2
Table of Contents
Overview ......................................................3
System Overview.......................................... 3
System Components ..................................... 3
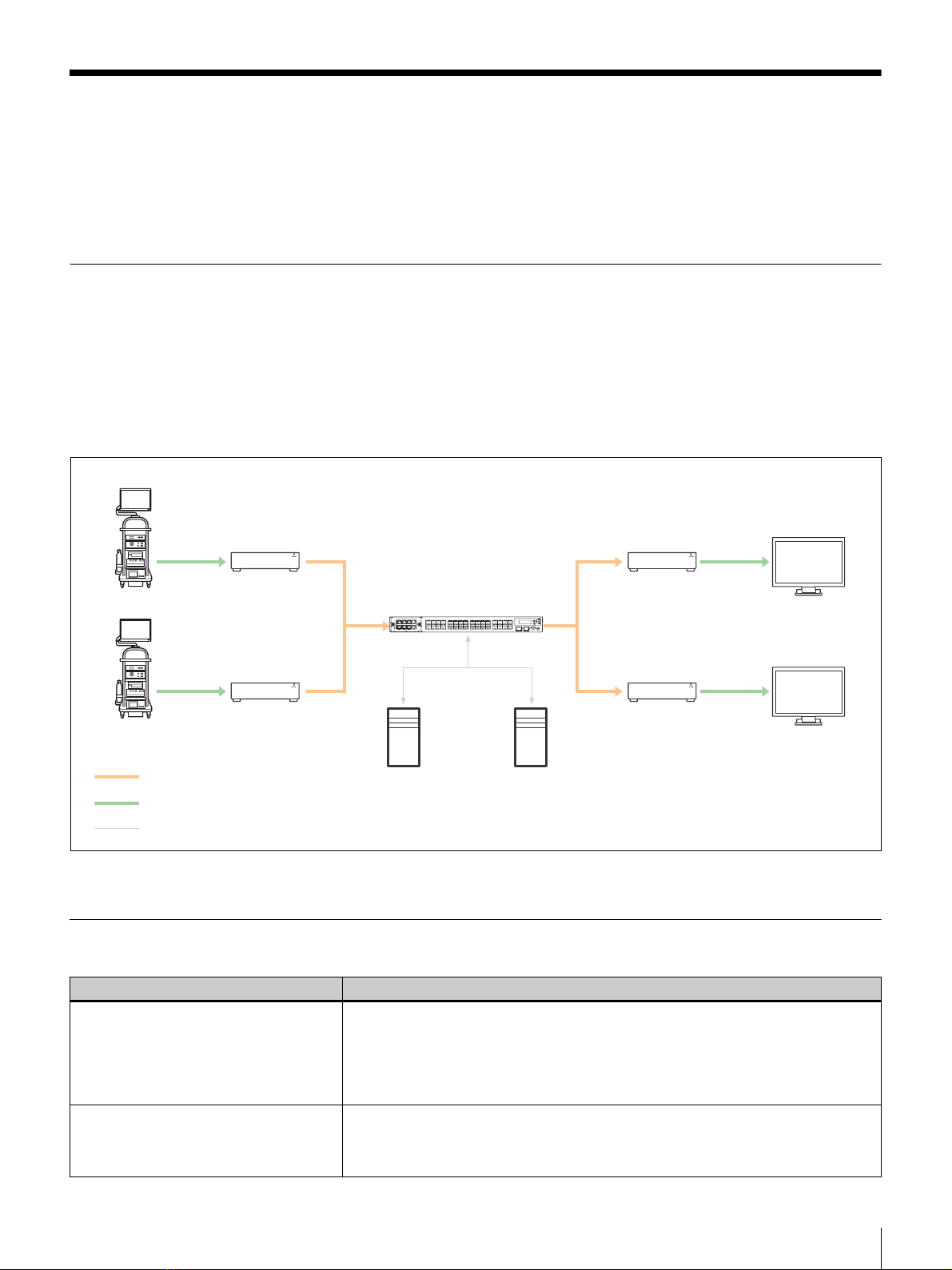
System Construction Workflow ................... 4
Step 1: Determining the Overall
System Structure..................................6
Choosing Source and Destination
Devices................................................ 6
Determining the Operation Mode................. 7
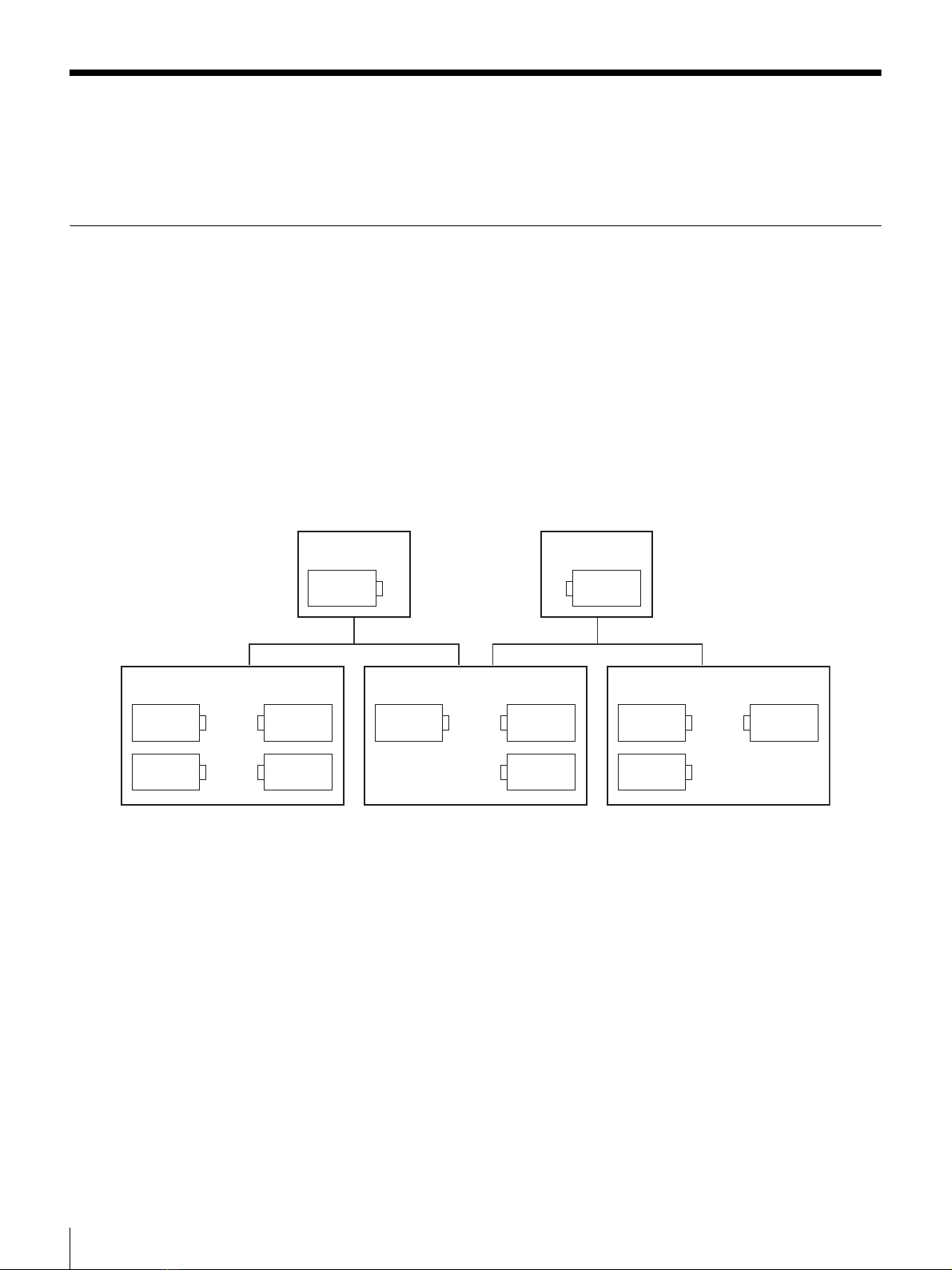
Determining the Sync Mode....................... 11
Calculating the Number of Required
Devices.............................................. 13
System Operation........................................ 14
Step 2: Installing a Network Switch.........15
Preparing a Network Switch....................... 15
Determining the Network Structure............ 16
Network Structure Examples...................... 18
Configuring a Network Switch................... 20
Step 3: Installing an NSM Server .............22
Preparing an NSM Server........................... 22
Connecting a Network Switch to an NSM
Server ................................................ 22
Configuring Windows Server (OS) ............ 22
Installing Network System Manager .......... 25
Activating a Network System Manager
License .............................................. 26
Changing the Password of the Default
Account ............................................. 27
Registering a User Account........................ 27
Step 4: Installing an IP Converter ............30
Preparing an IP converter ........................... 30
Connecting an IP Converter to a Network
Switch................................................ 30
Configuring a Workgroup........................... 31
Configuring an IP Converter ...................... 32
Basic IP Converter Configuration
Operations ......................................... 33
IP Converter Configuration Procedure ....... 35
Setting the Sync Mode................................ 39
Step 5: Connecting Source and Destination
Devices................................................42
Connecting to an SDI IP Converter ............ 42
Connecting to a DVI IP Converter ............. 42
