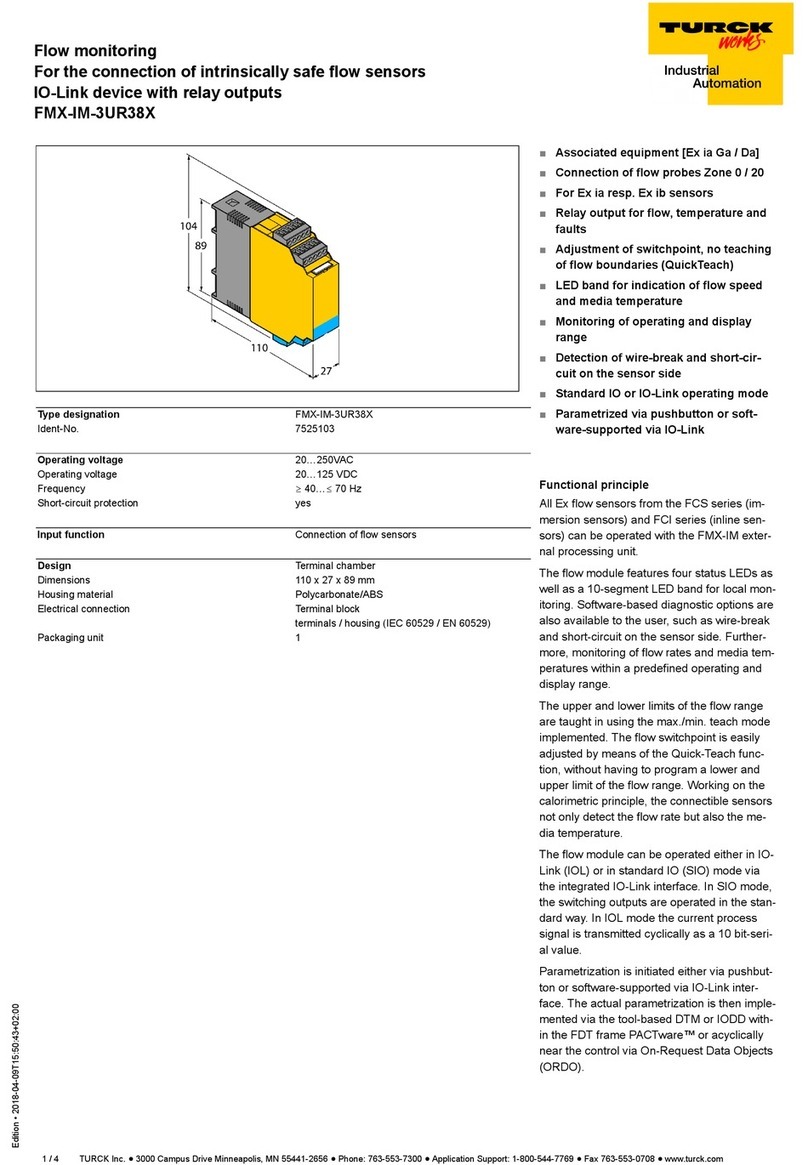
Table of Contents
4
Hans Turck GmbH & Co. KG | T +49 208 4952-0 | F +49 208 4952-264 | [email protected] | www.turck.com8.1.3 Setting the IP address via the web server .............................................................................32
8.2 ARGEE/FLC ......................................................................................................................33
8.3 Commissioning an IO-Link device with IO-Link V1.0..............................................33
8.4 Commissioning an IO-Link device with IO-Link V1.1..............................................34
8.5 Read in connected IO-Link devices: topology scan in the DTM ...........................36
8.6 Commissioning the device in PROFINET...................................................................37
8.6.1 PROFINET IO device model.........................................................................................................37
8.6.2 Device model – TBEN-L…-8IOL ................................................................................................38
8.6.3 Address setting in PROFINET .....................................................................................................39
8.6.4 FSU – Fast Start-Up (prioritized startup)................................................................................39
8.6.5 MRP (Media Redundancy Protocol).........................................................................................39
8.6.6 User data for acyclic services .....................................................................................................40
8.6.7 The IO-Link function block IOL_CALL.....................................................................................44
8.7 Connecting the device to a Siemens PLC in PROFINET..........................................48
8.7.1 Installing the GSDML file.............................................................................................................49
8.7.2 Connecting the devices to the PLC .........................................................................................50
8.7.3 Assigning the PROFINET device name...................................................................................51
8.7.4 Setting the IP address in TIA Portal .........................................................................................52
8.7.5 Configuring device functions....................................................................................................53
8.7.6 Going online with the PLC..........................................................................................................56
8.7.7 PROFINET – mapping ...................................................................................................................56
8.7.8 Use the IO_LINK_DEVICE function block in TIA Portal......................................................57
8.8 Commissioning the device in Modbus TCP..............................................................64
8.8.1 Implemented Modbus functions .............................................................................................64
8.8.2 Modbus registers ...........................................................................................................................64
8.8.3 Data width........................................................................................................................................67
8.8.4 Register mapping...........................................................................................................................68
8.8.5 Error Behavior (watchdog)..........................................................................................................70
8.9 Commissioning the Device in EtherNet/IP ...............................................................70
8.9.1 Common EtherNet/IP features..................................................................................................70
8.9.2 EDS files and catalog files............................................................................................................70
8.9.3 Device Level Ring (DLR)...............................................................................................................71
8.9.4 Diagnostic messages via process data...................................................................................71
8.9.5 EtherNet/IP standard classes .....................................................................................................72
8.9.6 VSC-Vendor Specific Classes ......................................................................................................92
8.10 Connecting the Devices to a Rockwell PLC with EtherNet/IP ............................ 106
8.10.1 Adding the devices from the catalog files to the new project................................... 107
8.10.2 Configuring the device in RS Logix ...................................................................................... 109
8.10.3 Parameterizing the device....................................................................................................... 110
8.10.4 Going online with the PLC....................................................................................................... 111
8.10.5 Reading process data ................................................................................................................ 113
9 Parameterizing and Configuring.................................................................................................114
9.1 Parameters................................................................................................................... 114
9.1.1 Adapting process data mapping........................................................................................... 120
9.1.2 PROFINET parameters ............................................................................................................... 121
9.2 IO-Link functions for acyclic communication ....................................................... 121
9.2.1 Port functions for Port 0 (IO-Link Master)........................................................................... 122
10 Operating .........................................................................................................................................127
10.1 Process input data...................................................................................................... 127
10.2 Process output data................................................................................................... 129
10.3 LED displays................................................................................................................. 130