i corti circuiti, atto a sezionare l’automazione dalla rete. Installare a
monte dell'automazione, se non già presente, un interruttore onnipolare
omologato con soglia 0,03A.
Qr) Quadro comando e ricevente incorporata.
S) Selettore a chiave.
AL) Lampeggiante con antenna accordata.
M) Attuatore.
E) Elettroserratura (obbligatoria per ante superiori a 2.5m di lunghez-
za).
Fte) Coppia fotocellule esterne (parte emittente).
Fre) Coppia fotocellule esterne (parte ricevente).
Fti) Coppia fotocellule interne con colonnine CF (parte emittente).
Fri) Coppia fotocellule interne con colonnine CF (parte ricevente).
T) Trasmittente 1-2-4 canali.
RG58)
Cavo per antenna.
D) Scatola di derivazione.
5.3) Predisposizione impianto elettrico
Predisporre l’impianto elettrico come indicato in fig.2 facendo riferimento
alle norme vigenti per gli impianti elettrici CEI 64-8, IEC364, armonizzazione
HD384 ed altre norme nazionali. Tenere nettamente separati i collegamenti di
alimentazione di rete dai collegamenti di servizio (fotocellule, coste sensibili,
dispositivi di comando ecc.).
ATTENZIONE! Per il collegamento alla rete, utilizzare cavo multipolare
di sezione minima 3x1.5mm2 e del tipo previsto dalle normative vigenti.
A titolo di esempio, se il cavo è all’esterno (all’aperto), deve essere
almeno pari a H07RN-F mentre, se all’interno (in canaletta), deve essere
almeno pari a H05 VV-F con sezione 3x1.5mm2 .
Realizzare i collegamenti dei dispositivi di comando e di sicurezza in armonia
con le norme per l’impiantistica precedentemente citate. In fig.2 è riportato
il numero di collegamenti e la sezione per una lunghezza dei conduttori di
circa 100 metri; per lunghezze superiori, calcolare la sezione per il carico
reale dell’automazione.
Attenzione! Per il cablaggio dell’attuatore e il collegamento degli accessori
riferirsi ai relativi manuali istruzio ne. I quadri di comando e gli accessori
devono essere adatti all’utilizzo e conformi alle normative vigenti.
5.4) Cementazione della cassa di fondazione
Deve essere cementata in posizione sottocardine considerando che l’albero
portante dell’attuatore deve risultare perfettamente allineato all’asse di rota-
zione dell’anta. Se il cancello è del tipo a cerniere fisse, rimuovere il cancello
e togliere la cerniera inferiore. Se l’anta è sufficientemente alta dal suolo
e non si può rimuovere, provvedere al suo sostegno tramite uno spessore
tra suolo ed anta stessa durante la messa in opera. Se il cancello è del
tipo a cerniere regolabili, togliere quella inferiore, allentare la cerniera
superiore e spostare lateralmente l’anta. Se il cancello è di nuova realiz-
zazione, prevedere una cerniera superiore del tipo regolabile. Eseguire uno
scavo di fondazione delle dimensioni indicate in fig.4. Prevedere un tubo di
scarico (fig.4) per l’acqua piovana in modo da evitare ristagni all’interno della
cassa di fondazione. Predisporre la canaletta per il cavo di alimentazione
fino alla vicina scatola di derivazione ”D”. Realizzare sul fondo, una solida
fondazione (fig.3) dove annegare il cassone di fondazione. Per ottenere una
buona ortogonalità tra casse e ante, traguardare l’allineamento delle stesse
con una corda tesa tra i 2 perni portanti, allineando i 2 riferimenti ”C” tra di
loro (vedi fig.12). Lasciare rapprendere il cemento per il tempo necessario.
6) MONTAGGIO DELL’ANTA
• Ingrassare abbondantemente il perno presente nella cassa di fondazione.
• Posizionare l’assieme leve infilando il tubo A nel perno della cassa di
fondazione come in fig. 9. Nel caso l’altezza delle leve assiemate non sia
sufficiente, prevedere uno spessore ”S” da interporre tra il gruppo leve
assiemate e l’anta del cancello come in fig.5.
• Posizionare le ante in chiusura ed in battuta nel fermo d’arresto centrale.
• Allineare perfettamente il gruppo leve assiemate al cardine.
• Se si usa uno spessore, saldarlo prima all’anta e poi saldare il gruppo
leve allo spessore.
• Verificare il funzionamento dell’anta.
• Se non si inserisce il motoriduttore, montare il coperchio della cassa di
fondazione e fissarlo con le apposite viti.
A questo punto il cancello si apre e si chiude manualmente.
Rimane da posizionare il motoriduttore.
