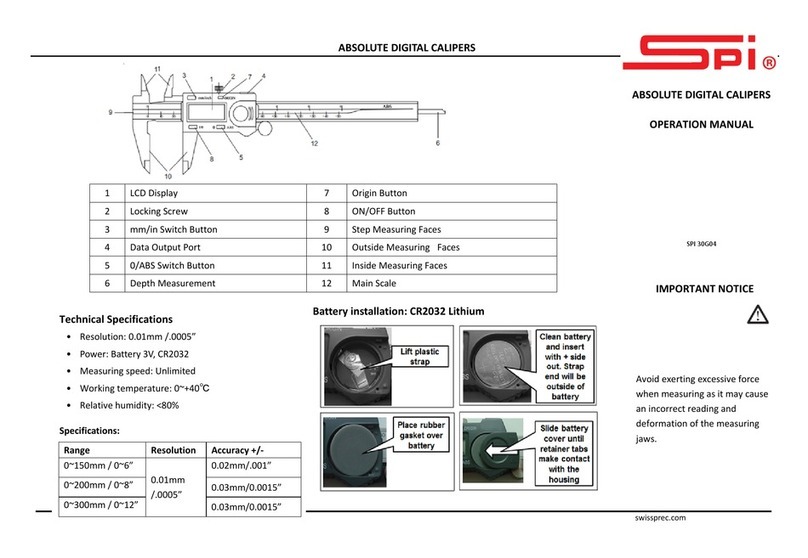
Siko SGP/1 Operation manual

SGP/1 Datum 03.03.2010 Art.Nr. 84050 Änd. Stand 65/10 1
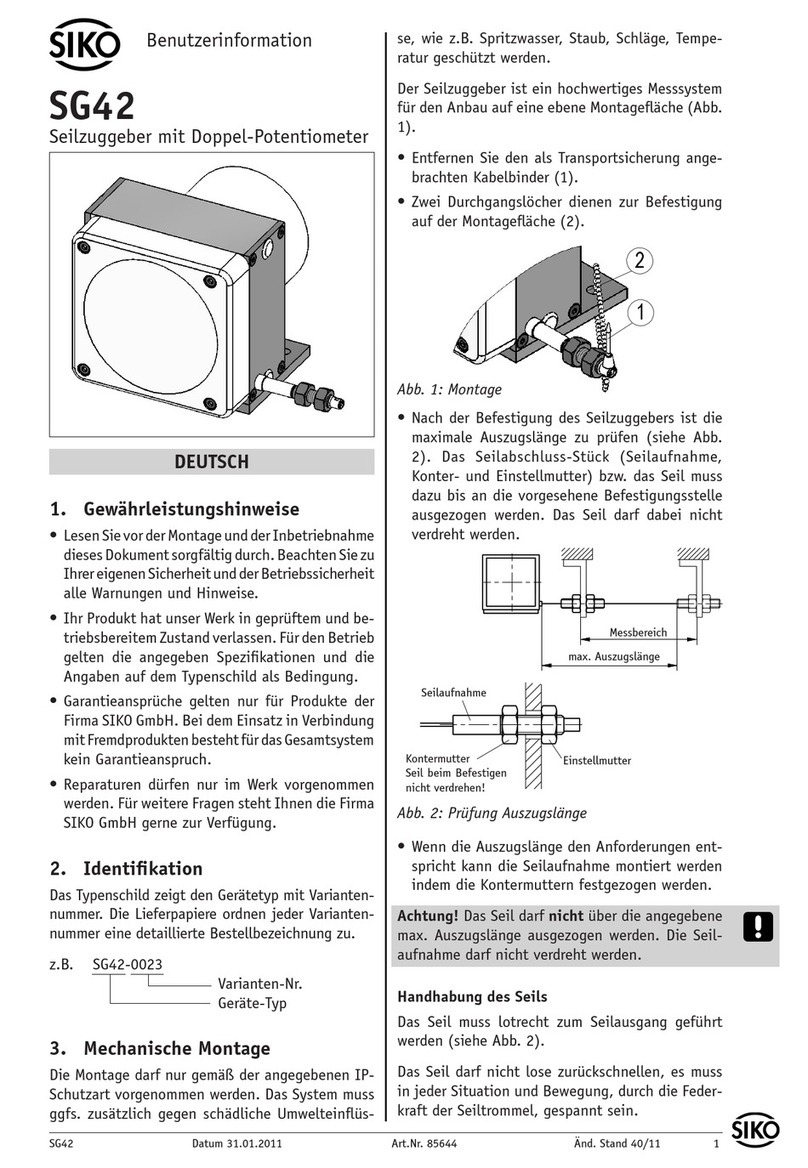
Abb. 1: Montage
Messbereich
max. Auszugslänge
Abb. 2: Prüfung Auszugslänge
Seilaufnahme
Einstellmutter
Kontermutter
Seil beim Befestigen
nicht verdrehen!
