3.2.10 Indicators....................................................................9
3.2.11 Solenoid closing drive (code nr: 3)...........................10
3.2.12 Current measurement system (code nr: 6). ...............10
3.2.13 Electronic control system..........................................11
3.3 Technical data tables.......................................................12
4. ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS...........................................14
4.1 Controls layout.................................................................14
4.2 Terminals wiring system.................................................15
4.3 Electrical diagrams..........................................................16
4.3.1 Wiring coding system.................................................16
4.3.2 Voltage converter........................................................17
4.3.3 ED coil with external capacity bank...........................18
4.3.4 NEKO control unit......................................................19
4.3.5 SU control unit............................................................20
4.3.6 Shunt trip control unit.................................................21
4.3.7 Zero voltage release control unit.................................22
4.3.8 Indicators....................................................................23
4.3.9 Auxiliary switches. .....................................................24
4.3.10 SEL Measuring system 25
5. DIMENSIONS & SAFETY DISTANCES ....................26
5.1 Safety distances. ..............................................................27
5.2 Outlined dimensions........................................................ 28
5.2.1 Gerapid 2607,4207, 6007 with arc chute 1x_.............28
5.2.2 Gerapid 2607, 4207, 6007with arc chute 2x_.............29
5.2.3 Gerapid 8007 with arc chute 1x_. ..............................30
5.2.4 Gerapid 8007 with arc chute 2x_. ..............................31
5.2.5 Gerapid 2607, 4207 with H / H terminals. .................32
5.2.6 Gerapid 2607, 4207 with V / V terminals. .................33
5.2.7 Gerapid 6007 terminals.............................................. 34
5.2.8 Gerapid 8007 terminals.............................................. 35
6. INSPECTIONS AND MAINTENANCE.......................36
6.1 List of inspections............................................................36
6.1.1 General visual inspection. ..........................................37
6.1.2 General functional inspection.....................................37
6.1.3 Inspection of the arc chute. ........................................37
6.1.4 Inspection of the contact system. ...............................38
6.1.5 Inspection of contacts’ tilt and gap.............................39
6.1.6 Inspection of the screw connections...........................39
6.1.7 Inspection of the mechanic components..................... 39
6.2 List of maintenance works..............................................40
6.2.1 Maintenance of contact system (after 11/2003). ........ 40
6.2.2. Maintenance of contact system (before 11/2003)......42
6.2.3 Layout of control PCBs inside control box................ 44
6.2.4 Replacement of the control boards.............................44
6.2.5 Adjusting the auxiliary switches. ...............................46
6.3 Spare parts list.................................................................47
7. CUSTOMER SUPPORT.............................................48
7.1 PST coding system...........................................................48
7.2 Ordering Form. ...............................................................49
7.2.1 Example of order 1.....................................................50
7.2.1 Example of order 2.....................................................51
7.3 Glossary ...........................................................................52
7.4 Troubleshooting. .............................................................53