7) MONTAGGIO MOTORIDUTTORE
Togliere i dadi dal fondo della cassa con chiave a tubo CH19.
Il motoriduttore si fissa alla cassa di fondazione nella posizione indicata in
fig.6 e 8, utilizzando i 4 dadi precedentemente tolti.
• Avvitare le viti ”VR” (fig.7) e rispettivi controdadi alle staffe finecorsa ed
individuare la posizione di fissaggio destra o sinistra (fig.8).
• Fissare le staffe dei finecorsa meccanici utilizzando le viti M8 in dota-
zione (fig.7).
• Montare i particolari della leva di collegamento motore-perno, nella
sequenza corretta indicata in fig.9.
Nel caso, la posizione assunta dalle leve, intralci il montaggio dei parti-
colari, dare alimentazione ai motori (tramite la centralina) fino a quando
le leve raggiungono la posizione desiderata.
• Ingrassare il mozzo dentro il quale andrà infilato il tubo A.
• Verificare l’operazione di apertura e chiusura.
• Applicare all’anta le etichette di sblocco interne ed esterne, nel verso e
nella posizione indicata in fig.14. Il simbolo del lucchetto aperto, deve
essere sempre rivolto verso l’asse di rotazione dell’anta.
• E’ necessario fare la connessione del cavo del motoriduttore in una scatola
di derivazione posta all'esterno della cassa di fondazione senza tagliare
il cavo fornito in dotazione (Fig.2-4-5 Rif.D).
8) REGOLAZIONE FINECORSA
Nel caso non ci siano i fermi d’arresto al suolo ”FA”, regolare i fermi d’arresto
interni agendo sulle viti ”VRC-VRO” (fig.10-11) fino a quando l’anta si arresta
nel punto desiderato. La battuta d’arresto meccanica in chiusura e apertura,
si regola agendo nelle apposite viti ”VRC-VRO”.
• In CHIUSURA (fig.10). La vite regolazione finecorsa ”VRC”, deve inter-
cettare la leva ”L” dopo che l’anta è arrivata in battuta nel fermo d’arresto
centrale ”FA” (fig.8). In questo modo è garantito l’appoggio dell’anta al
fermo d’arresto centrale ”FA” che, se fornito di tappo in gomma, evita an-
che i rumori di sbattimento. Qualora nella regolazione del fermo finecorsa
”VRC” la misura ”Z” (fig.8) risultasse maggiore di 18÷20mm, si consiglia
di girare il fermo come in fig.13a.
• In APERTURA (fig.11). La vite regolazione finecorsa ”VRO”, deve inter-
cettare la leva ”L” dopo che l’anta è arrivata in battuta nel fermo d’arresto
di apertura ”FA” (fig.8).
• Ultimata la regolazione, bloccare il controdado delle viti di regolazione finecorsa
”VRO” e la vite che blocca il grano di regolazione finecorsa ”VRC”.
• Ripetere le stesse operazioni anche per il secondo attuatore.
• Se la cassa di fondazione non fosse ortogonale all'anta è possibile
effettuare una compensazione di 10° sia in senso orario che in senso
antiorario, posizionando la staffa di supporto ed il fermo di arresto come
indicato in fig 13b.
9) REGOLAZIONE DELLA COPPIA MOTORE
ATTENZIONE! Se viene utilizzata la centralina mod. ARIES con la coppia
regolata in ”F4” (massima coppia), sono obbligatori i fermi d’arresto al suolo
”FA” sia in apertura che in chiusura. La regolazione di coppia del motore
(antischiacciamento), viene regolata nella centralina di comando. Lo schema
di collegamento del motore è riportata nelle istruzioni d’uso della relativa
centralina di comando. Vedere il manuale istruzione della centralina di co-
mando. La regolazione deve essere tarata per la minima forza necessaria
ad effettuare la corsa di apertura e chiusura completa e comunque entro i
limiti previsti dalle norme vigenti.
ATTENZIONE: Verificare che il valore della forza d’impatto misu-
rato nei punti previsti dalla norma EN12445, sia inferiore a quanto
indicato nella norma EN 12453.
ATTENZIONE! Una regolazione di coppia eccessiva, può compromettere
la sicurezza antischiacciamento. Al contrario, una regolazione di coppia
insufficiente, può non garantire una corsa di apertura o chiusura corretta.
