METER TEROS 54 User manual





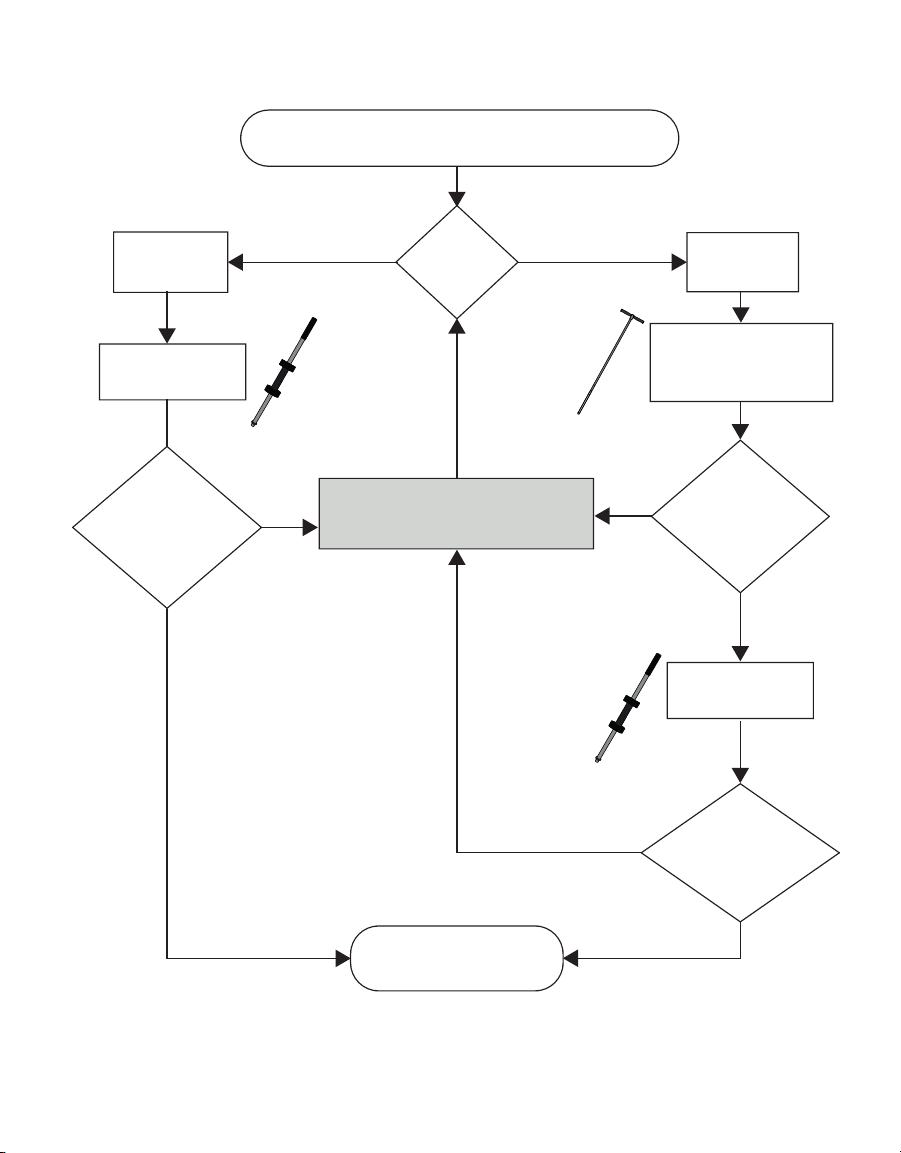