DEUTSCH
1. Gewährleistungshinweise
Lesen Sie vor der Montage und der Inbetriebnahme
dieses Dokument sorgfältig durch. Beachten Sie zu
Ihrer eigenen Sicherheit und der Betriebssicherheit
alle Warnungen und Hinweise.
Ihr Produkt hat unser Werk in geprüftem und be-
triebsbereitem Zustand verlassen. Für den Betrieb
gelten die angegeben Spezifikationen und die
Angaben auf dem Typenschild als Bedingung.
Garantieansprüche gelten nur für Produkte der
Firma SIKO GmbH. Bei dem Einsatz in Verbindung
mit Fremdprodukten besteht für das Gesamtsystem
kein Garantieanspruch.
Reparaturen dürfen nur im Werk vorgenommen
werden. Für weitere Fragen steht Ihnen die Firma
SIKO GmbH gerne zur Verfügung.
2. Identifikation
Das Typenschild zeigt den Gerätetyp mit Varianten-
nummer. Die Lieferpapiere ordnen jeder Varianten-
nummer eine detaillierte Bestellbezeichnung zu.
z.B. SGP/1-0023
Varianten-Nr.
Geräte-Typ
3. Mechnische Montage
Die Montage darf nur gemäß der angegebenen IP-
Schutzart vorgenommen werden. Das System muss
ggfs. zusätzlich gegen schädliche Umwelteinflüs-
•
•
•
•
se, wie z.B. Spritzwasser, Staub, Schläge, Tempe-
ratur geschützt werden.
Der Seilzuggeber ist ein hochwertiges Messsystem
für den Anbau auf eine ebene Montagefläche (Abb.
1).
Entfernen Sie den als Transportsicherung ange-
brachten Kabelbinder (1).
Zwei Durchgangslöcher dienen zur Befestigung
auf der Montagefläche (2).
•
•
Benutzerinformation
SGP/1
Seilzuggeber mit Potentiometer
Nach der Befestigung des Seilzuggebers ist die
maximale Auszugslänge zu prüfen (Abb. 2). Das
Seilabschluss-Stück bzw. das Seil muss dazu bis
an die vorgesehene Befestigungsstelle ausgezo-
gen werden. Das Seil darf dabei nicht verdreht
werden.
•
Wenn die Auszugslänge den Anforderungen ent-
spricht kann die Seilaufnahme montiert werden
indem die Kontermuttern festgezogen werden.
Achtung! Das Seil darf nicht über die angegebene
max. Auszugslänge ausgezogen werden. Die Seil-
aufnahme darf nicht verdreht werden.
Handhabung des Seils
Das Seil muss lotrecht zum Seilausgang geführt
werden (Abb. 2).
Das Seil darf nicht lose zurückschnellen, es muss
in jeder Situation und Bewegung, durch die Feder-
kraft der Seiltrommel, gespannt sein.
