Contents
Notice......................................................................................................................................................i
Notes about structure and electric circuit design.....................................................................................ii
1 Specifications ..................................................................................................................................... 1
1-1 Technical specifications .............................................................................................................. 1
1-2 Default settings for various types of barcode .............................................................................. 3
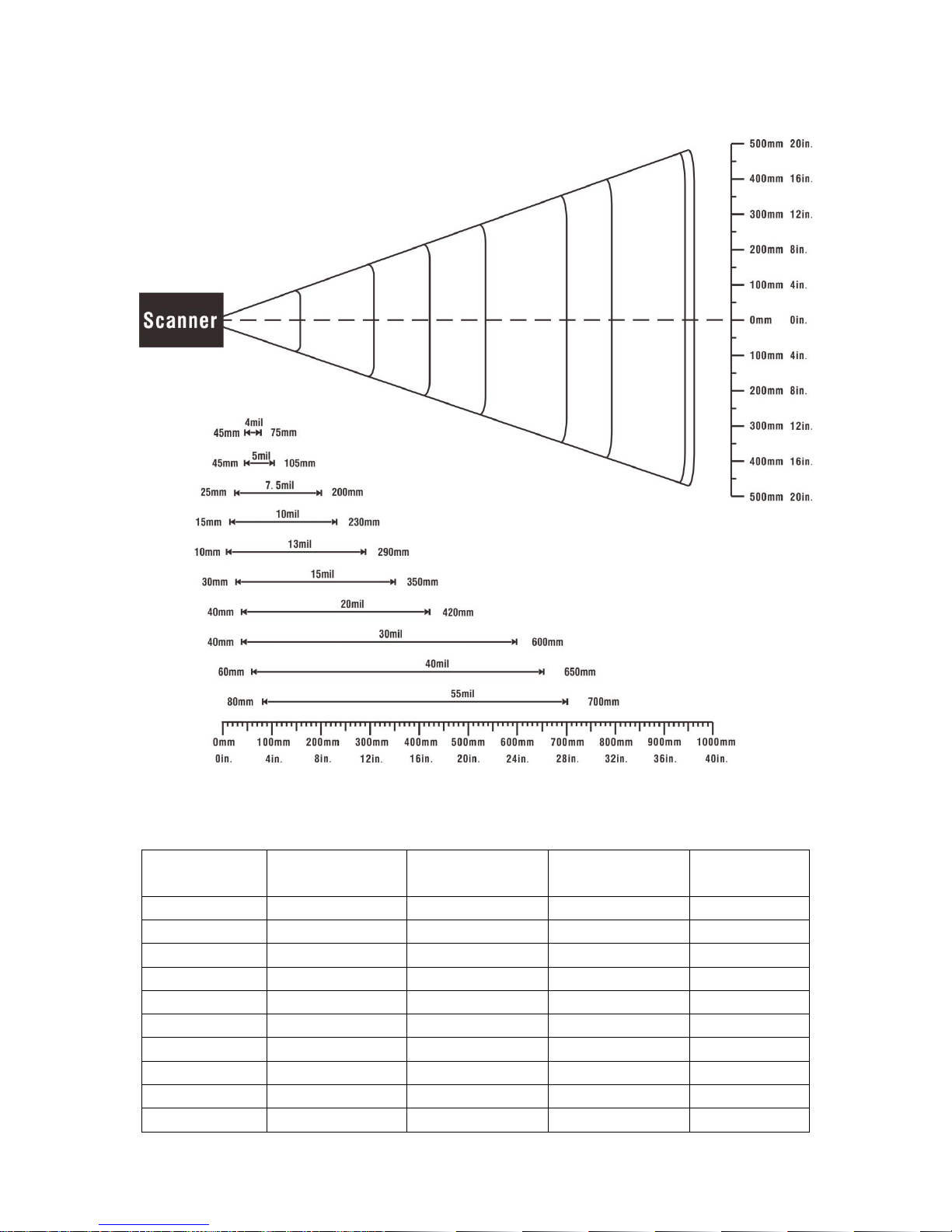
1-3 Decode zone............................................................................................................................... 4
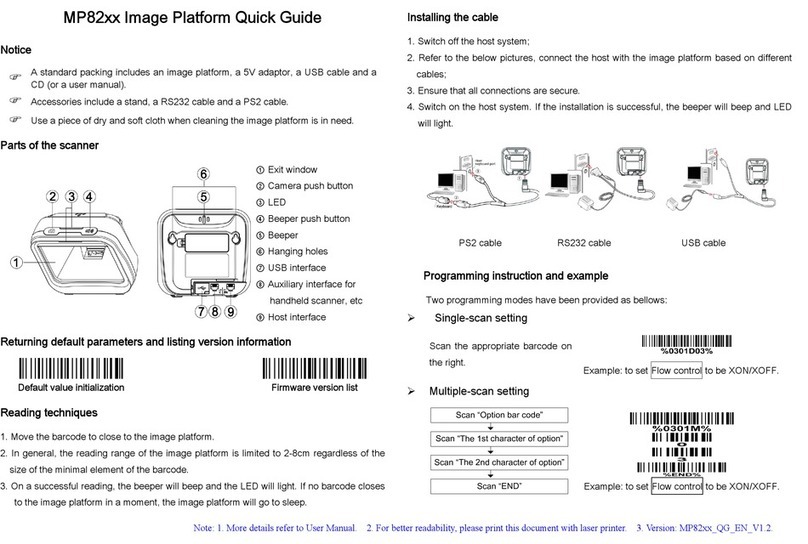
2 Get started ......................................................................................................................................... 5
2-1 Electrical interface/Pin assignment ............................................................................................. 5
2-2 Power management.................................................................................................................... 6
3 Installation guide ................................................................................................................................ 7
3-1 Notes of installation..................................................................................................................... 7
3-2 Mounting ..................................................................................................................................... 8
3-3 Appearance of the scanner ......................................................................................................... 9
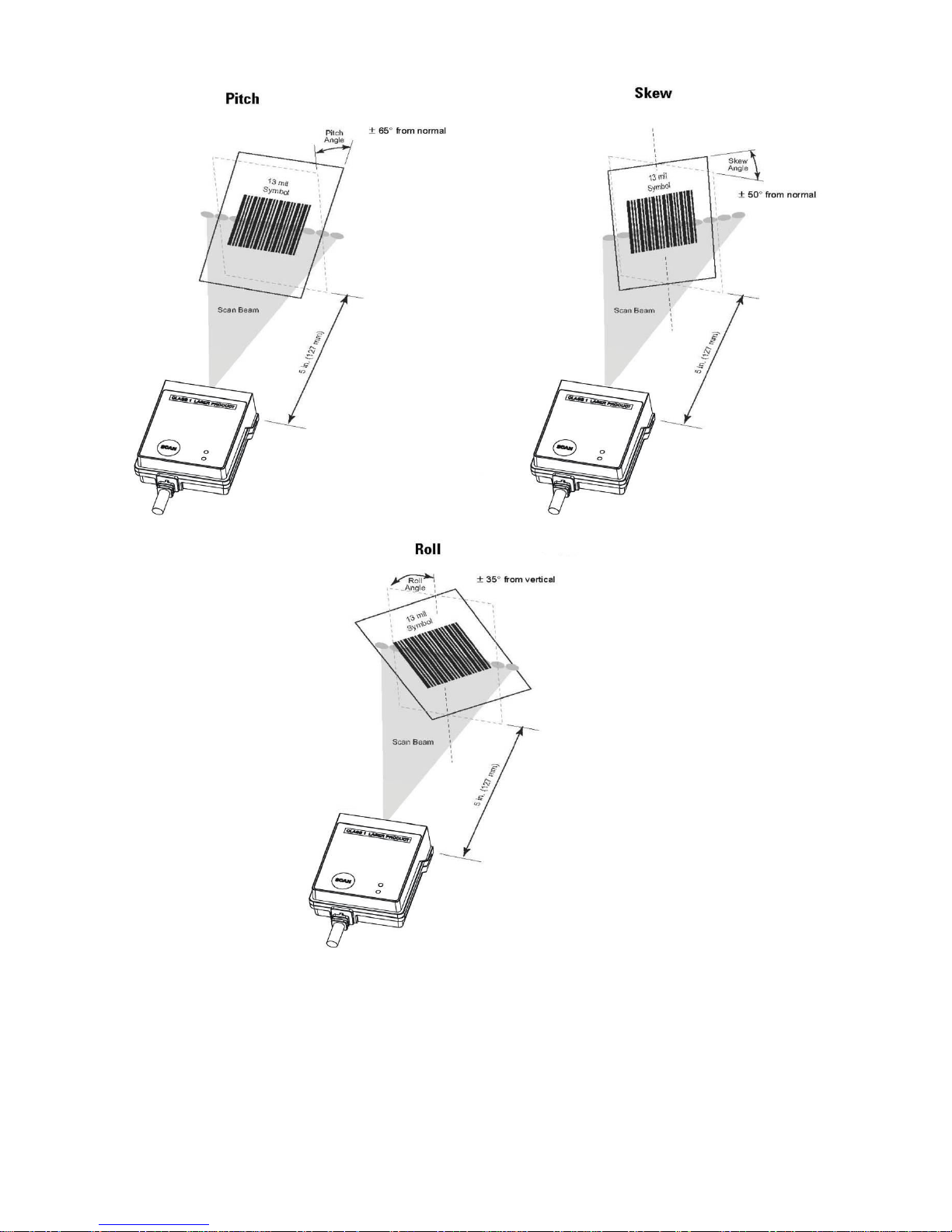
3-4 Scan angle ................................................................................................................................ 10
3-5 Tilt angle and dead zone........................................................................................................... 11
4 Parameter menus..............................................................................................................................12
4-1 Introduction ............................................................................................................................... 12
4-2 Example: configure scanner...................................................................................................... 13
4-3 RS232 interface ........................................................................................................................ 15
4-4 USB interface............................................................................................................................ 18
4-5 Scan mode & some global settings........................................................................................... 21
4-6 Indication................................................................................................................................... 27
4-7 UPC-A....................................................................................................................................... 28
4-8 UPC-E....................................................................................................................................... 30
4-9 UPC-E1..................................................................................................................................... 32
4-10 EAN-13 (ISBN/ISSN) .............................................................................................................. 34
4-11 EAN-8 ..................................................................................................................................... 36
4-12 Code 39 (Code 32, Trioptic Code 39) ..................................................................................... 38
4-13 Interleaved 2 of 5 .................................................................................................................... 41
4-14 Industrial 2 of 5........................................................................................................................ 43
4-15 Matrix 2 of 5 ............................................................................................................................ 44
4-16 Codabar .................................................................................................................................. 46
4-17 Code 128 ................................................................................................................................ 48
4-18 UCC/EAN 128......................................................................................................................... 50
4-19 ISBT 128 ................................................................................................................................. 52
4-20 Code 93 .................................................................................................................................. 54
4-21 Code 11 .................................................................................................................................. 56
4-22 MSI/Plessey ............................................................................................................................ 58