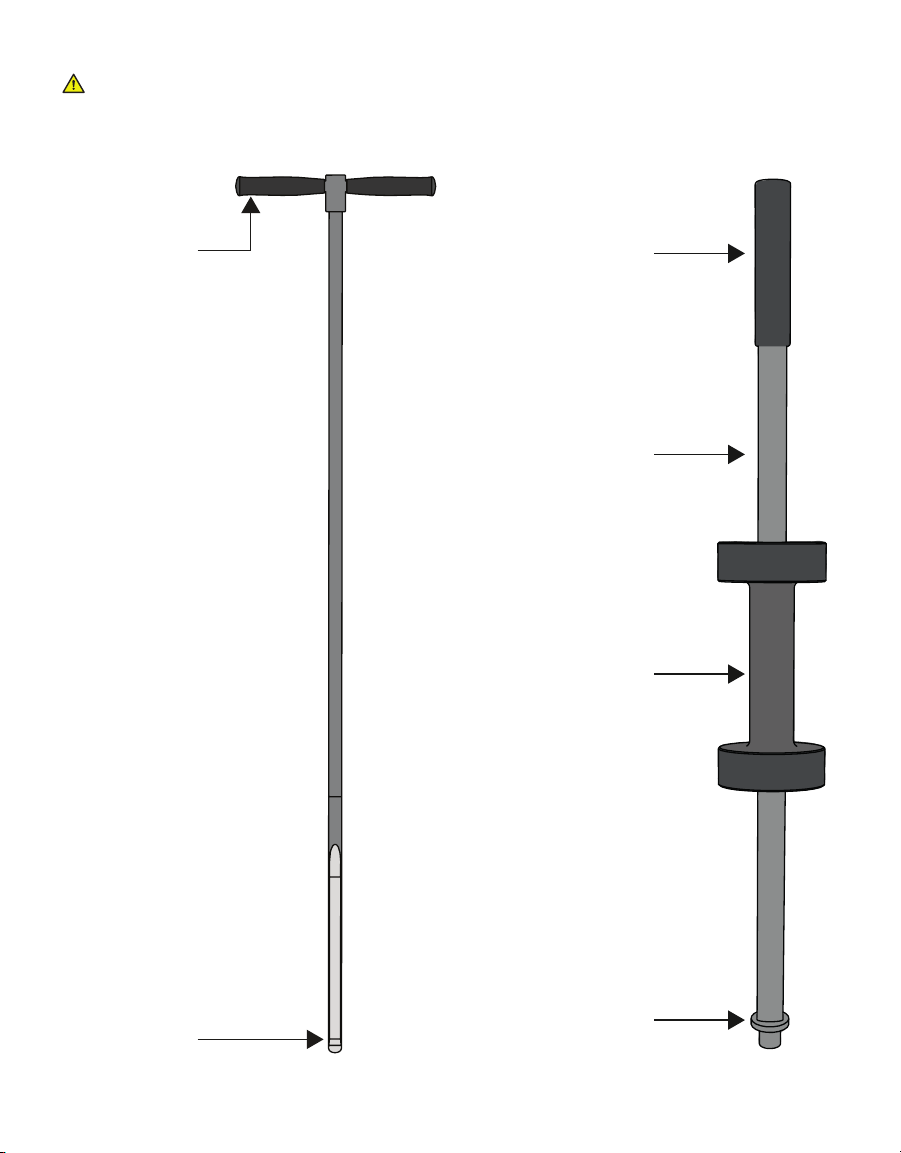