•

2 SGP/1 Datum 03.03.2010 Art.Nr. 84050 Änd. Stand 65/10
Ansichtseite = Steckseite
Abb. 4: Montage der Seilverlängerung
Abb. 3: Seilverlängerung, Umlenkrolle
Seilverlängerung
Seilzuggeber
Umlenkrolle
Messbereich
Für eine korrekte Funktion darf das Seil nicht ge-
quetscht oder geknickt werden.
Seilverlängerung (Zubehör)
Falls erforderlich kann eine Seilverlängerung ein-
gesetzt werden.
Achtung! Durch eine Seilverlängerung kann der
eigentliche Messbereich jedoch nicht vergrößert
werden. Die maximale Auszugslänge darf nicht
überschritten werden.
4. Elektrischer Anschluss
Anschlussverbindungen dürfen nicht unter
Spannung geschlossen oder gelöst werden!!
Verdrahtungsarbeiten dürfen nur spannungslos
erfolgen.
Litzen sind mit Aderendhülsen zu versehen.
Vor dem Einschalten sind alle Leitungsanschlüsse
und Steckverbindungen zu überprüfen.
Hinweise zur Störsicherheit
Alle Anschlüsse sind gegen äußere Störeinflüsse
geschützt. Der Einsatzort ist aber so zu wählen,
dass induktive oder kapazitive Störungen nicht
auf das Geräte oder deren Anschlussleitungen
einwirken können! Durch geeignete Kabelfüh-
rung und Verdrahtung können Störeinflüsse (z.B.
von Schaltnetzteilen, Motoren, getakteten Reg-
lern oder Schützen) vermindert werden.
Erforderliche Maßnahmen:
Nur geschirmtes Kabel verwenden. Den Kabel-
schirm beidseitig auflegen. Litzenquerschnitt der
Leitungen min. 0,14mm², max. 0,5mm².
Die Verdrahtung von Abschirmung und Masse (0V)
muss sternförmig und großflächig erfolgen. Der An-
schluss der Abschirmung an den Potentialausgleich
muss großflächig (niederimpedant) erfolgen.
Das System muss in möglichst großem Abstand von
Leitungen eingebaut werden, die mit Störungen
belastet sind; ggfs. sind zusätzliche Maßnahmen
wie Schirmbleche oder metallisierte Gehäuse
vorzusehen. Leitungsführungen parallel zu Energie-
leitungen vermeiden.
Litzenquerschnitt für Verbindungen von Ab-
schirmung zur Maschine und zum Schaltschrank
(Erdung) min. 4mm².
Metallische Teile des Gebergehäuses müssen
gemäß den EMV-Bestimmungen geerdet sein und
dürfen nicht potentialfrei montiert werden.
4.1 Steckerbelegung
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Die Montage der Seilverlängerung erfolgt durch
Aufstecken des Anschlussstückes (3) auf die
Schraubverbindung (1). Mittels eingepresster
Spannhülse (2) werden beide Teile formschlüssig
miteinander verbunden.
Umlenkrolle (Zubehör)
Wenn das Seil nicht lotrecht zum Seilausgang be-
festigt werden kann, ermöglicht der Einsatz einer
Umlenkrolle den Auszug in jede beliebige Richtung
(Abb. 3).
Die Umlekrolle muss parallel zum Seil montiert
werden.
Starke Schmutzbildung ist im Bereich der Umle-
krolle zu vermeiden, Die Funktion muss in regel-
mässigen Abständen kotrolliert werden.
Achtung! Bei Verwendung von Seilverlängerungen
ist darauf zu achten, dass das Verbindungsstück
nicht über die Umlenkrolle geführt werden kann.
•
•

SGP/1 Datum 03.03.2010 Art.Nr. 84050 Änd. Stand 65/10 3
Abb. 5: Gegenstecker
Abb. 6: Öffnen
entgegen
Uhrzeigersinn
axial
Abb. 7: Schließen
im
Uhrzeigersinn
axial
Abb. 8: Kabelvorbereitung
mit/ohne Messwandler
Aderendhülse
evtl. Schrumpf-
schlauch
Steuerleitung:
2x0.25mm² bzw.
