Contents
1 About this document........................................................................ 5
1.1 Scope......................................................................................................... 5
1.2 Target groups of these operating instructions........................................ 5
1.3 Additional information.............................................................................. 5
1.4 Symbols and document conventions...................................................... 5
2 Safety information............................................................................ 7
2.1 General safety notes................................................................................ 7
2.2 Intended use............................................................................................. 7
2.3 Improper use............................................................................................. 7
2.4 Requirements for the qualification of personnel.................................... 8
3 Product description........................................................................... 9
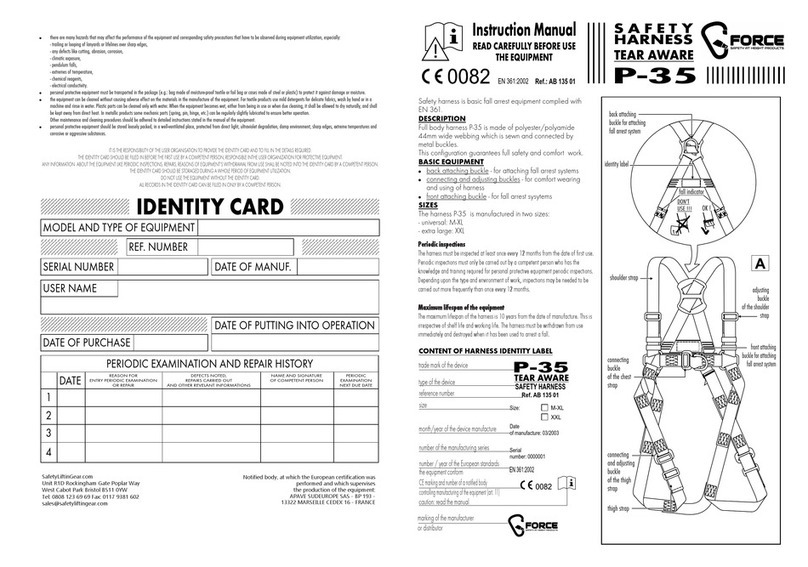
3.1 Design and function................................................................................. 9
3.2 Product characteristics............................................................................ 9
3.3 Manual unlocking..................................................................................... 11
4 Project planning................................................................................ 13
4.1 Manufacturer of the machine.................................................................. 13
4.2 Operating entity of the machine.............................................................. 13
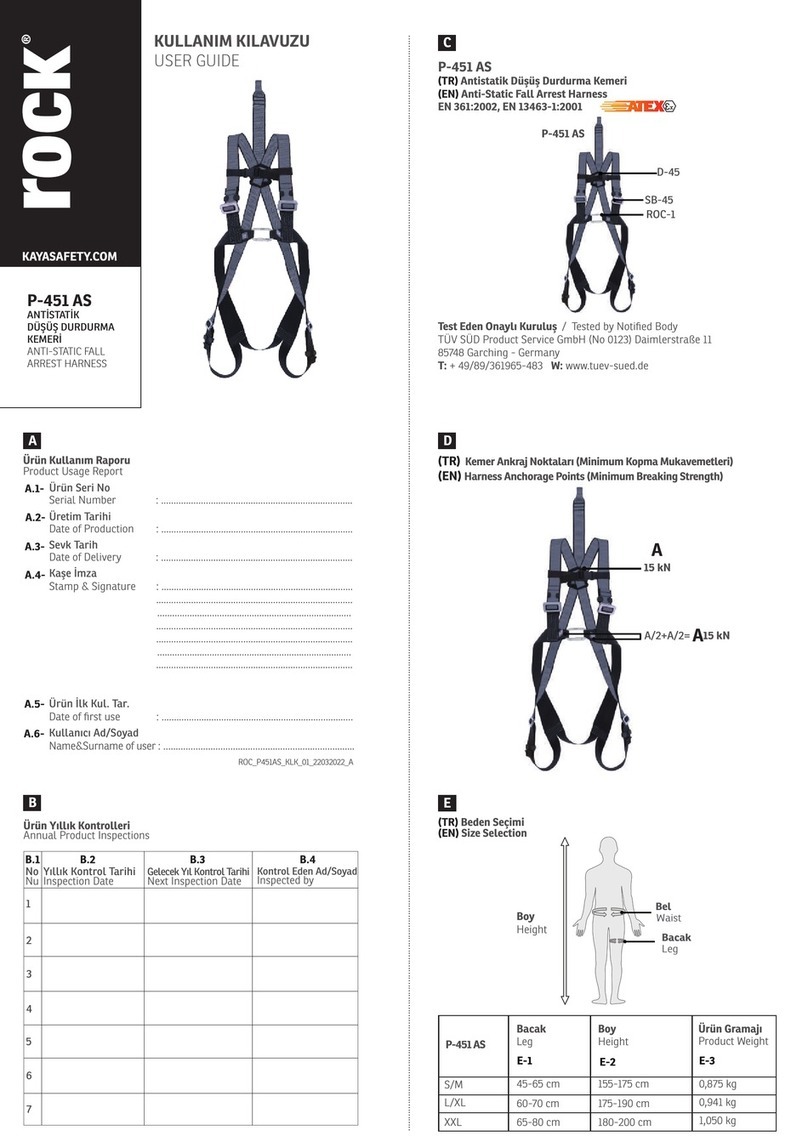
4.3 Design........................................................................................................ 13
4.4 Integration in the electrical control system............................................. 16
4.5 Testing plan............................................................................................... 19
5 Mounting............................................................................................. 21
5.1 Orientation of the safety switch............................................................... 21
5.2 Mounting several safety switches............................................................ 21
5.3 Mounting the safety switch...................................................................... 21
5.4 Mounting the actuator.............................................................................. 23
5.5 Mounting the escape release.................................................................. 24
6 Electrical installation........................................................................ 25
6.1 Notes on cULus......................................................................................... 25
6.2 Device connection.................................................................................... 25
6.3 Connection of a safe series connection.................................................. 25
7 Commissioning.................................................................................. 28
7.1 Teach-in..................................................................................................... 28
7.2 Thorough check during commissioning and modifications................... 30
8 Operation............................................................................................ 31
8.1 Actuating the auxiliary release................................................................. 31
8.2 Actuating the escape release.................................................................. 31
8.3 Preventing unintentional closing of the movable physical guard.......... 31
CONTENTS
8020562/2022-07-07 | SICK O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | flexLock 3
Subject to change without notice