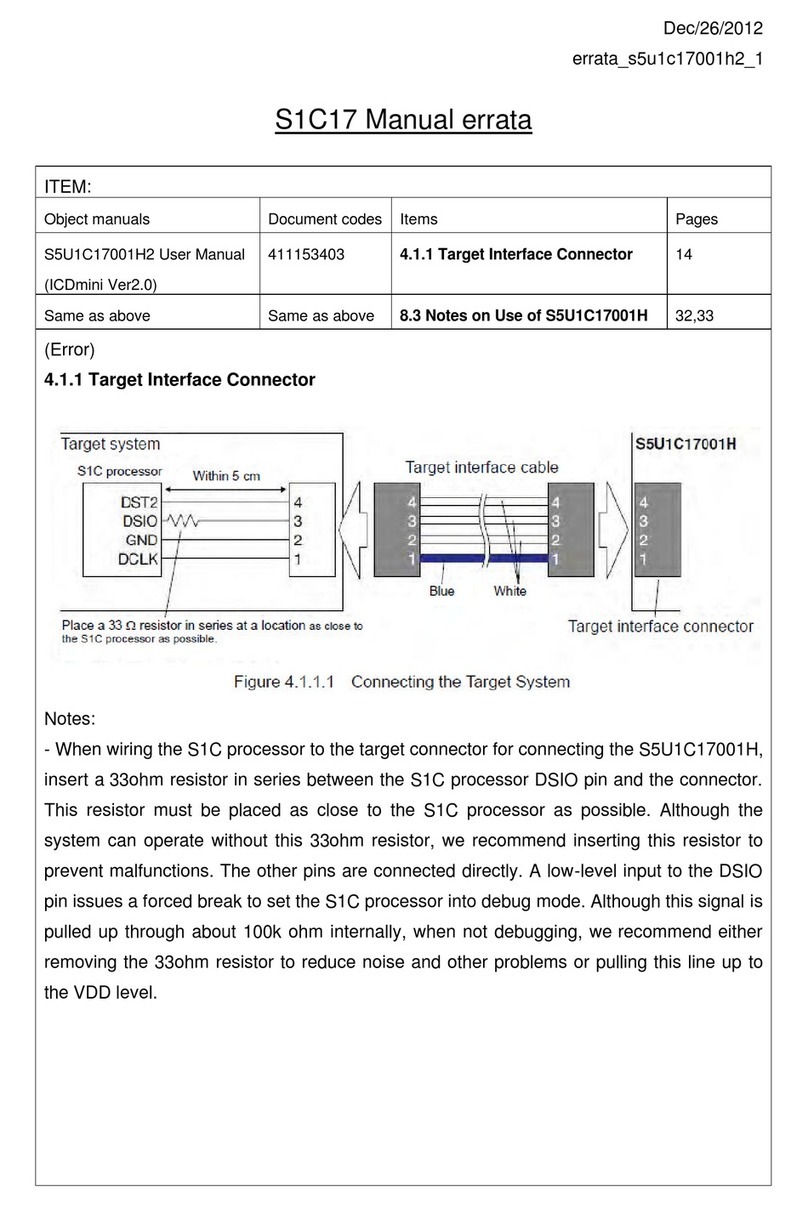
CONTENTS
S1C17 CORE MANUAL Seiko Epson Corporation v
(Rev. 1.2)
ld.b [%rb]+, %rs ....................................................................................................................... 7-93
ld.b [%rb]-, %rs ........................................................................................................................ 7-93
ld.b -[%rb], %rs ........................................................................................................................ 7-93
ld.b [%sp + imm7], %rs ........................................................................................................... 7-95
ld.b [imm7], %rs ....................................................................................................................... 7-96
ld.ca %rd, %rs ............................................................................................................................ 7-97
ld.ca %rd, imm7 ......................................................................................................................... 7-98
ld.cf %rd, %rs ............................................................................................................................ 7-99
ld.cf %rd, imm7 ........................................................................................................................ 7-100
ld.cw %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-101
ld.cw %rd, imm7 ........................................................................................................................ 7-102
ld.ub %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-103
ld.ub %rd, [%rb]........................................................................................................................ 7-104
ld.ub %rd, [%rb]+ ...................................................................................................................... 7-105
ld.ub %rd, [%rb]- ....................................................................................................................... 7-105
ld.ub %rd, -[%rb]....................................................................................................................... 7-105
ld.ub %rd, [%sp + imm7].......................................................................................................... 7-107
ld.ub %rd, [imm7]...................................................................................................................... 7-108
nop .......................................................................................................................................... 7-109
not %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-110
not/c %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-110
not/nc %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-110
not %rd, sign7 ........................................................................................................................ 7-111
or %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-112
or/c %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-112
or/nc %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-112
or %rd, sign7 ........................................................................................................................ 7-113
ret .......................................................................................................................................... 7-114
ret.d .......................................................................................................................................... 7-114
retd .......................................................................................................................................... 7-115
reti .......................................................................................................................................... 7-116
reti.d .......................................................................................................................................... 7-116
sa %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-117
sa %rd, imm7 ........................................................................................................................ 7-118
sbc %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-119
sbc/c %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-119
sbc/nc %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-119
sbc %rd, imm7 ........................................................................................................................ 7-120
sl %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-121
sl %rd, imm7 ........................................................................................................................ 7-122
slp .......................................................................................................................................... 7-123
sr %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-124
sr %rd, imm7 ........................................................................................................................ 7-125
sub %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-126
sub/c %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-126
sub/nc %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-126
sub %rd, imm7 ........................................................................................................................ 7-127
sub.a %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-128
sub.a/c %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-128
sub.a/nc %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-128
sub.a %rd, imm7 ........................................................................................................................ 7-129
sub.a %sp, %rs .......................................................................................................................... 7-130
sub.a %sp, imm7 ....................................................................................................................... 7-131
swap %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-132
xor %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-133
xor/c %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-133
xor/nc %rd, %rs ........................................................................................................................... 7-133
xor %rd, sign7 ........................................................................................................................ 7-134