3
stehen, die bei etwa gleicher Beanspruchung hinsichtlich Druck und
Temperatur durchgeführt wird. Versuchsautoklaven müssen in beson-
deren Kammern / Schutzeinrichtung betrieben werden.
Wiederkehrende Prüfungen
Die Aufschlussgefäße sind wiederkehrenden Prüfungen (innere
Prüfungen und Druckprüfungen) durch den Sachkundigen zu unter-
ziehen, deren Zeitpunkt aufgrund der Erfahrungen, der Betriebsweise
und des Beschickungsgutes vom Betreiber festzulegen ist.
Die Garantie wird ungültig, wenn an den Versuchsautoklaven
mechanische Veränderungen vorgenommen werden oder wenn
infolge sehr starker Korrosion (z.B. Lochfraß durch Halogene) die
Festigkeit nicht mehr gewährleistet ist.
Besonders die Gewinde am Körper des Aufschlussgefäßes und der
Überwurfmutter unterliegen einer hohen Beanspruchung und sind
darum regelmäßig auf Verschleiß zu kontrollieren.
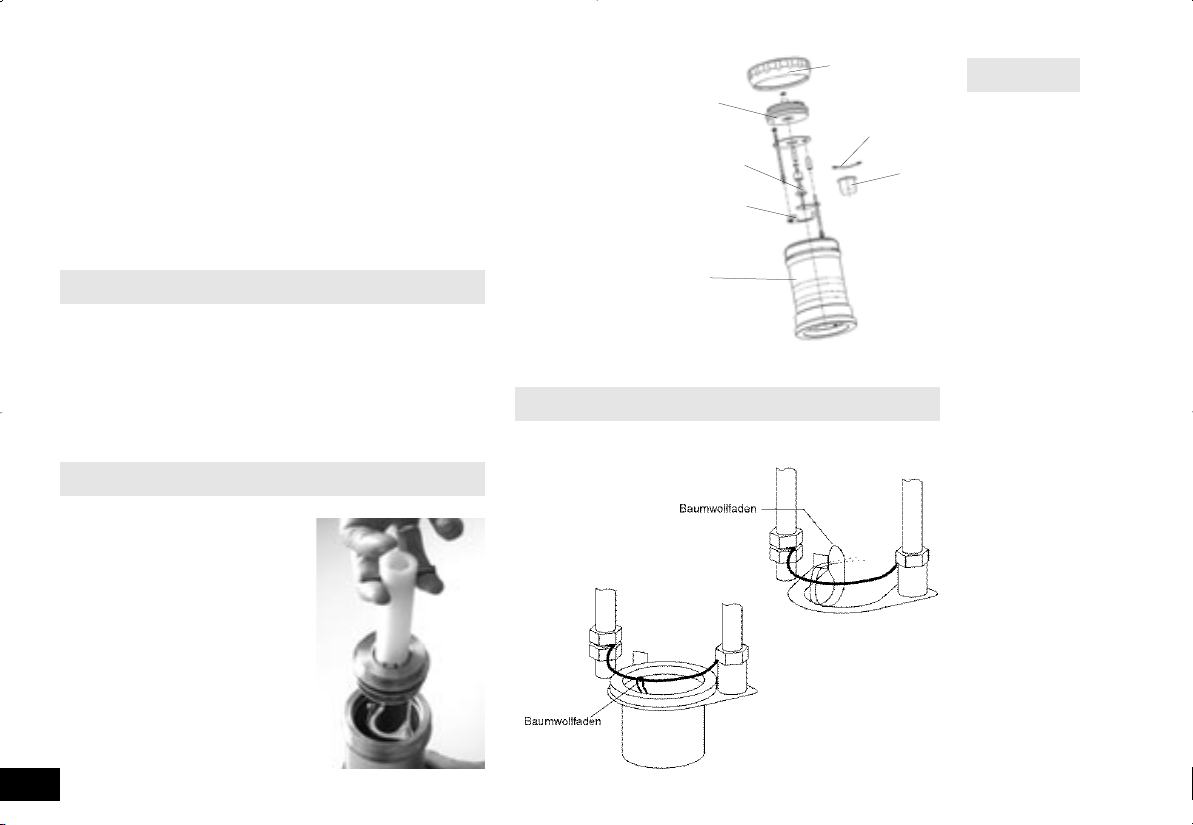
Der Zustand der Dichtungen ist zu kontrollieren und durch eine
Dichtigkeitsprüfung die Funktion sicherzustellen.
