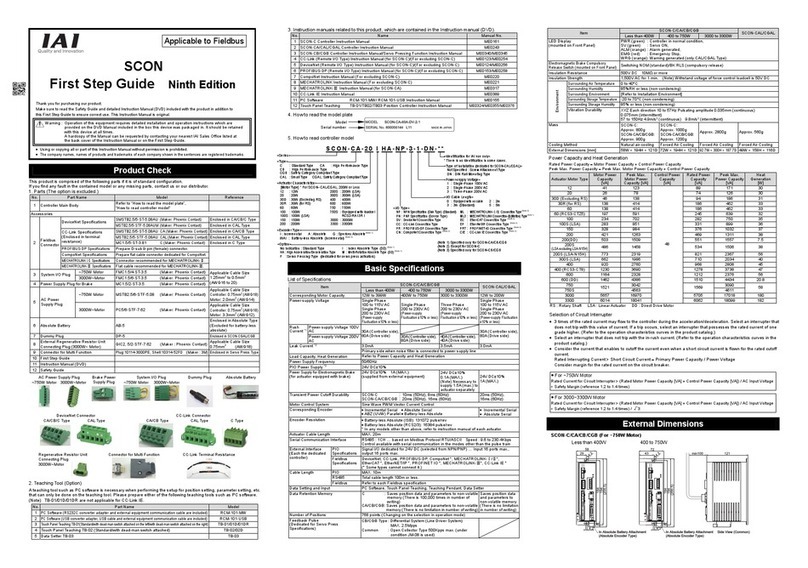
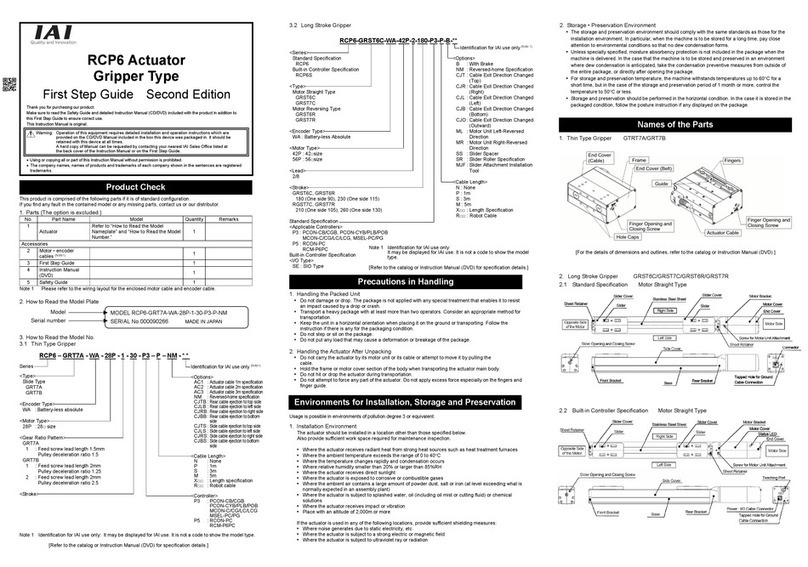
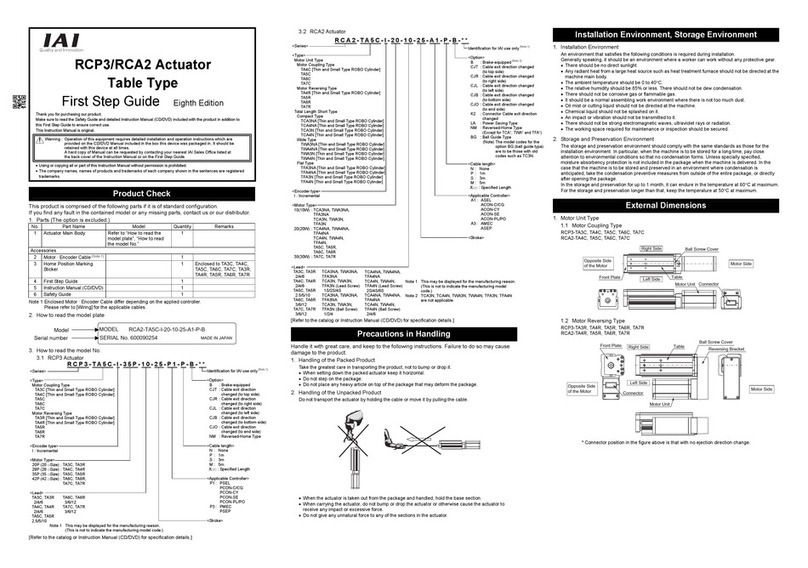
ME0342-4B
2.7 Installation and Storage Environment ············································ 2-26
2.7.1 Installation Environment···········································································2-26
2.7.2 Storage and Preservation Environment·······················································2-26
2.8 Noise Elimination and Mounting Method ········································ 2-27
2.8.1 Noise Elimination····················································································2-27
2.8.2 Installation and Mounting ·········································································2-28
Chapter 3 Wiring
3.1 Positioner Mode (PIO Control) ····················································· 3-1
3.1.1 Wiring Diagram (Connection of Devices) ·····················································3-1
3.1.2 PIO Pattern Selection and PIO Signal·························································3-2
3.1.3 Wiring ··································································································3-7
3.2 Pulse Train Control Mode···························································· 3-26
3.2.1 Wiring Diagram (Connection of Devices) ·····················································3-26
3.2.2 I/O Signals in Pulse Train Control Mode and Each Functions ··························3-27
3.2.3 Wiring ··································································································3-29
3.3 Wiring Method ·········································································· 3-42
3.3.1 Wiring Layout of Power Supply Connector···················································3-42
3.3.2 Connection to Actuator ············································································3-43
3.3.3 Connection of PIO ··················································································3-44
3.3.4 Connection of Pulse Train Signal ·······························································3-45
3.3.5 SIO Connector Connection·······································································3-47
3.3.6 Field Network Connector of PIO ································································3-48
Chapter 4 Operation
4.1 Basic Operation ········································································ 4-1
4.1.1 How to Turn on Power ·············································································4-1
4.1.2 Basic Operation Methods ·········································································4-2
4.1.3 Parameter Settings ·················································································4-8
4.2 Operation in Positioner Mode······················································· 4-9
4.2.1 Operation Modes of Rotary Actuator in Multiple Rotation Mode and
Command Limitations··············································································4-11
4.2.2 Set of Position Table (This section is not required in selection of
pulse train control mode.)·········································································4-12
4.2.3 Control of Input Signal ·············································································4-21
4.2.4 Operation Ready and Auxiliary Signals (Common to Patterns 0 to 7) ················4-22
4.2.5 Operation with the Position No. Input (PIO Patterns 0 to 3 and 6)·····················4-36
4.2.6 Direct Position Specification (Operation of PIO Pattern 4 and 7) ······················4-63