3x0.25mm²
Steckerbelegung ohne Messwandler
Pin Belegung
1 Po Anfangsstellung Potentiometer
2 Pe Endstellung Potentiometer
3 S Schleifer Potentiometer
4 ---
Steckerbelegung mit R/I-Wandler (MWI)
Pin Belegung
1 I+ 4...20mA
2 I-
3 ---
4 ---
Steckerbelegung mit R/U-Wandler (MWU)
Pin Belegung
1 +24VDC
2 GND
3 Uout
4 ---
4.2 Montage Gegenstecker
Bei SIKO als Zubehör unter Art.Nr. 83419 (4-pol.
Buchse) erhältlich. Litzenquerschnitt der Leitungen
max.0,75mm². Kabeldurchlass: 4-6mm.
Bei der Steckermontage bitte schrittweise vor ge-
hen (Abb. 5):
Teile 1 ... 4 über Kabelmantel schieben.
Kabel abmanteln (35mm), Leiter abisolieren
(4mm) und verzinnen.
Litzen in Einsatz (5) schrauben (entsprechend
Anschlussplan).
Teile 2 ... 4 montieren.
Druckschraube (1) mit Kupplungshülse (4)
verschrauben.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Schließen (Abb. 7):
Die Haube (1) so auf das Getriebegehäuse (2)
setzten, dass die beiden breiten Markierungen
eine Linie bilden.
Getriebegehäuse (2) festhalten und die Haube (1)
im Uhrzeigesinn drehen bis der Bajonettverschluss
einrastet und die beiden dünnen Markierungen
auf einer Linie sind (Abb. 7).
•
•
4.3 Öffnen und Schließen des Geräts
Öffnen (Abb. 6):
Zum Öffnen des Gerätes den Seilzuggeber mit
dem Getriebegehäuse (2) fixieren und die Haube
(1) entgegen dem Uhrzeigersinn um eine 1/4
Umdrehung drehen bis der Bajonettverschluss
ausrastet.
Die Haube (1) axial vom Getriebegehäuse (2)
abnehmen.
•
•
4.4 Anschluss des Kabels
Die Kabel gemäß Abb. 8 vorbereiten.•
Öffnen Sie das Gerät (siehe Kapitel 4.3) und
demontieren Sie die PG-Verschraubung.
•

4 SGP/1 Datum 03.03.2010 Art.Nr. 84050 Änd. Stand 65/10
Folgeelektronik
Abb. 12: Anschluss Bürde gegen +UB (MWI)
Schraubklemme
Abb. 10: Litzenanschluss
Abb. 9: Kabelanschluss PG7
Abb. 11: Anschluss Bürde gegen Masse (MWI)
Folgeelektronik
Abb. 13: Lageänderung Kabel- oder Steckerabgang
Die Mutter (1) und den Kunststoffeinsatz (2) auf
das Kabel schieben (Abb. 9).
Das Abschirmgeflecht (3) über den Kunststoff-
einsatz (2) zurückstülpen.
Litzen durch die Verschraubung (4) schieben.
Kunststoffeinsatz (2) in die Verschraubung
einpassen.
Die Mutter (1) aufschrauben und die komplette
Verschraubung (mit O-Ring (5) zur Abdichtung)
an der Haube anbringen.
•
•
•
•
Schraubklemmenbelegung mit R/U-Wandler
(MWU)
Klemme Belegung
1 +24VDC
2 GND
3 Uout
Schließen Sie das Gerät (siehe Kapitel 4.3).•
5. Lageänderung Kabel- oder Stecke-
rabgang
Um die Lage des Kabel- oder Steckerabgangs zu
ändern, Haube öffnen (siehe Kapitel 4.3).
Die beiden Innensechskantschrauben (1) leicht
lösen (siehe Abb. 13).
Nun lässt sich das Getriebegehäuse (2) verdrehen,
~220° gegen den Uhrzeigersinn und ~90° in
Richtung des Uhrzeigersinns.