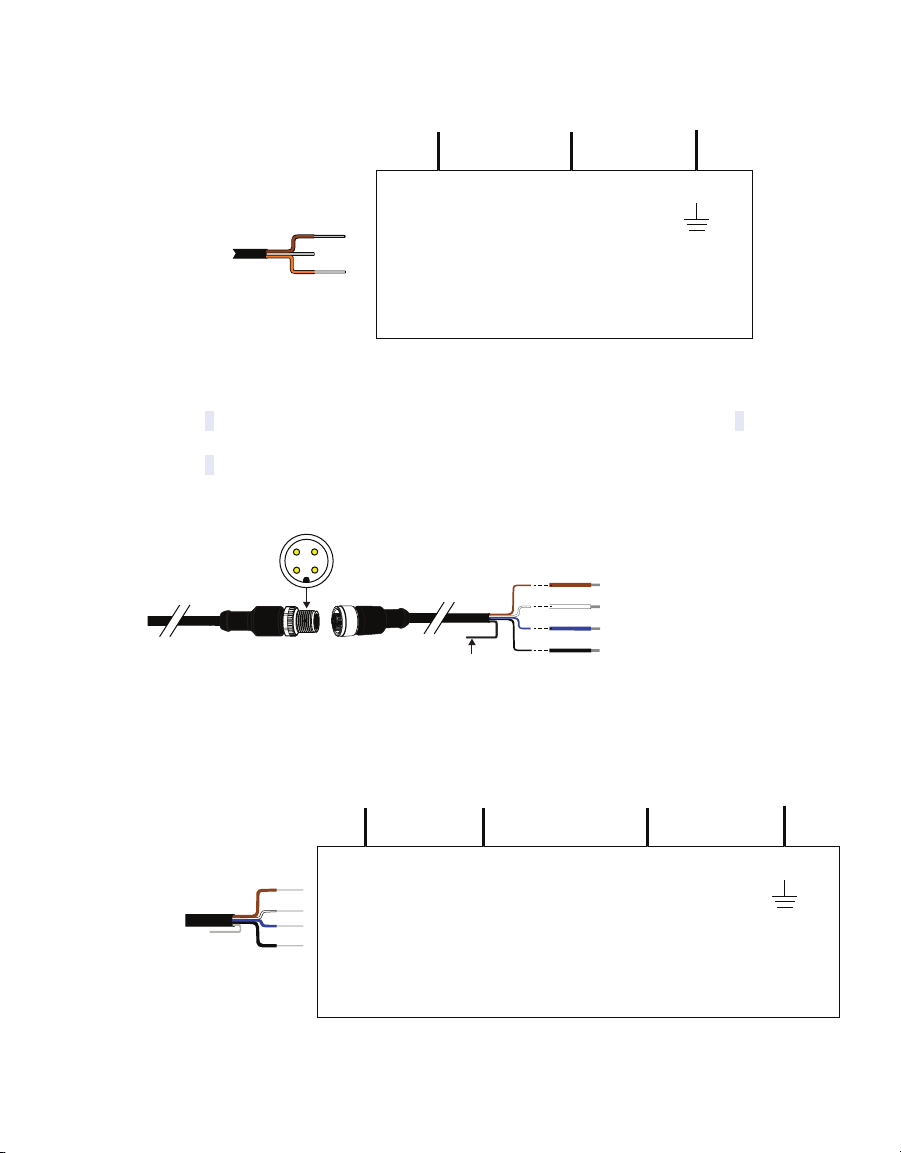
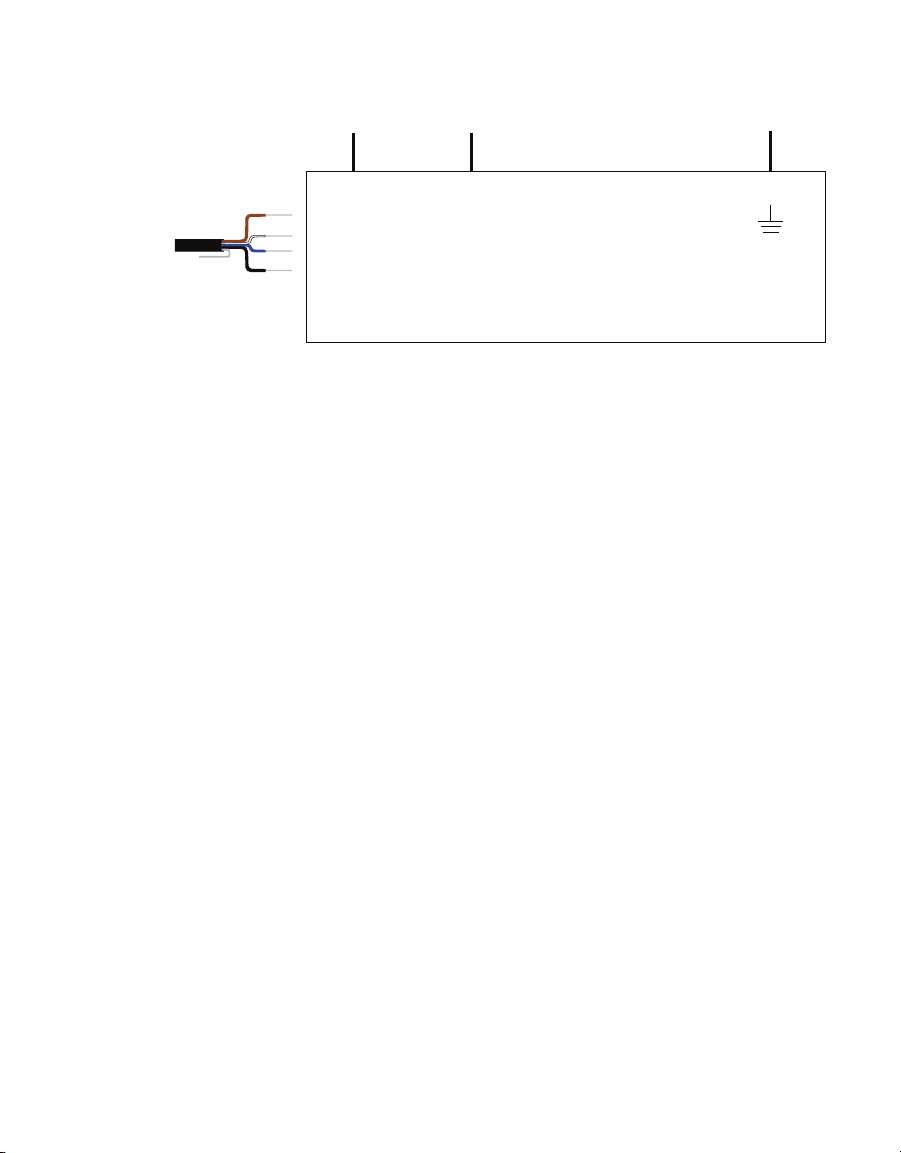
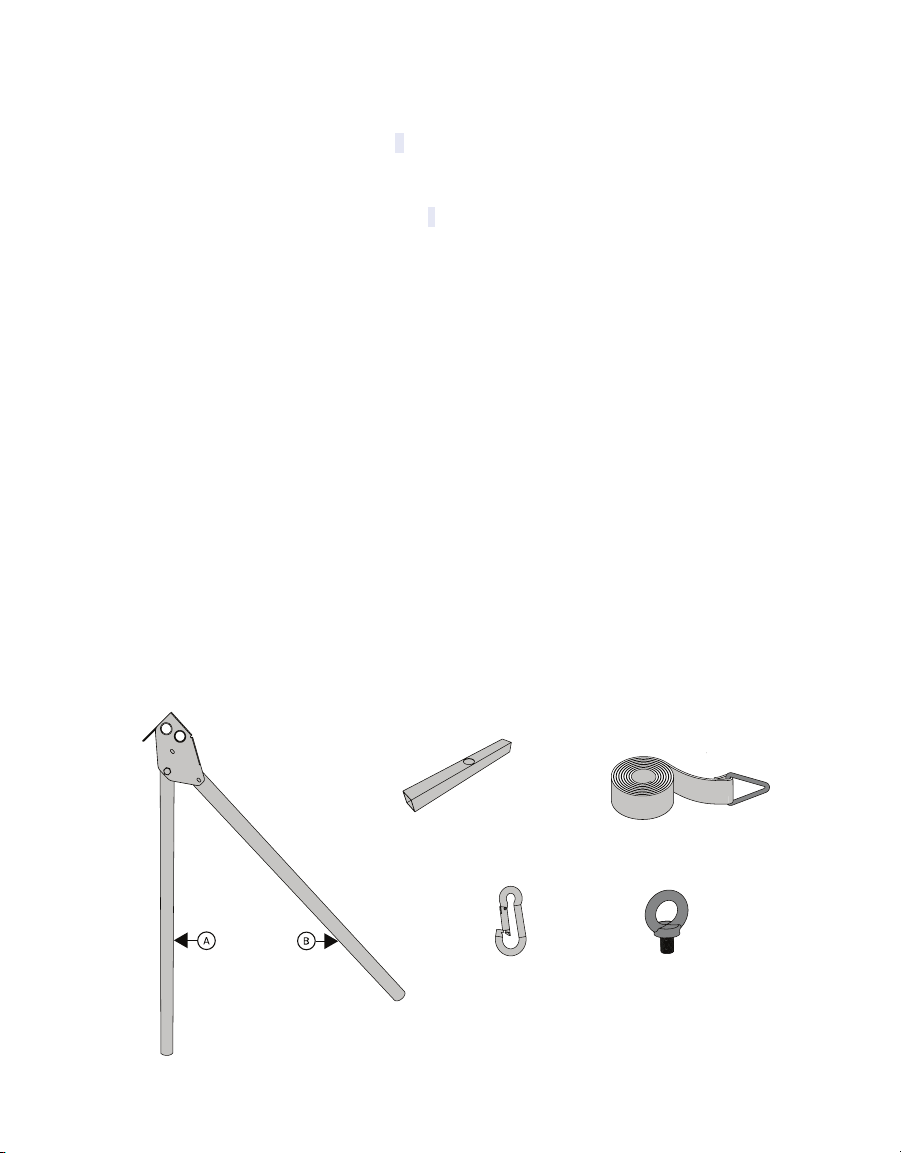
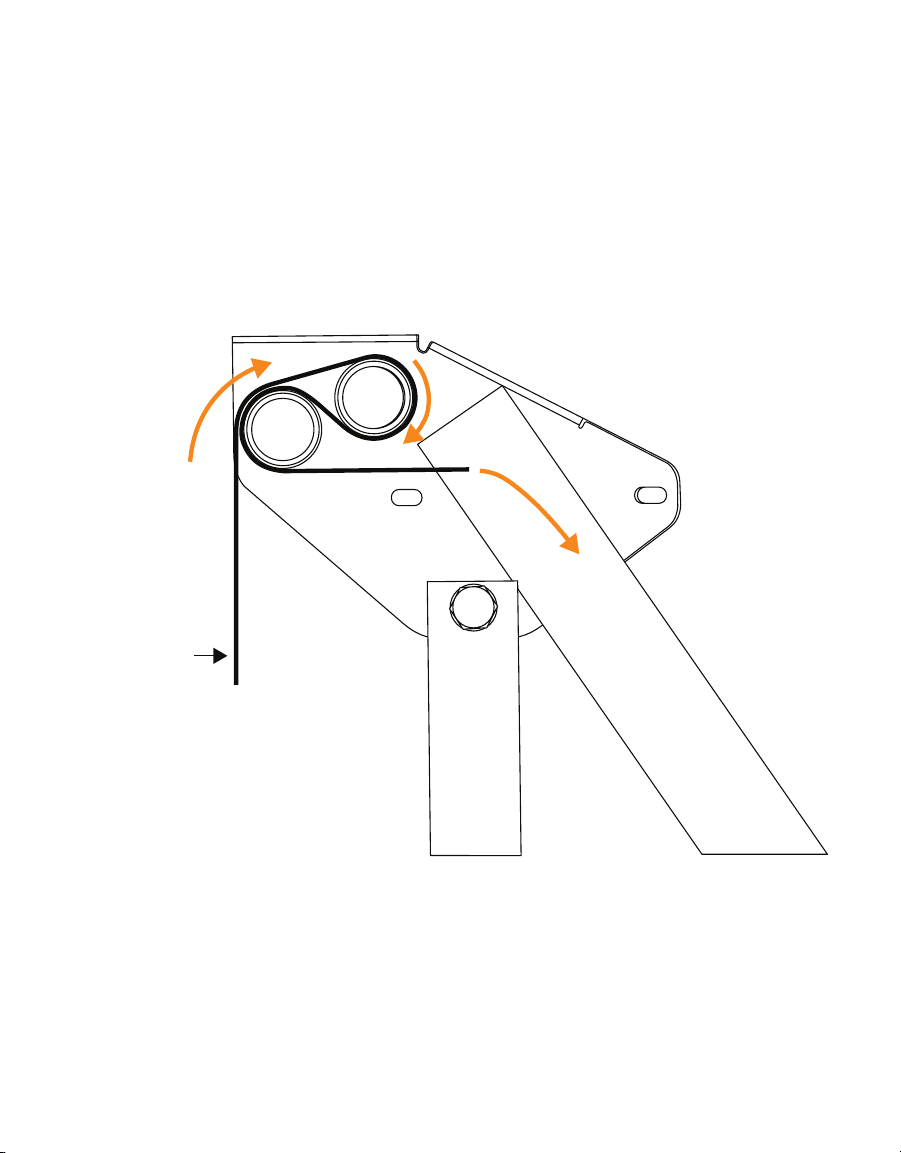
Other manuals for TEROS 54
1
Table of contents
Other METER Measuring Instrument manuals

METER
METER PROCHECK User manual

METER
METER SATURO User manual

METER
METER VARIOS User manual

METER
METER ACCUPAR LP-80 User manual

METER
METER TEROS 32 User manual

METER
METER AQUALAB 3 User manual

METER
METER APOGEE SQ-521 User manual

METER
METER ATMOS 22 User manual

METER
METER AQUALAB TDL User manual

METER
METER SATURO User manual

METER
METER AQUALAB TDL User manual

METER
METER TEROS 11 User manual

METER
METER TEROS 06 User manual

METER
METER APOGEE SU-221 User manual

METER
METER ROS 1 User manual

METER
METER AQUALAB 3 User manual

METER
METER THERMOLINK User manual

METER
METER AQUALAB PAWKIT User manual

METER
METER SI-400 Series User manual

METER
METER AQUALAB User manual
Popular Measuring Instrument manuals by other brands

Desco
Desco 19258 Installation, operation and maintenance

Magnescale
Magnescale LY71 Instruction and installation manual

Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi ME110NSR user manual
Keysight Technologies
Keysight Technologies N9030B Installation note

Keysight
Keysight PNA-X N5241A Installation note

Endress+Hauser
Endress+Hauser Proline Promass S 500 operating instructions