4.2.7 Direct Position Specification (PIO Pattern 5) ················································4-85
4.2.8 Preparation for Operation in Force Sensor Pressing (Loadcell Calibration)·········4-96
ME0342-4B
4.3 Pulse Train Control Mode···························································· 4-101
4.3.1 I/O Signal Controls··················································································4-103
4.3.2 Operation Ready and Auxiliary Signals ·······················································4-104
4.3.3 Pulse Train Input Operation ······································································4-116
4.3.4 Settings of Basic Parameters Required for Operation ····································4-120
4.3.5 Parameter Settings Required for Advanced Operations··································4-124
4.4 Operation of Field Network Type··················································· 4-128
4.5 Absolute Reset ········································································· 4-129
4.5.1 How to Perform Absolute Reset·································································4-130
4.5.2 Absolute Battery Charge ··········································································4-135
Chapter 5 Various Functions
5.1 Collision Detection Feature·························································· 5-1
5.1.1 Collision Detection Judgement ··································································5-2
5.1.2 How to Settings······················································································5-3
5.1.3 How to Adjustment··················································································5-4
5.2 Power-saving Function ······························································· 5-5
5.2.1 AUTO Servo OFF and Full Servo Function ··················································5-5
5.2.2 Auto current down function ·······································································5-9
Chapter 6 Parameter
6.1 Parameter················································································ 6-1
6.1.1 Parameter List ·······················································································6-2
6.1.2 Parameter Details···················································································6-7
6.2 Servo Adjustment ······································································ 6-58
Chapter 7 Maintenance and Inspection
7.1 Periodic Inspection ···································································· 7-1
7.1.1 Periodic Inspection Items ·········································································7-2
7.2 Requests When Replacing Units ·················································· 7-4
7.3 Consumable Parts ····································································· 7-5
7.4 Component Replacement···························································· 7-6
7.4.1 Replacement of Absolute Battery·······························································7-6
7.4.2 How to Replace Fan Unit ·········································································7-8
7.5 Preventive Maintenance Function ················································· 7-9
7.5.1 Maintenance Information··········································································7-9
7.6 Predictive Maintenance Function ·················································· 7-12
7.6.1 Fan······································································································7-12
7.6.2 Overload Warning···················································································7-13