Table of contents
6ARC 100 Operating Manual 900-100_IFU-V1.0_11587-S0-20141209-EN
3.7.2. Cyclical test during operation ............................................................................22
3.8. Neutral electrode monitoring.............................................................................................22
3.8.1. General information...........................................................................................22
3.8.2. EASY neutral electrode monitoring (EASY monitoring) ....................................23
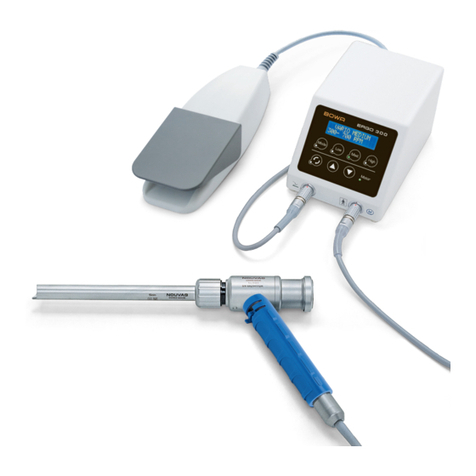
3.9. Foot switches ....................................................................................................................23
4. Description......................................................................................................................................24
4.1. Symbols on the device......................................................................................................24
4.1.1. Rating label........................................................................................................24
4.2. Scope of delivery ..............................................................................................................25
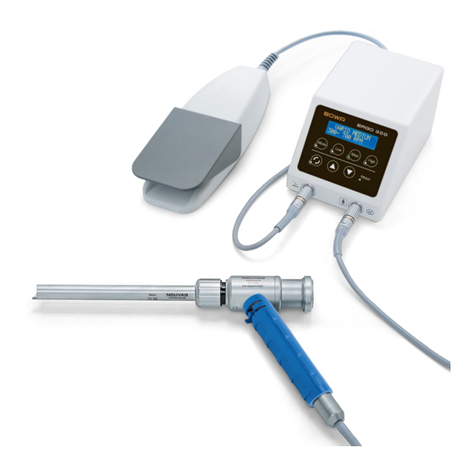
4.3. Components required for operation ..................................................................................25
4.4. Operating conditions .........................................................................................................25
5. Preparation......................................................................................................................................26
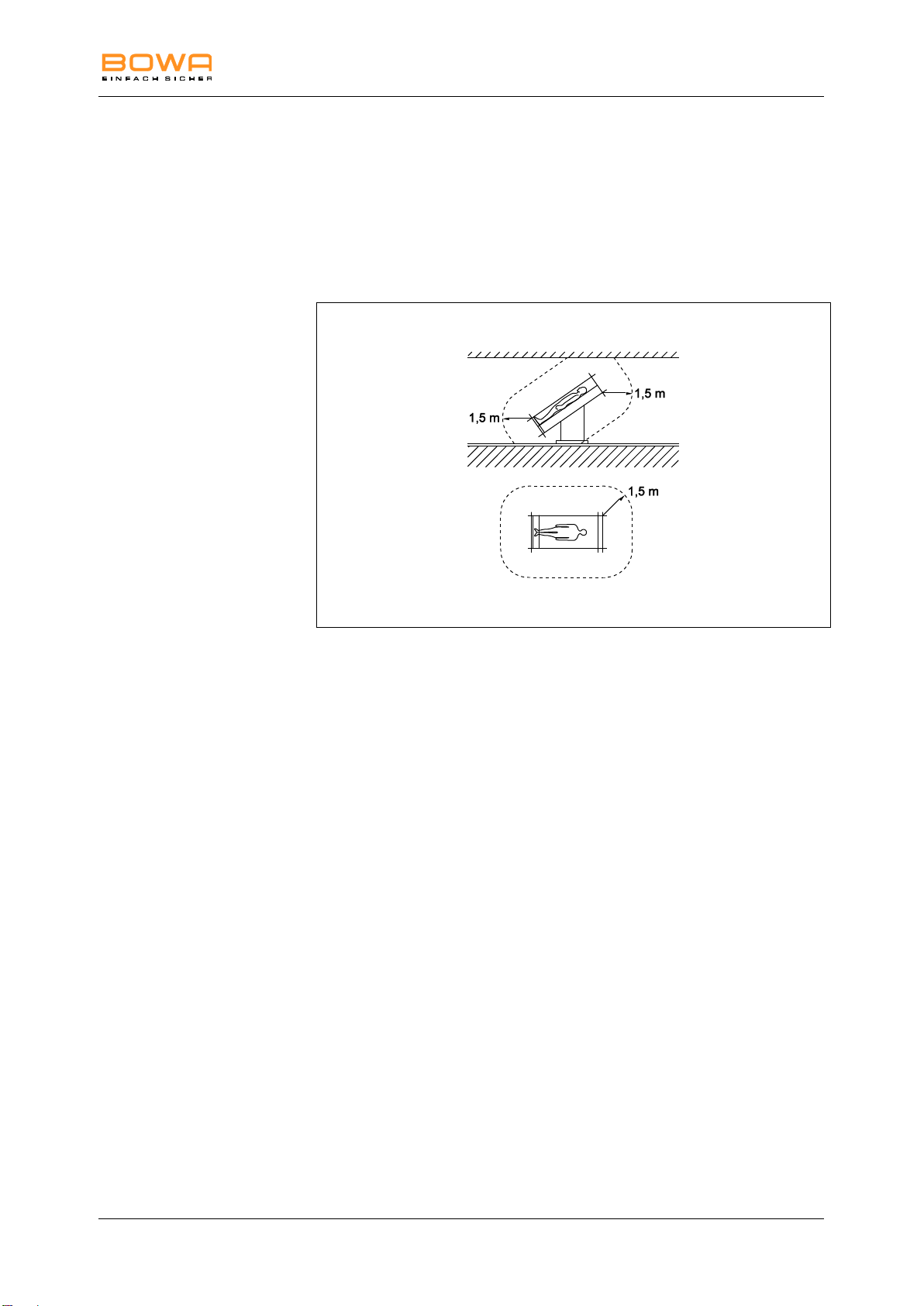
5.1. Setting up the HF device...................................................................................................26
5.2. Switching on the HF device ..............................................................................................27
5.3. Connecting instruments ....................................................................................................27
5.3.1. Instruments for monopolar applications ............................................................27
5.3.2. Instruments for bipolar applications...................................................................27
5.3.3. Connecting the foot switch ................................................................................28
5.3.4. Assigning a foot switch output...........................................................................28
5.4. Functional test...................................................................................................................28
5.4.1. Autotest function................................................................................................28
5.4.2. Functional test execution...................................................................................28
5.4.3. Actions in case of problems...............................................................................29
5.4.4. EASY neutral electrode monitoring (EASY monitoring) ...................................29
6. Operation.........................................................................................................................................30
6.1. Mode overview..................................................................................................................30
6.2. Basic settings....................................................................................................................31
6.2.1. Selecting the mode............................................................................................31
6.2.2. Setting power levels ..........................................................................................31
6.2.3. Changing the volume.........................................................................................31
6.3. Mode descriptions.............................................................................................................31
6.3.1. Monopolar cutting, "Pure"..................................................................................31
6.3.2. Monopolar cutting, "Dry"....................................................................................31
6.3.3. Monopolar coagulation, "Moderate" ..................................................................32
6.3.4. Monopolar coagulation, "Forced" ......................................................................32