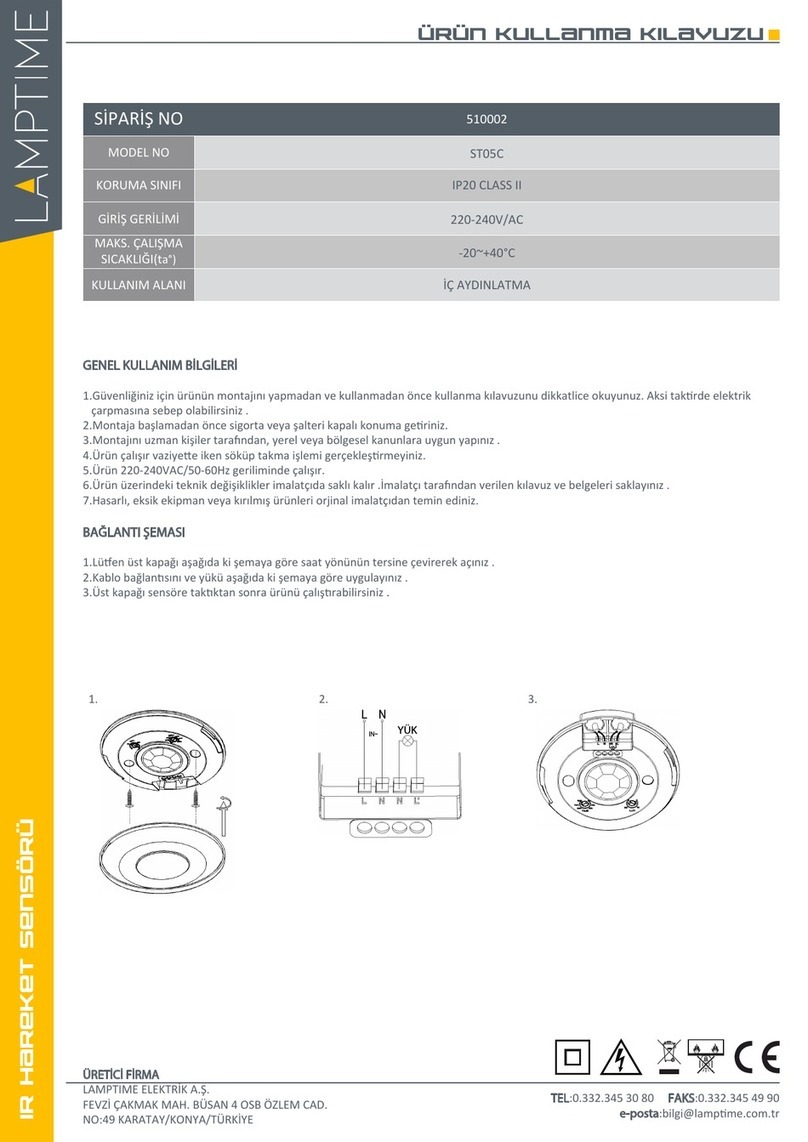
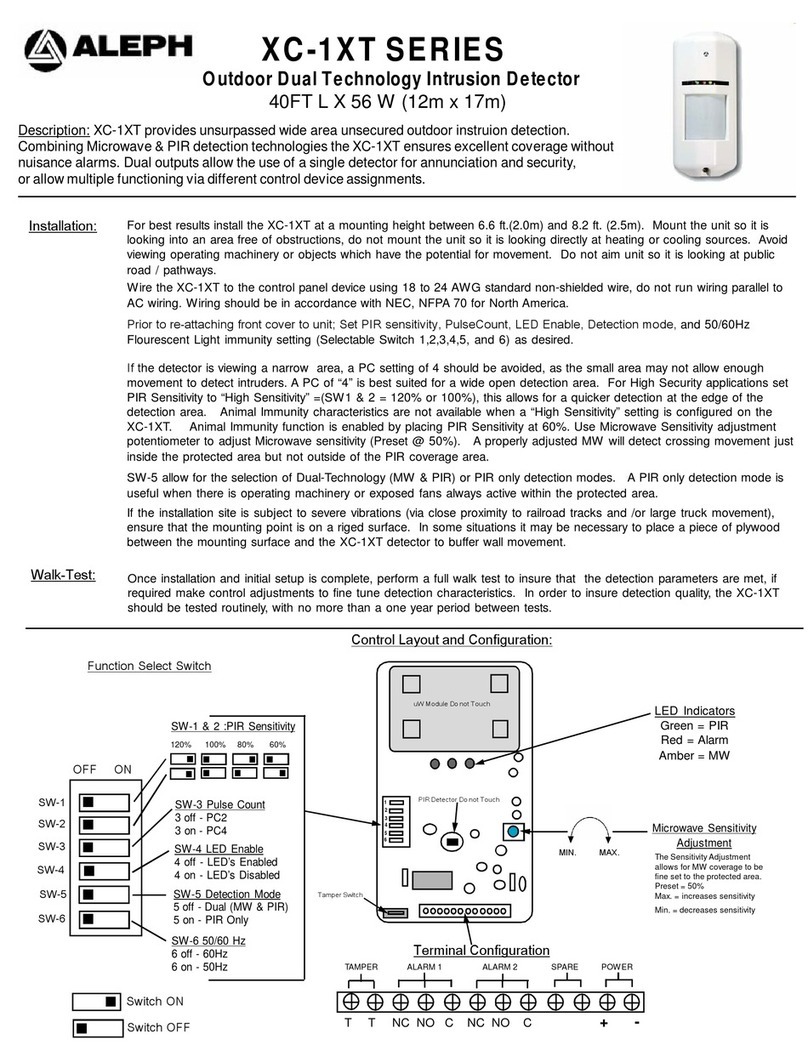
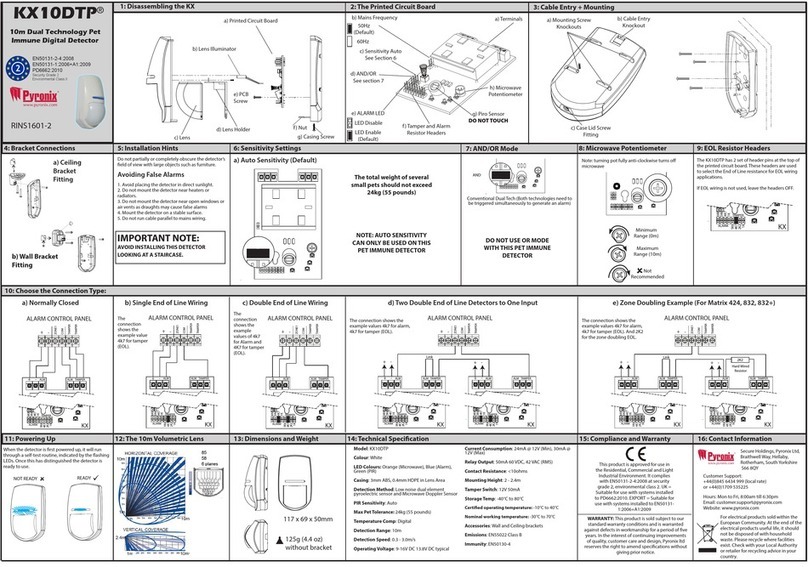
6 ACTIVA SATEL
4. Configuration
Start-up and basic configuration of the ACTIVA barriers can be done manually by placing jumpers
over pins directly on the device electronics board. Full configuration and diagnostics of the devices is
only possible from a computer with the ACTIVA program installed.
4.1 Manual configuration
1. Connect the power supply cables and sync cable to the device.
2. Position the transmitter and the receiver opposite each other so that nothing can block the path of
their IR beams.
3. Remove the jumper from the SAP pins (see description of pins designated in Fig. 3).
4. Power up the transmitter and receiver. The indicator LED will start blinking rapidly.
5. Wait until the LED blinking goes slower and then place a jumper over the SAP pins – this will
complete the synchronization process and restore the factory default settings of the barrier
(Beam sensitivity is set at 120 ms, alarm is triggered by interruption of two beams, Autobypass
of the beams is disabled, Maximum time of all beams interruption is set at 0).
6. If the LED is to signal interruption of the beams (irrespective of the LED input status – terminal 8),
place a jumper over the LED pins.
4.2 Configuration by using computer
The barrier delivery set includes the ACTIVA configuration/diagnostics program intended for IBM
PC/AT compatible computers. It operates on any hardware configuration in the WINDOWS
environment. The program should be installed on the computer hard disk (by launching the
Activa.exe program).
The ACTIVA barriers communicated with the computer through the RS-232 interface. To connect the
