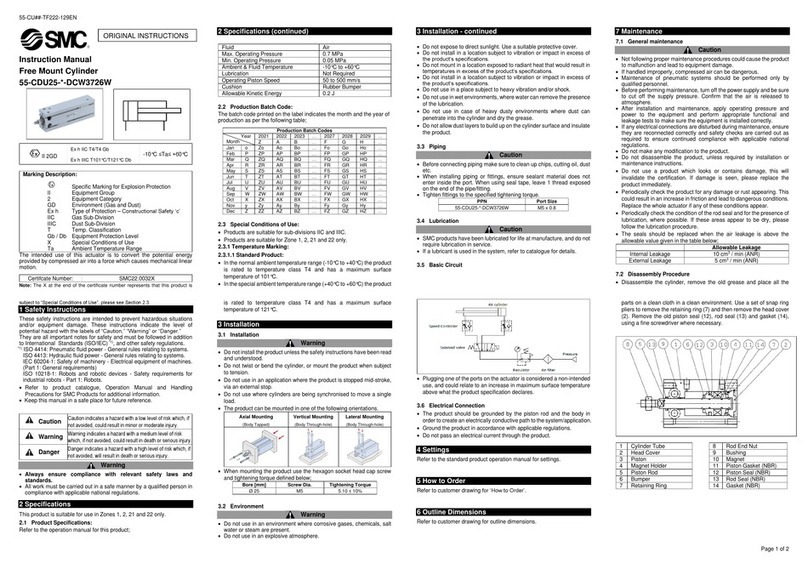
QCR = Amount of air consumption of rotary actuator [l (ANR)]
QCP = Amount of air consumption of tube or piping [l (ANR)]
V
= Inner volume of the rotary table [cm3]
P= Operating pressure [MPa]
l
= Length of piping [mm]
a = Inner sectional area of piping [mm2]
Rotary Table
Air Consumption
Air consumption is the volume of air which is expended by the rotary actuator’s reciprocal operation inside
the actuator and in the piping between the actuator and the switching valve, etc. This is necessary for
selection of a compressor and for calculation of its running cost.
Formula
Qc2 = Qcx n x No. of actuators x Margin rate
Qc2= Amount of exhaust air from a compressor [l/min (ANR)]
n = Actuator oscillations per minute
To select a compressor, it is important to select one that has
plenty of margin to accommodate the total air volume that is
consumed by the pneumatic actuators that are located
downstream. The total air consumption volume is affected by the
leakage in the tube, the consumption in the drain valves and pilot
valves, as well as by the reduction in air volume due to reduced
temperature.
Internal Cross Section of Tubing and Steel Piping
O.D. (mm)
4
6
8
8
—
10
12
12
—
16
—
16
—
—
—
I.D. (mm)
2.5
4
5
6
6.5
7.5
8
9
9.2
12
12.7
13
16.1
21.6
27.6
Internal cross section
a (mm2)
4.9
12.6
19.6
28.3
33.2
44.2
50.3
63.6
66.5
113
127
133
204
366
598
Nominal
T쏔0425
T쏔0604
TU 0805
T쏔0806
1/8B
T쏔1075
TU 1208
T쏔1209
1/4B
TS 1612
3/8B
T쏔1613
1/2B
3/4B
1B
Internal volume changes depending on the rotating direction
(refer to the figure shown in the lower right). Because of this, to
obtain the total air consumption, first calculate the air
consumption of each stroke respectively by using formula (1),
then add up each result.
Air in the tubing is consumed only when the table rotates from
end to center. The air consumption in the tubing can be obtained
by using formula (2).
The internal volume for each rotating direction and air
consumption at each operating pressure calculated using formula
(1) are shown in the table below.
[Calculation example]
Size: 10 Operating pressure: 0.5 MPa Inner sectional area of piping: 12.6 mm2
Lengh of piping: 1000mm Stroke: Center 씮Counterclockwise씮Center씮Clockwise씮Center
Total air consumption, Q1, is obtained by adding up the air consumption of each stroke,
which is shown in the table below.
Air consumed in the tubing is calculated using formula (2), as shown below.
An entire stroke includes two rotations from end to center where the air is consumed.
Thus, the total air consumption Q of the rotary table and tubing is obtained as shown
below.
Air Consumption
Air consumption of rotary table: QCR l(ANR)
10
20
30
50
90°
6.69
3.11
13.2
6.40
20.0
9.52
32.6
16.2
Size Operating
direction
End씮Center
Center씮End
End씮Center
Center씮End
End씮Center
Center씮End
End씮Center
Center씮End
Inner volume
(cm3)
Rotation Operating pressure (MPa)
0.2
0.020
0.009
0.040
0.019
0.060
0.029
0.098
0.049
0.3
0.027
0.012
0.053
0.026
0.080
0.038
0.130
0.065
0.4
0.033
0.016
0.066
0.032
0.100
0.048
0.163
0.081
0.5
0.040
0.019
0.079
0.038
0.120
0.057
0.195
0.097
0.6
0.047
0.022
0.093
0.045
0.140
0.067
0.228
0.113
0.7
0.054
0.025
0.106
0.051
0.160
0.076
0.261
0.130
0.8
0.060
0.028
0.119
0.058
0.180
0.086
0.293
0.146
0.9
0.067
0.031
0.132
0.064
0.200
0.095
0.326
0.162
1.0
0.074
0.034
0.145
0.070
0.220
0.105
0.358
0.178
End
Center씮End Center씮End
End씮Center End씮Center
Center
End
P+0.1
0.1
P
0.1
QCR = V x x 10–3 ···(1)
···(2)
QCP = a x l x x 10–6
Front matter 6
0.5
0.1
Q1= 0.019 + 0.040 + 0.019 + 0.040 = 0.118l (ANR)
Q2= 12.6 x 1000 x x 10-6 = 0.063l (ANR)
Q = Q1+ Q2 + 2 = 0.244l (ANR)