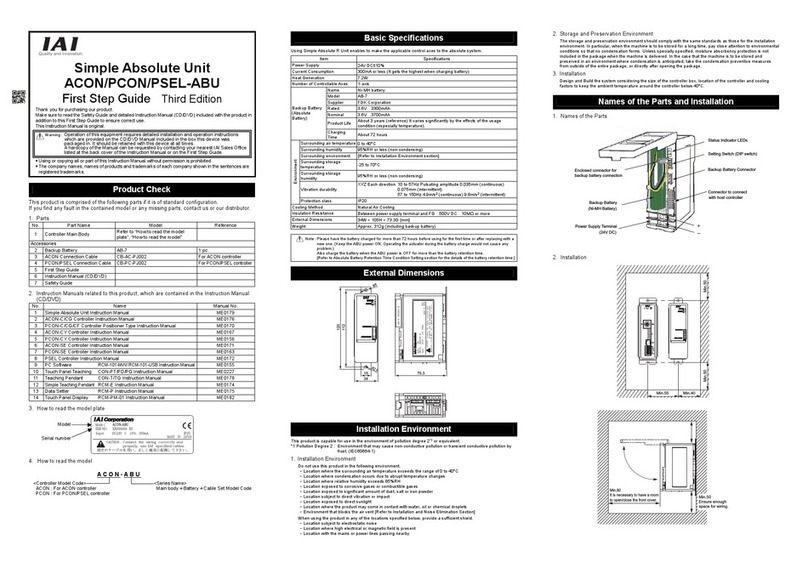
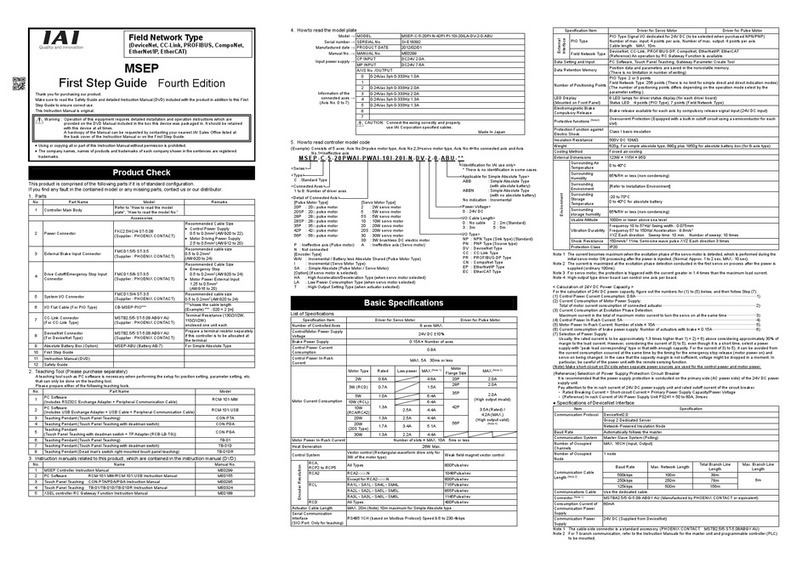
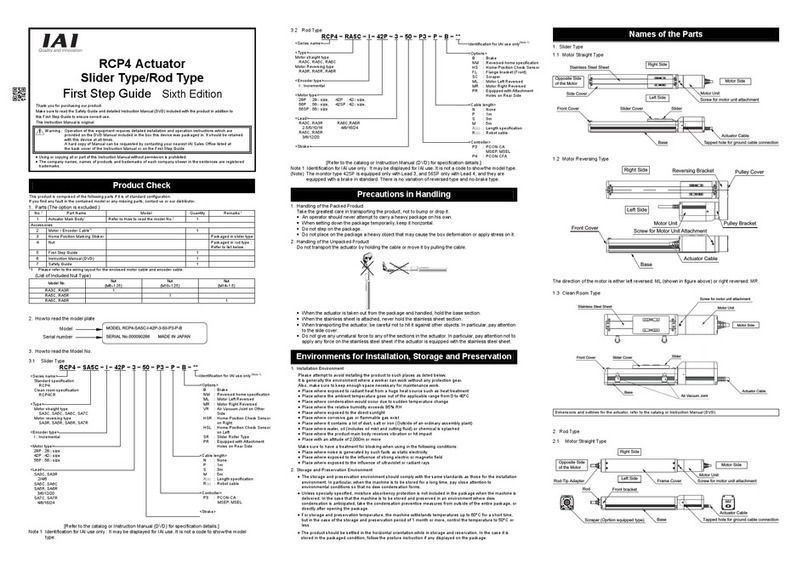
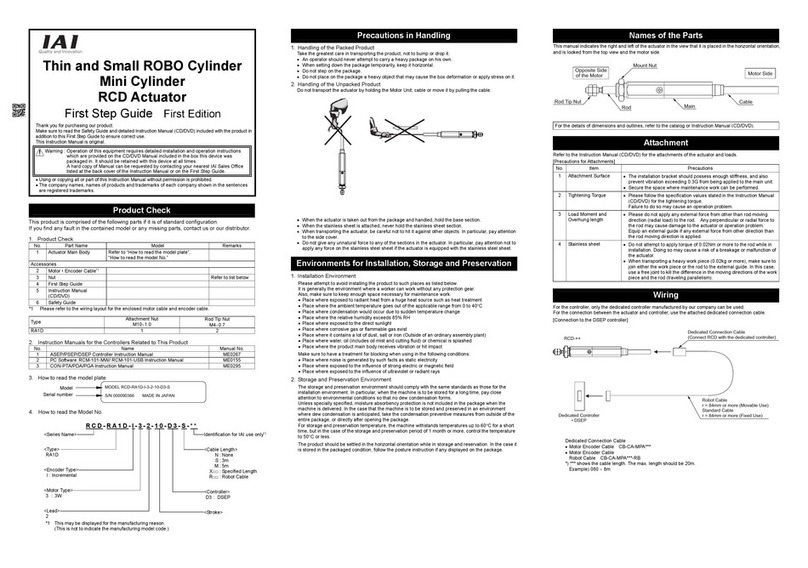
INTELLIGENT ACTUATOR Table of Contents
1.24 Extended Commands..................................................................................................... 292
Chapter 3 Key Characteristics of Actuator Control Commands and Points to Note......................... 298
1. Continuous Movement Commands [PATH, CIR, ARC, PSPL, CIR2, ARC2, ARCD, ARCC,
CIRS, ARCS].................................................................................................................... 298
2. PATH/PSPL Commands .................................................................................................. 300
3. CIR/ARC Commands....................................................................................................... 300
4. CIR2/ARC2/ARCD/ARCC Commands............................................................................ 300
Chapter 4 Palletizing Function.......................................................................................................... 301
1. How to Use ......................................................................................................................301
2. Palletizing Setting ............................................................................................................ 301
A. 3-point teaching method................................................................................................. 303
B. Method to set palletizing positions in parallel with the actuators ................................... 304
3. Palletizing Calculation...................................................................................................... 307
4. Palletizing Movement....................................................................................................... 308
5. Program Examples .......................................................................................................... 310
Chapter 5 Pseudo-Ladder Task........................................................................................................ 318
1. Basic Frame.....................................................................................................................318
2. Ladder Statement Field.................................................................................................... 319
3. Points to Note ..................................................................................................................319
4. Program Example............................................................................................................ 320
Chapter 6 Application Program Examples........................................................................................ 321
1. Operation by Jog Command [Doll-Picking Game Machine]............................................ 321
2. Operation by Point Movement Command [Riveting System] .......................................... 324
3. Palletizing Operation [Palletizing System]....................................................................... 327
Part 5 Multi-Tasking................................................................................................. 330
Chapter 1 Real-Time Multi-Tasking .................................................................................................. 330
1. SEL Language ................................................................................................................. 330
2. Multi-Tasking.................................................................................................................... 331
3. Difference from a Sequencer........................................................................................... 332
4. Release of Emergency Stop............................................................................................ 333
5. Program Switching........................................................................................................... 334
Chapter 2 Example of Building a System......................................................................................... 335
1. Equipment........................................................................................................................ 335
2. Operation......................................................................................................................... 335
3. Overview of the Screw-Tightening System...................................................................... 336
4. Hardware ......................................................................................................................... 337
5. Software........................................................................................................................... 339
Appendix...................................................................................................................... 341
1. Position Table................................................................................................................. 347
2. Programming Format .....................................................................................................348
3. Positioning to Five Positions .......................................................................................... 349
4. How to Use TAG and GOTO.......................................................................................... 350
5. Moving Back and Forth between Two Points................................................................. 351
6. Path Operation ............................................................................................................... 352
7. Output Control during Path Movement........................................................................... 353