*
May also be referred to as “ transcutaneous pacing” , “ noninvasive external pacing” , or
“ transcutaneous cardiac stimulation” .
2
b-
blockers, verapamil, etc.), and unexpected circulatory arrest (due to anesthesia,
surgery, angiography, and other therapeutic or diagnostic procedures). It is safer, more
reliable, and more rapidly applied in an emergency than endocardial or other tempo-
rary electrodes.
2. As a standby when standstill or bradycardia might be expected
As a stand-by when arrest or symptomatic bradycardia might be expected, the external
pacer is used especially in pacemaker procedures (e.g., acute myocardial infarction,
drug toxicity, anesthesia, or surgery, especially when disturbances of rhythmicity or
(ECG)
on the monitor during external pacing, without offset or distortion.zyxwvutsrqponmlkjihgfedcbaZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
Intended Use -- Pacemaker
This product may be used for cardiac pacing for any purpose in conscious or unconscious patients
for up to a few hours duration as an alternative to endocardial stimulation. The purposes of
pacing include:
1.
Resuscitation from standstill or bradycardia of any etiology
Noninvasive pacing has been used for resuscitation from standstill or temporary accel-
eration of bradycardia in Stokes-Adams disease, sick-sinus syndrome, reflex vagal
standstill and drug-induced standstill (due to procainamide, quinidine, digitalis,
(ppm).
The pacing output pulse is delivered to the heart by specially designed ZOLL NTP pacing elec-
trodes or ZOLL PD multi-function electrodes placed on the back and the precordium.Only
ZOLL NTP or ZOLL PD electrodes should be connected to this instrument.
The characteristics of the output pulse, together with the design and placement of the elec-
trodes, minimize cutaneous nerve stimulation, lower cardiac stimulation thresholds, and reduce
discomfort due to skeletal muscle contraction.
The unique design of the ZOLL PD allows clear viewing and interpretation of the electrocardi-
ogram
mA
and the rate is continuously variable from 30 to 180 pulses per minute
(PD)
contains a demand pacemaker consisting of a pulse
generator and ECG sensing circuitry. The output current of the pacemaker is continuously variable
up to 140
WTP)*
is an established and proven technique. This therapy is
safe and is easily and rapidly applied in both emergency and non-emergency situations when
temporary cardiac stimulation is indicated.
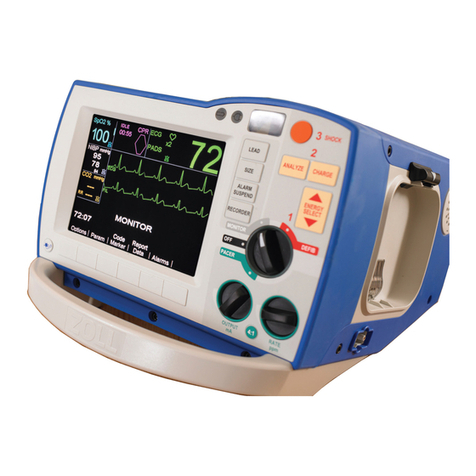
The ZOLL Pacemaker/ Defibrillator
OPERATOR’S GUIDE
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The ZOLL PD 1200 Pacemaker/ Defibrillator combines a patented noninvasive temporary
pacemaker, a DC defibrillator, a non-fade monitor, and an annotating strip chart recorder in an
integral, self-contained instrument. The PD 1200 is lightweight, compact, and can be
transported with a patient. It can be operated by either an AC line or batteries. Built-in
batteries are kept at full charge when the unit is connected to line power. The batteries are
rechargeable and can be easily replaced by the user.
PACEMAKER FUNCTION
Noninvasive temporary pacing