(siehe Kap. “Wartung und Pflege; Dichtigkeitsprüfung”)
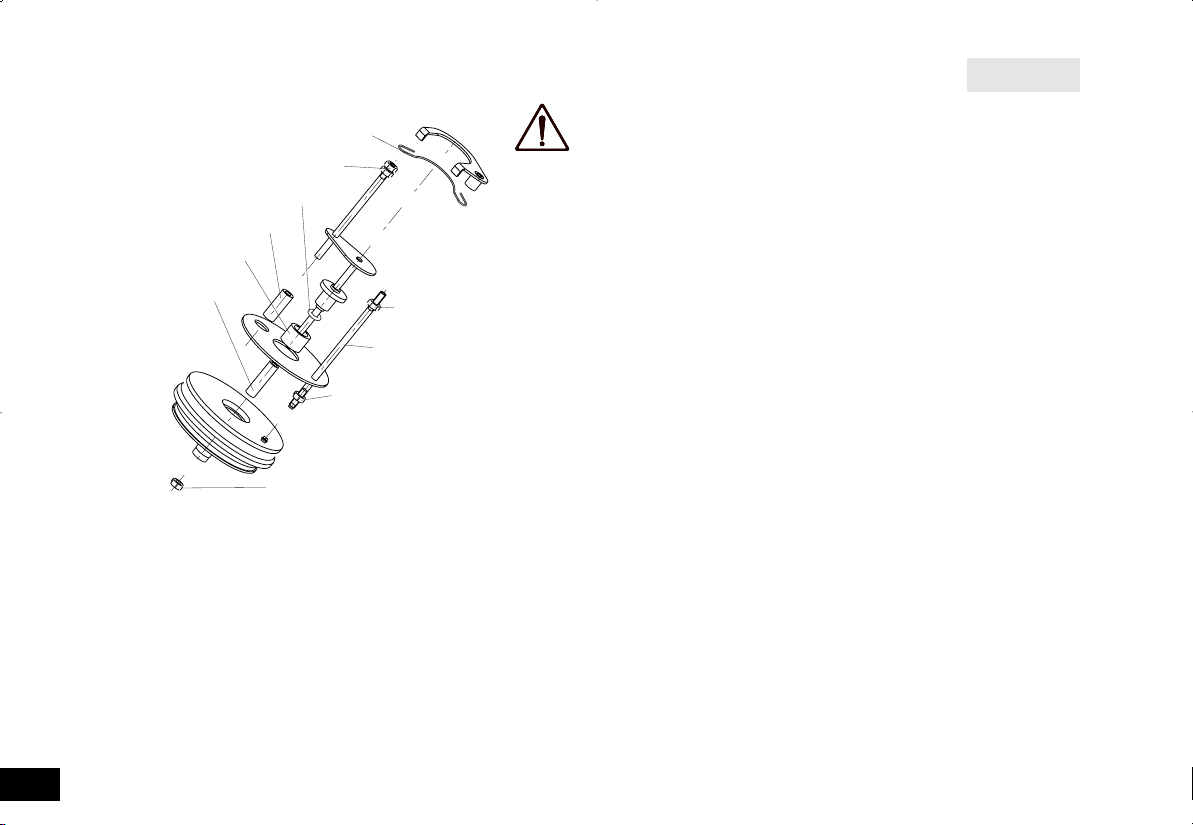
Druckprüfungen und Servicearbeiten am Aufschlussgefäß dürfen nur
von Sachkundigen vorgenommen werden.
Wir schreiben vor, das Aufschlußgefäß nach jeweils 1000
Versuchen oder nach einem Jahr oder je nach Anwendung auch
früher zur Überprüfung ggf. zur Reparatur in unser Werk einzu-
senden.
Definition Sachkundiger
Sachkundiger im Sinne dieser Betriebsanleitung ist nur, wer
1. auf Grund seiner Ausbildung, seiner Kenntnisse und seiner durch
praktische Tätigkeit gewonnenen Erfahrungen die Gewähr dafür
bietet, dass er die Prüfungen ordnungsgemäß durchführt
2. die erforderliche Zuverlässgkeit besitzt
3. hinsichtlich der Prüftätigkeit keinen Weisungen unterliegt
4. falls erforderlich, über geeignete Prüfeinrichtungen verfügt
5. einen geeigneten Nachweis für die in 1. genannten Vorraus-
setzungen erbringt.
Betrieb von Druckbehältern
Für den Betrieb von Druckbehältern sind die nationalen Richtlinien und
Gesetze zu berücksichtigen!
Verbrennungsrückstände, Hilfsstoffe
Weiterhin sind z.B. toxische Verbrennungsrückstände in Form von
Gasen, Asche oder Niederschlägen an der Innenwand des
Aufschlußgefäßes möglich.
Beachten Sie die für die Tätigkeit und den Arbeitsplatz geltenden
Unfallverhütungsvorschriften. Tragen Sie Ihre persönliche
Schutzausrüstung.
