2
Operation manual
ACO Clara
1 Introduction............................................................................3
1.1 What water we can treat .......................................................3
2 Safety......................................................................................4
2.1 General requirements regarding occupational safety .............4
2.2 Protection against accidents ..................................................4
2.3 Protection against infections caused by waste water.............4
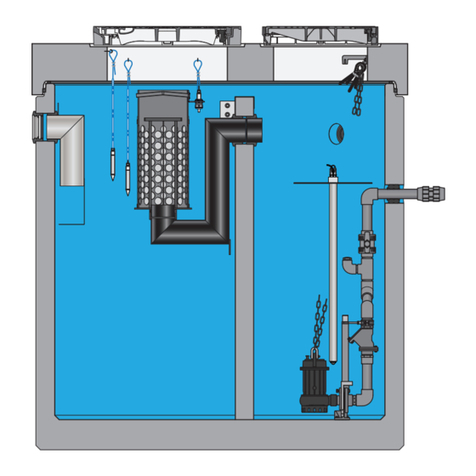
3 Description of plant................................................................5
3.1 General description.................................................................5
3.2 Check of plant type, nameplate..............................................7
3.3 Cover ......................................................................................7
3.4 Inlet and outlet pipes..............................................................8
3.5 Air-lift pumps..........................................................................8
3.6 Blower.....................................................................................8
3.7 Mechanical pretreatment .......................................................9
3.8 Activation tank .......................................................................9
3.9 Final sedimentation tank........................................................9
3.10 Ventilation pipe ......................................................................9
4 How the plant works ............................................................10
5 Installation ...........................................................................10
5.1 Transport and storage..........................................................10
5.2 Installation of blower ...........................................................10
5.3 Plant ventilation...................................................................10
5.4 Construction requirements....................................................10
5.5 Electrical installation ............................................................11
5.5.1 1 phase motor ......................................................................11
5.5.2 3 phase motor ......................................................................11
6 Operation and maintenance instructions.............................13
6.1 Plant commissioning ............................................................13
6.2 Records of plant operation...................................................13
6.3 Accessories for plant operation.............................................13
6.4 Description of individual checks and maintenance work......14
6.4.1 Check of blower function......................................................14
6.4.2 Aeration in activation tank ..................................................14
6.4.3 Functions of air-lift pumps....................................................15
6.4.4 Tank level of mechanical pretreatment, inlet pipe ................15
6.4.5 Level of final sedimentation tank and outlet object .............15
6.4.6
Quality of treated water
........................................................15
6.4.7
Check of concentration of activated sludge – sedimentation test
.....15
6.4.8 Check of treated water .........................................................15
6.4.9 Discharging of condensate water from aeration system ......16
6.4.10 Discharging of surplus sludge...............................................16
6.4.11 Discharging of mechanical pretreatment tank .....................16
6.4.12 Cleaning of tank walls..........................................................16
6.4.13 Cleaning of air-lift pumps.....................................................16
6.4.14 Replacement of aeration elements........................................17
6.5 Sampling ..............................................................................17
6.5.1 Sample at inlet .....................................................................17
6.5.2 Sample at outlet ...................................................................17
6.5.3 Sample of activated sludge...................................................17
6.6 Plant breakdown ..................................................................18
6.6.1 Short-term operational constraints ......................................18
6.6.2 Long-term shutdown ............................................................18
7 Troubleshooting....................................................................19
8 Certification..........................................................................20
9 Operation manual for blowers .............................................21
9.1 Installation ...........................................................................21
9.2 Ambience ..............................................................................21
9.3 Medium quality ....................................................................21
9.4 Piping ...................................................................................21
9.5 Storage .................................................................................21
9.6 Maintenance and service......................................................21
9.6.1 Filter element cleaning..........................................................22
9.6.2 Filter element replacement....................................................22
9.6.3 Valve box, diaphragm replacement......................................22
9.6.4 Reset of auto stopper............................................................23
9.6.5 Magnet replacement.............................................................24
9.7 Pictograms for maintenance and service..............................25
9.8
Maintenance and service for lamella blowers DT 4.25 and DT 4.40....
26
9.9
Maintenance and service for side channel blower SV 5.250/2
......30
9.10
Maintenance and service for side channel blower SV 8.190
..........34
List of contents: