V1.00/EN/00398477
Data Sheet 703590JUMO GmbH & Co. KG • 36035 Fulda, Germany Page 3/12
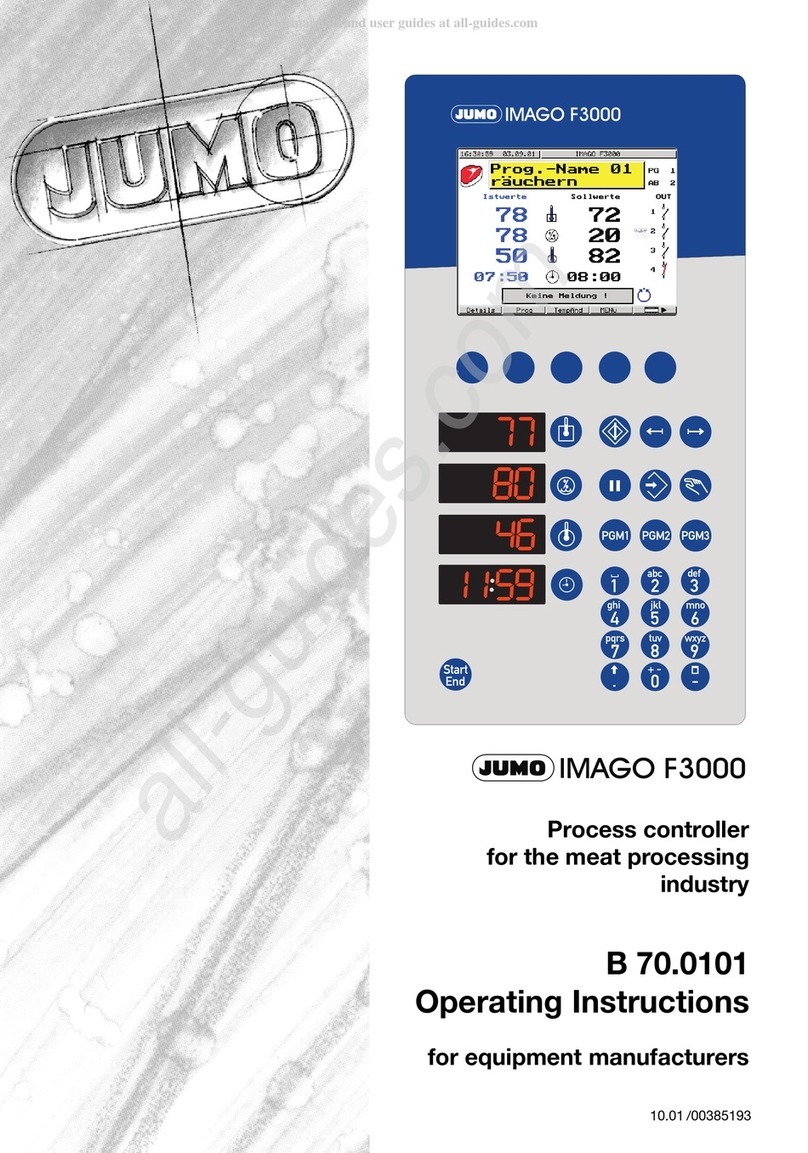
Recording
The recording function is used to create a
graphical representation of the develop-
ment of process values. This can be used
to monitor and check control processes.
Features:
• free choice of signals for 4 analog
channels and 3 logic channels
• memory storage cycle 60 to 3600
measurements per hour
• ring memory for 43,200 measurements
• readout of data via the interface
Self-optimization
Standard features include self-optimiza-
tion, making it possible for the controller to
be matched to the control loop by a user
who is not a control-technology expert.
This functions by evaluating the response
of the control loop to specific changes in
the manipulating variable. Either an
oscillatory method or a step response test
can be selected. The controller parameters
that are calculated are: proportional band,
reset time, derivative time, filter time
constant, and cycle time.
Ramp function
In a fixed-setpoint controller, the ramp
function enables a defined run-up of the
process value from t0 until it reaches the
given setpoint value.
The rate of change is defined as a gradient
(°C/min, °C/hour or °C/day).
When the setpoint changes, this function is
activated in the rising or falling direction.
The ramp function can be activated
individually for each channel.
Customer-specific
linearization
In addition to the linearizations for the usual
transducers, up to four customer-specific
linearizations can be created. The
programming is carried out in the setup
program, in the form of a table of values or
a formula.
Configurable
screen templates
Two freely configurable screen templates
are available for arrangement into user-
specific layouts.
Using the accessory setup program,
representations of process values and
graphics are selected from a library and
assembled into the screen template within
a graphics editor.
Some graphical elements can also be
incorporated.
Configurable texts
The accessory setup program can be used
to define up to 100 texts for use as
messages and representations in the
screen templates. Furthermore, all
instrument texts can be changed or
translated into other languages.
Event list
Important events, such as alarm
messages, external texts or system
messages, are collected together in an
event list.
User level
Parameters which frequently have to be
changed by the user can be collected
together and displayed in the screen
template “User level” (only through the
setup program).
Math and
logic module (option)
The math module makes it possible to
combine values such as setpoints, output
levels and measurements into a
mathematical formula.
The logic module can be used to make a
logical combination of such elements as
logic inputs and limit comparator states.
Up to 16 math or logic formulae can be
entered through the setup program, and
the results of the calculations can be
presented at the outputs or used for
internal purposes.
Difference, ratio, and
humidity control
Controllers for difference, ratio, and humid-
ity can be achieved through standard for-
mulae that have been included.
Cascade controller
Demanding control tasks can be handled
by configuring the instrument as a cascade
or trimmer cascade controller. Four cas-
cade controllers can be implemented by
using eight controller channels.
C-level controller (option)
The instrument can be used as a C-level
controller, to regulate the level of carbon in
the atmosphere of a gas coking furnace.
The sensing device in this case is a zircon
dioxide probe.
Logic functions
• Start/cancel of self-optimization
• Change to manual mode
• Inhibit manual mode
• Ramp stop/OFF
• Setpoint changeover
• Process value changeover
• Parameter set switching
• Key/level inhibit
•Textdisplay
• Screen saving
• Screen switching
• Acknowledge limit comparators
• Program start/stop/cancel
• Inhibit program start
• Program selection
•Fastforwards
• Segment change
• Time synchronization
• Timer start/stop
The logic functions can be combined with
one another.
Functions of the
Outputs
• Analog input variables
•Math
• Process value
•Setpoint
• Ramp end value
• Control deviation
•Outputlevel
• Cascade output level
• Program end value
• Controller outputs
• Limit comparators
• Control contacts
• Logic inputs
•Logic
• Program end
•Rampend
• Manual mode signal
• Timer signals
• Program/automatic signals