Die Innensechskanntschrauben (1) wieder anzie-
hen, Haube aufsetzen und schließen.
Achtung! Bei einer Lageänderung des Kabel- oder
Steckerabgangs ändern sich die Ausgabewerte!
•
•
•
•
Litzen an der Schraubklemme des Gerätes an-
schliessen (Abb. 10).
•
Schraubklemmenbelegung ohne Messwandler
Klemme Belegung
1 PE Endstellung Potentiometer
2 S Schleifer Potentiometer
3 PO Anfangsstellung Potentiometer
Schraubklemmenbelegung mit R/I-Wandler
(MWI)
Klemme Belegung
1 I+ 4...20mA
2 I-

SGP/1 Datum 03.03.2010 Art.Nr. 84050 Änd. Stand 65/10 5
Abb. 15: Abgleich
Strom
Messweg
20mA
4mA (Po)
(Pe)
0
Abb. 14: Einstellen der Trimmpotentiometer
Trimmpotentiometer Po
10-Wendel-Potentiomter
Trimmpotentiometer Pe
Abb. 16: Einstellen des Trimmpotentiometers
10-Wendel-Potentiomter
Trimmpotentiometer Pe
6. Einstellung und Abgleich
6.1 Einrichtung Potentiometer
Der Messbereich des Potentiometers erstreckt sich
über die gesamte Auszugslänge des Seil. Im Werk
wird für die Seillänge 0mm (vollständig eingezo-
gen) der Wert 0 Ohm voreingestellt.
Nach ordnungsgemäßem Anschluss zeigt das Gerät
bei Einschalten der Betriebsspannung den aktuellen
Istwert.
6.2 Abgleich des Messwandlers
6.2.1 Messwandler R/I-Wandler (MWI)
Das Gerät ist mit einem Widerstandsstromwand-
ler ausgestattet. Der Potentiometer-Widerstand
wird in einen Strom von 4...20mA umgewandelt.
Es handelt sich um eine Zweileitertechnik. Der
Messstrom dient gleichzeitig zur Versorgung des
Wandlers.
Der Messwandler ist bei Auslieferung auf Standard-
werte 4mA für die Anfangs- (Po) und 20mA für
die Endstellungen (Pe) des Potentiometers abge-
glichen.
Durch zwei Trimmpotentiometer Po und Pe (sie-
he Abb. 14) können diese Werte an die tatsäch-
lichen Anfangs- und Endstellungen der Anwen-
dung angepaßt werden:
Abgleich
Masch. auf Anfangsstellung fahren.
Linkes Potentiometer (Po) drehen, bis Anfangs-
wert (4mA) gemessen wird.
Masch. auf Endstellung fahren.
Rechtes Potentiometer (Pe) drehen, bis Endwert
(20mA) gemessen wird.
Die Schritte 1 bis 4 sind solange zu wiederholen,
bis die Werte austariert sind (iterativer Abgleich).
1.
2.
3.
4.
6.2.2 Messwandler R/U-Wandler (MWU)
Ist das Gerät mit einem Widerstands-Spannungs-
wandler ausgestattet, wird der Potentiometer-
Widerstand in eine Spannung von 0...10VDC
umgewandelt. Der Anschluss erfolgt über eine
Dreileitertechnik.
Der Messwandler ist bei Auslieferung auf den An-
fangswert 0V Ausgangsspannung (Po) und den
Endwert 10V Ausgangsspannung (Pe) abgeglichen.
Der Ausgang des Messwandlers sollte mit einem
Widerstand 2...10KΩ gegen GND beschaltet wer-
den, damit sich der Anfangswert 0V einstellt. Die
Ausgangslast sollte jedoch so dimensioniert sein,
dass in der Endstellung (10V) ein Ausgangsstrom
von 10mA nicht überschritten wird.
Mit dem Trimmpotentiometer Pe (siehe Abb.