Beim Umgang mit Verbrennungsproben, Verbrennungsrückstän-
den und Hilfsstoffen sind die jeweiligen Sicherheitsvorschriften zu
beachten. Gefahren können z.B. von folgenden Stoffen ausgehen:
ätzenden
leicht entzündlichen
explosionsfähigen
bakteriologisch verseuchten
toxischen
Sauerstoff
Beachten Sie beim Umgang mit Sauerstoff die entsprechenden
Vorschriften.
Gefahrenhinweis: Sauerstoff ist als verdichtetes Gas brandfördernd;
unterstützt intensiv Verbrennungen; kann heftig mit brennbaren Stoffen
reagieren. Kein Öl oder Fett verwenden!
Verwendung von Tiegel aus Edelstahl
Bei Verwendung von Tiegeln aus Edelstahl ist nach jedem Versuch
deren Zustand genau zu kontrollieren.
Durch eine Veringerung der Materialstärke kann der Tiegel verbrennen
und das Aufschlußgefäß AOD 1.1 beschädigen.
Nach max. 25 Verbrennungen dürfen die Tiegel aus Sicherheitsgründen
nicht mehr benutzt werden.
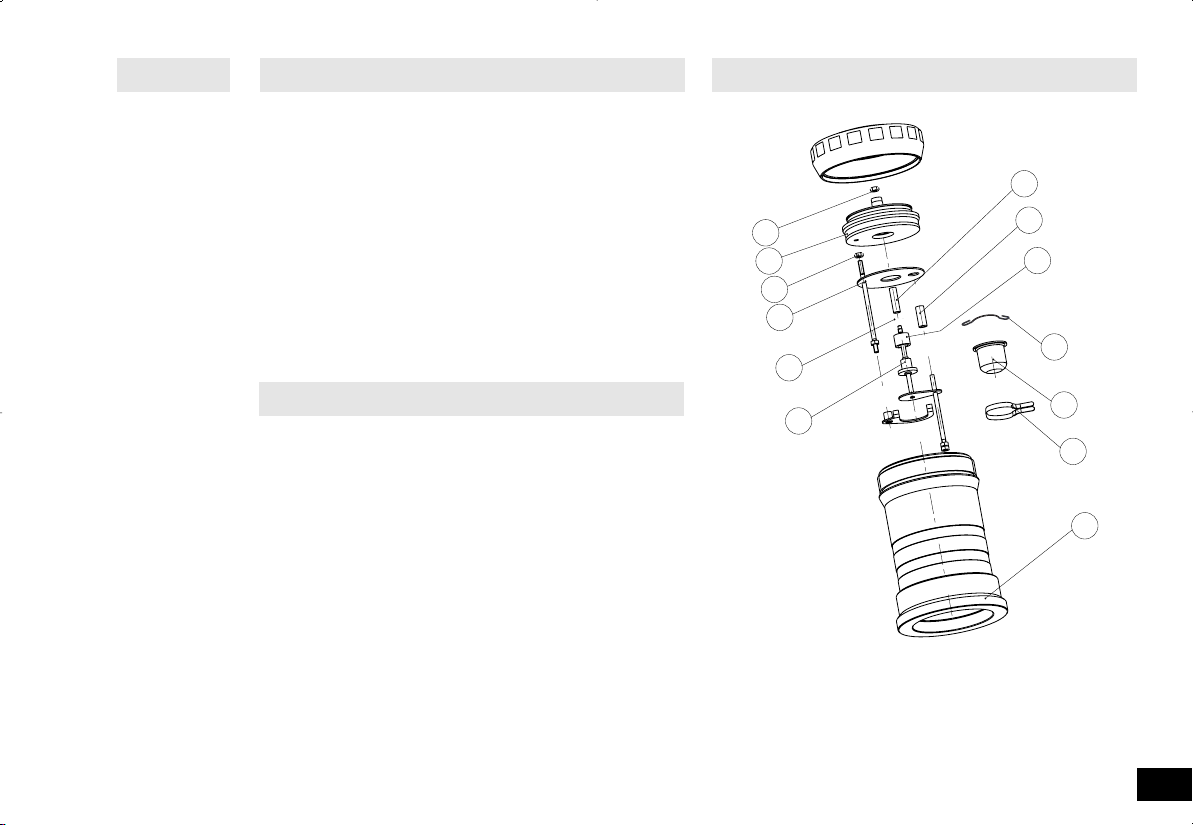
Spezifikation des Aufschlussgefäßes:
Das Aufschlussgefäß wird nach der Richlinie für Druckgeräte 97/23/EG
hergestellt.
Das Aufschlussgefäß wurde einer Druckprüfung mit dem
Prüfdruck von 280 bar und einer Dichtigkeitsprüfung mit Sauerstoff
von 30 bar unterzogen.
Das Aufschlussgefäß AOD 1.1 ist ein Versuchsautoklav und muss
nach jeder Verwendung von einem Sachkundigen geprüft werden.
Unter einer einzelnen Verwendung ist auch eine Versuchsreihe zu ver-