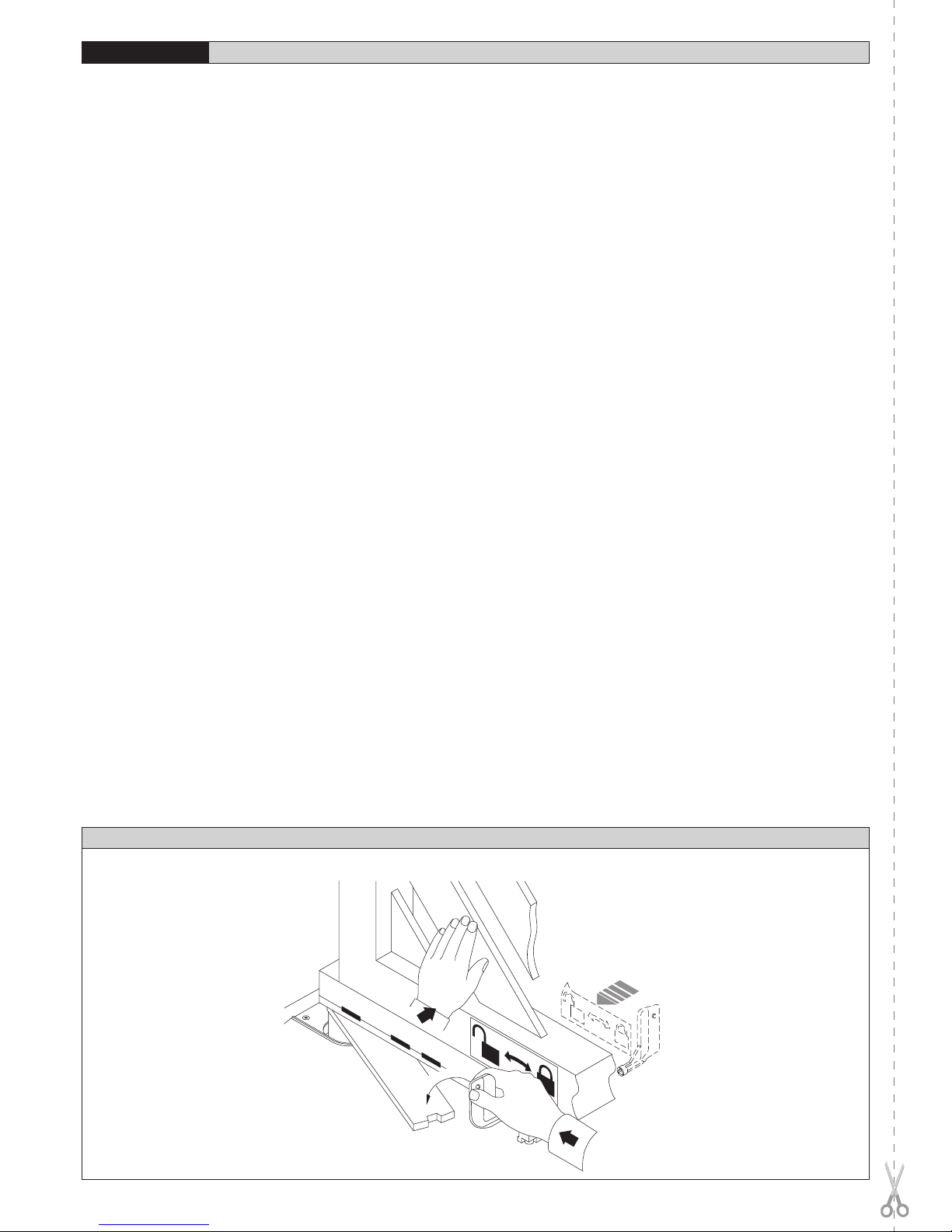
10) MANOVRA DI EMERGENZA
Lo sblocco di emergenza si effettua agendo, con l’apposita chiave in dota-
zione, sul gruppetto sblocco situato sotto il cancello sulla parte sporgente
della leva-perno. Per sbloccare, inserire la chiave nel triangolo di sblocco e
ruotare la chiave verso l’indicazione del lucchetto aperto per circa 90° (fig.14).
Se l’anta è dotata di elettroserratura, sbloccare anche l’elettroserratura.
Spingere manualmente l’anta per aprire/chiudere il cancello. Per ripristinare
l’operazione motorizzata, riposizionare il cancello allineato con la leva che
porta il gruppo blocco e girare la chiave verso l’indicazione del lucchetto
chiuso (fig.14) avendo cura di controllare l’avvenuto aggancio dell’anta. Ri-
porre la chiave di sblocco anta (e dell’elettroserratura se presente) in luogo
conosciuto agli utilizzatori.
11) VERIFICA DELL’AUTOMAZIONE
Prima di rendere definitivamente operativa l’automazione, controllare scru-
polosamente quanto segue:
MANUALE PER L’INSTALLAZIONE
ITALIANO
10 - ELI-250 - Ver. 07
D811232_07