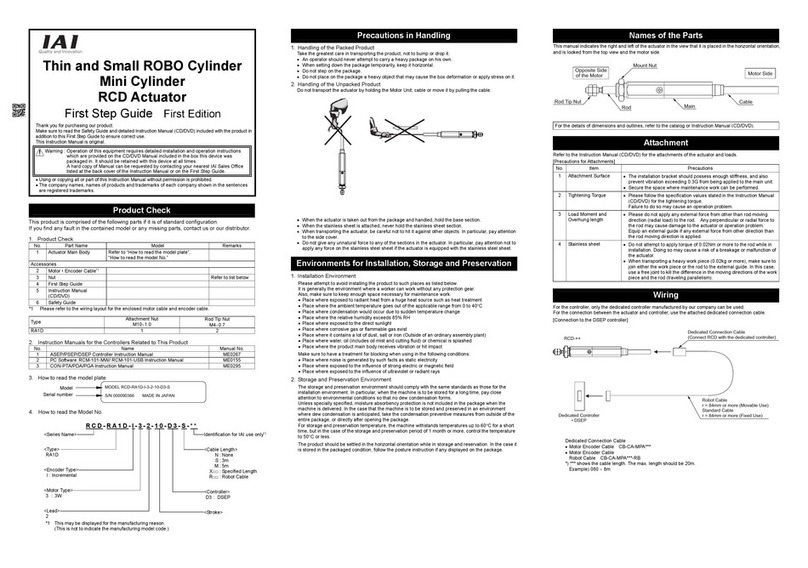
zTurn off the power to the product in the event of power failure. Failure to do so may cause the product
to suddenly start moving when the power is restored, thus resulting in injury or product damage.
zIf the product is generating heat, smoke or a strange smell, turn off the power immediately. Continuing
to use the product may result in product damage or fire.
zIf any of the internal protective devices (alarms) of the product has actuated, turn off the power
immediately. Continuing to use the product may result in product damage or injury due to malfunction.
Once the power supply is cut off, investigate and remove the cause and then turn on the power again.
zIf the LEDs on the product do not illuminate after turning on the power, turn off the power immediately.
The protective device (fuse, etc.) on the live side may remain active. Request repair to the IAI sales
office from which you purchased the product.
[Maintenance, Inspection, Repair]
zBefore conducting maintenance/inspection, parts replacement or other operations on the product,
completely shut down the power supply. At this time, take the following measures:
1. Display a sign that reads, “WORK IN PROGRESS. DO NOT TURN ON POWER” at a conspicuous
place, in order to prevent a person other than the operator from accidentally turning on the power
while the operation is working.
2. When two or more operators are to perform maintenance/inspection together, always call out every
time the power is turned on/off or an axis is moved in order to ensure safety.
[Disposal]
zDo not throw the product into fire. The product may burst or generate toxic gases.
Caution
[Installation]
zDo not use the product under direct sunlight (UV ray), in a place exposed to dust, salt or iron powder,
in a humid place, or in an atmosphere of organic solvent, phosphate-ester machine oil, sulfur dioxide
gas, chlorine gas, acids, etc. The product may lose its function over a short period of time, or exhibit a
sudden drop in performance or its service life may be significantly reduced.
zDo not use the product in an atmosphere of corrosive gases (sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid),
inflammable gases or ignitable liquids. Rust may form and reduce the structural strength or the motor
may ignite or explode.
zWhen using the product in any of the places specified below, provide a sufficient shield. Failure to do
so may result in malfunction:
1. Place where large current or high magnetic field is present
2. Place where welding or other operations are performed that cause arc discharge
3. Place subject to electrostatic noise
4. Place with potential exposure to radiation
zInstall the main unit and controller in a place subject to as little dust as possible. Installing them in a
dusty place may result in malfunction.
zDo not install the product in a place subject to large vibration or impact (4.9 m/s2 or more). Doing so
may result in the malfunctioning of the product.
zProvide an emergency-stop device in a readily accessible position so the device can be actuated
immediately upon occurrence of a dangerous situation during operation. Lack of such device in an
appropriate position may result in injury.
zProvide sufficient maintenance space when installing the product. Routine inspection and maintenance
cannot be performed without sufficient space, which will eventually cause the equipment to stop or the
product to sustain damage.
zDo not hold the moving parts of the product or its cables during installation. It may result in injury.
zAlways use IAI’s genuine cables for connection between the controller and the actuator. Also use IAI’s
genuine products for the key component units such as the actuator, controller and teaching pendant.