16) kann der Endwert an die tatsächliche End-
stellung der Anwendung angepaßt werden:
Einstellbarkeit:
Mit Trimmpotentiometer Po kann ein Strom von
4mA bei Potentiometerwerten von 0 bis 15% des
Gesamtwertes eingestellt werden.
Mit Trimmpotentiometer Pe kann ein Strom von
20mA bei Potentiometerwerten von 90 bis 100%
des Gesamtwertes eingestellt werden.
Der kleinste nutzbare Bereich des Potentiome-
ters, in dem 4...20mA abgegeben werden, beträgt
demnach 15% bis 90% des Potentiometer-Wider-
standsbereichs.
•
•

6 SGP/1 Datum 03.03.2010 Art.Nr. 84050 Änd. Stand 65/10
Einstellbarkeit:
Mit Trimmpotentiometer Pe kann eine Spannung
von 10V bei Potentiometerwerten von 60 bis 100%
des Gesamtwertes eingestellt werden.
Abgleich
Masch. auf Endstellung fahren.
Potentiometer (Pe) drehen, bis eine Ausgangs-
spannung (10V) gemessen wird.
Die Schritte 1 bis 2 sind solange zu wiederholen,
bis die Werte austariert sind (iterativer Abgleich).
6.3 Was tun wenn... (Messwandler)
...die Drehrichtung grundsätzlich falsch ist?
Dann können Sie:
das Gerät bei der Firma SIKO umtauschen
oder den Strom 4...20mA invertiert auswerten
(4mA würde dann dem Endwert entsprechen.
Machbar z.B. bei Auswertung mit Software).
oder die Spannung 0...10V invertiert auswerten
(0V würde dann dem Endwert entsprechen. Mach-
bar z.B. bei Auswertung mit Software).
... sich die Anfangs- und Endwerte des Stromwand-
lers nicht auf 4 bzw. 20mA bringen lassen?
Dann ist vermutlich der Verstellbereich des
Potentiometers zu klein (Schleifer bewegt
sich innerhalb des minimalen Bereichs von
15...90% und überstreicht einen zu kleinen
Widerstandsbereich).
Prüfen Sie, ob Sie mit dem kleineren Strombe-
reich auskommen können, andernfalls müssen
Sie die Übersetzung des Getriebes entsprechen
anpassen (durch Bestellung/Umtausch einer
anderen Übersetzung bei SIKO).
... sich der Endwert des Spannungswandlers nicht
auf 10V bringen läßt?
Dann ist vermutlich der Verstellbereich des Poten-
tiometers zu klein (Schleifer bewegt sich unterhalb
des minimalen Bereichs von 60% und überstreicht
einen zu kleinen Widerstandsbereich).
Prüfen Sie, ob Sie mit dem kleineren Spanungs-
bereich auskommen können, andernfalls müssen
Sie die Übersetzung des Getriebes entsprechen
anpassen (durch Bestellung/Umtausch einer
anderen Übersetzung bei SIKO).
•
1.
2.
•
•
•
1.
2.
•
•
7. Inbetriebnahme
Bitte beachten Sie die Hinweise auf ordnungsge-
mäßen mechanischen und elektrischen Anschluss
in Kapiteln 3 bis 6. Nur dann sind die Vorausset-
zungen für eine problemlose Inbetriebnahme und
einwandfreien Betrieb gegeben.
Prüfen Sie vor der Inbetriebnahme nochmals auf:
korrekte Polung der Betriebsspannung
korrekten Anschluss der Kabel
einwandfreie Montage des Geräts
•
•
•

SGP/1 Datum 03.03.2010 Art.Nr. 84050 Änd. Stand 65/10 7
Fig. 1: Mounting
Wire insert
Setting nut
Lock nut
Do not distort
wire when fixing!
Measuring range
max. extension length
Fig. 2: Extension length check
ENGLISH
1. Warranty information
In order to carry out installation correctly, we
strongly recommend this document is read very
carefully. This will ensure your own safety and
the operating reliability of the device.
