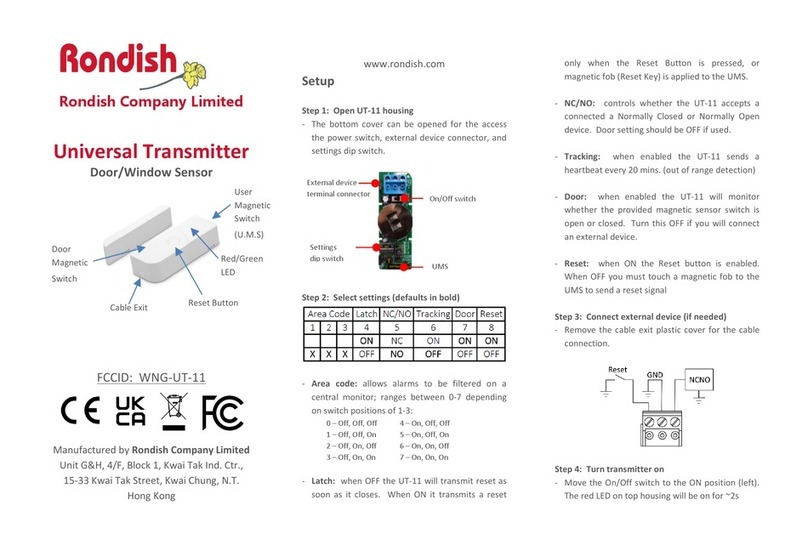
8
3 Inductive conductivity measurement
3.1 Area of application
General The inductive measurement method permits largely maintenance-free
acquisition of the specific conductivity, even in difficult media conditions.
Unlike the conductive measurement method, problems such as electrode
decomposition and polarization do not occur.
Brief
description The instrument is used for the measurement/control of conductivity or
concentration in liquid media. It is particularly recommended for use in media
where severe deposits of dirt, oil, grease or gypsum/lime precipitates are to be
expected. The integrated temperature measurement enables fast and
accurate temperature compensation, which is of particular importance when
measuring conductivity. Additional functions, such as the combined
changeover of measurement range and temperature coefficient, enable
optimum application in CIP processes.
Two built-in switching outputs can be freely programmed to monitor limits for
conductivity/concentration and/or temperature. It is also possible to assign
alarm and control functions (dilution).
The instrument is operated either from the membrane keypad and plain-text
graphics display (operator language can be changed over) or through the user-
friendly PC setup program. Simply rotating the housing cover makes it
possible to read the display, regardless of whether the installation is in
horizontally or vertically arranged pipes. By using the setup program, the
instrument configuration data for plant documentation can be saved and
printed out. To prevent any tampering, the instrument can also be supplied
without keypad or display. In this case, the setup program is needed for
programming.
The JUMO CTI-750 is available either as a combined unit (transmitter and
measuring cell together in one unit) or as a split version (transmitter and cell
connected by cable). The split version is particularly suitable for plant
subjected to strong vibration and/or significant heat radiation at the point of
measurement, or for installation on sites that are difficult to access.
Typical areas of
application - CIP cleaning (CIP = Clean In Place/Process)
- concentration monitoring or dosing of chemicals
- food/beverage and pharmaceutical industries
- product monitoring (phase separation of product / product mix / water)
in the beverage industry, breweries, dairies
- control (e.g. phase separation of detergent / rinsing water in
cleaning processes, e.g. bottle cleaning plant, or for container
cleaning)