barrier to the computer, use the USB-RS converter for programming SATEL devices.
In order to configure the barrier by using computer, follow the procedure below:
1. Connect the power supply cables and the sync cable to the device.
2. Connect the barrier to the computer.
3. Make sure that the beam path is not obstructed by any obstacles.
4. Power up the transmitter and receiver.
5. Start the ACTIVA program and select the port through which communication will be effected
(Configuration RS-232). If connection with the barrier is established, the color of the program
status bar will change to green (gray color means no connection).
6. Carry out synchronization of the transmitter and the receiver. For this purpose, enter in the
program the factory assigned Receiver serial number (the serial number sticker is placed on the
transmitter) and save the data to the barrier memory.
7. Program the device as required and save the data to the barrier memory.
Explanations for Figure 11:
1 - Transmitter serial number – a unique identification code of the device (5-digit number from 0–
65535 range).
2 - Beams parameters:
Sensitivity – the amount of time (counted in milliseconds, within the 40–1000 range) a beam
must be interrupted to barrier detect the interruption (entering 0 will permanently disable the
beam).
Autobypass – number of interruptions of a given beam (within the 0–255 range) after which it
will be automatically bypassed (0 – no bypassing).
Autobypass counting time – the amount of time (counted in seconds, within the 0–255 range)
during which consecutive beam interruptions are counted until the beam is automatically
bypassed (0 – no counting).