Your device has been quality controlled, tested
and is ready for use. Please observe all warnings
and information which are marked either directly
on the device or specified in this document.
Warranty can only be claimed for components
supplied by SIKO GmbH. If the system is used
together with other products, there is no warranty
for the complete system.
Repairs should be carried out only at our works.
If any information is missing or unclear, please
contact the SIKO sales staff.
2. Identification
Please check the particular type of unit and type
number from the identification plate. Type number
and the corresponding version are indicated in the
delivery documentation.
e.g. SGP/1-0023
version number
type of unit
3. Installation
For mounting, the degree of protection specified
must be observed. If necessary, protect the unit
•
•
•
•
against environmental influences such as sprayed
water, dust, knocks, extreme temperatures.
The wire actuated transmitter is a high quality
measurring device and should be mounted to a
flat surface (fig. 1).
Remove the transport safety cable tie (1).
Use the two through holes for fixing the unit to
the mounting surface (2).
•
•
User Information
SGP/1
Wire Actuated Potentiometer
After mounting, check that the maximum exten-
sion length complies with the application (fig.
2). The wire end piece / wire must be pulled out
up to the planned fixation point. Wire torsion
should be avoided.
•
Extend the wire up to the fixing point, ensuring
it is aligned and is not twisted. Tighten the lock
nut to fix the wire connector.
Attention! Do not extend the wire beyond the
max. allowable extension length and do not twist
wire insert.
Wire handling
Pull out the wire perpendicular to the wire outlet
(fig. 2).
Do not let the wire go; in every position and du-
ring every move the wire must be stretched by the
cable drum's spring force.
For correction function the wire must remain wit-
hout kinks or flattening.
•

8 SGP/1 Datum 03.03.2010 Art.Nr. 84050 Änd. Stand 65/10
viewing side = plug-in-side
Fig. 4: Mounting of the wire extension
Fig. 3: Extension wire, Guide roller
Extension wire
Wire actuated transducer
Guide rollers
Measuring range
Extension wire (acessory)
If necessary an extension wire can be used.
Attention! By using an extension wire the maxi-
mum measuring length can not be altered. Make
sure that the maximum extension length is not
exceeded.
For mounting the wire extension: Push the con-
necting piece (3) onto the screw connector (1).
The press-fit clamping sleeve (2) will neatly join
both elements.
Connector connection without instrument
transformer
Pin Designation
1 Po Start point
2 Pe End point
3 S Moving contact
4 ---
Guide rollers (accessory)
Are used for applications where wire actuated
transducer and wire cannot be mounted in one
line. Using guide rollers the wire can be pulled out
in any direction (fig. 3).
Guide rollers must be mounted in line with the
wire.
Maintain cleanliness of guide rollers at all
times.
Attention! When using an extension wire make
sure that the wire connector dois not go over the
guide roller.
4. Electrical connection
Switch power off before any plug is inserted
or removed!!
Wiring must only be carried out with power off.
•
•
•
•
Provide standed wires with ferrules.
Check all lines and connections before switching
on the equipment.
Interference and distortion
All connections are protected against the effects
of interference. The location should be selected
to ensure that no capacitive or inductive in-
terferences can affect the encoder or the con-
nection lines! Suitable wiring layout and choice
of cable can minimise the effects of interference
(eg. interference caused by SMPS, motors, cyclic
controls and contactors).
Necessary measures:
Only screened cable should be used. Screen
should be connected to earth at both ends.
Wire cross section is to be at least 0,14mm²,
max. 0,5mm².
Wiring to screen and to ground (0V) must be via
a good earth point having a large surface area
for minimum impedance.
The unit should be positioned well away from
cables with interference; if necessary a protective
screen or metal housing must be provided. The
running of wiring parallel to the mains supply
should be avoided.
Cross section of cables connecting from screen to
machine or to control cabinet (GROUND) schould
be at least 4 mm².
Metallic components of the transmitter housing
should be earthed according to local regulations
and should not be connected potential free.