Step 6: Configuring the Routing and
Monitoring Screens ............................43
Configuring the Routing Screen ................. 43
Configuring the Monitoring Screen............ 44
Step 7: Collecting Logs ............................47
Collecting IP Converter Logs ..................... 47
Collecting Network System Manager
Logs................................................... 48
Step 8: Checking System Settings and
Device Connections (Checklist)........49
OR IP Solution System Checklist............... 50
Checklist Details......................................... 51
Step 9: Creating Backup Data..................55
Windows Server 2012 Backup Function .... 55
Acquiring Backup Data .............................. 55
Recovering from a Backup ......................... 56
Notes on System Operation .....................59
Starting Each Device .................................. 59
Turning Off Each Device............................ 60
Turning Off a Network Switch ................... 60
System Fault Troubleshooting ................61
Faults Preventing Access to Network
System Manager................................ 62
Faults Due to Errors when Enabling/
Disabling Settings ............................. 62
Faults Due to System Errors ....................... 63
Faults Preventing Connection of IP
Converters ......................................... 63
Faults with Network GenLock Leader
Devices .............................................. 64
Faults with Network Switches .................... 66
Replacement Procedures when IP
Converter Fault Occurs .....................67
Changing an IP Converter .......................... 67
Changing a Network GenLock Leader
Device................................................ 68
Changing a Network GenLock Follower
Device................................................ 70
Changing a Network InputLock Device ..... 72
IP Converter Expansion Procedures.......74
Device Settings ........................................... 74
GenLock Settings........................................ 74
InputLock Settings...................................... 76
For customers in the U.S.A.
Caution
Federal law (United States of America) restricts this device to
sale by or on the order of a licensed healthcare practitioner.