4.1 Pin assigment
•
•
•
•
•
•
•

SGP/1 Datum 03.03.2010 Art.Nr. 84050 Änd. Stand 65/10 9
Fig. 5: Counter-plug
Fig. 6: Opening
contrary to clock-
wise-rotating
axial
Fig. 7: Closing
clockwise-
rotating
axial
Fig. 8: Cable preparing
Potentiometer/transducer
Ferrule
possibel
Shrink sleeve
Wire cross section:
2x0.25mm²
or 3x0.25mm²
Connector connection with R/I-transformer
(MWI)
Pin Designation
1 I+ 4...20mA
2 I-
3 ---
4 ---
Connector connection mit R/U-transformer
(MWU)
Pin Designation
1 +24VDC
2 GND
3 Uout
4 ---
4.2 Mounting instruction for counter-plug
Available from SIKO as accessory art.no. 83419 (4
pins male connector). Wire cross section is to be at
least max. 0,75mm². Cable channel: 4-6mm.
Please proceed as follows (fig. 5):
Slip parts 1 ... 4 over outer cable.
Dismantle cable (35mm), strip (4mm) and tin
conductor.
Screw wires into socket (5) (follow connection
diagram).
Mount parts 2 ... 4.
Screw pressing screw (1) and coupling sleeve
(4) together.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
For closing (fig.7):
Place the hood (1) onto the gear's housing (2) so
that the two broad markings are on one line.
Fix the gear's housing (2) and turn the hood (1)
clockwise until the bayonet fastening engages and
the two thin markings are on one line (fig. 7).
•
•
4.3 How to open and close the device
For opening (fig. 6):
For opening the device, fix the gear's housing
(2) and turn the hood (1) counter-clockwise
by 1/4 revolution until the bayonet fastening
disengages.
Axially remove the hood (1) from the gear's
housing (2).
•
•
4.3 Cable connection
Prepare wire accord. to fig. 8.•
Open the device (see chapter 4.3) and unscrew
the PG-screws.
Push the nut (1) and the plastic bushing (2)
onto the cable.
Put the wire screening (3) over the plastic
bushing (2).
Slide strands through screw hole (4). Insert plastic
bushing (2) into the screw fitting.
Screw on the nut (1) and attach the complete bol-
ting (with O ring (5) for sealing) to the hood.
•
•
•
•
•

10 SGP/1 Datum 03.03.2010 Art.Nr. 84050 Änd. Stand 65/10
Screw connector
Fig. 10: Wire connection
Fig. 9: Cable connection PG7
Fig. 11: Conection load against mass (MWI)
follower electronics
follower electronics
Fig. 12: Connection load against +UB (MWI)
Fig. 13: Changing the position of the cabele or
connector outlet
Connect strands to the terminal of the device
(fig. 10).
•
5. Changing the position of cable or
connector outlet
Open the hood to be able to change the position
of the cable or connector outlet (see chapter
4.2).
Slightly lossen teh two Allen screws (1) (see
fig. 13).
Now you can rotate the drive's housing (2), ~220°
counter-clockwise and ~90° clockwise.
Tighten the Allen screws (1) , put the hood on
the device and close it.
Attention! By changing the position of cable or
connector outlet the readings will also change!
•
•
•
•
Screw connector connection without intstru-
ment transformer
Terminal Designation
1 Pe End point
2 S Moving contact
3 Po Start point
Screw connector connection with R/I-transfor-
mer (MWI)
Terminal Designation
1 I+ 4...20mA
2 I-
Screw connector connection with R/U-transfor-
mer (MWU)
Terminal Designation
1 +24VDC
2 GND
3 Uout
Close the geared potentiometer (see chapter
4.3).
•
6. Adjustment and alignment
6.1 Potentiometer setting
The measuring range of the poteniometer is mat-
ched to the total pull-out length of the wire. Ex
works value 0 Ohm is preset for wire length 0mm
(wire completely pulled in).

SGP/1 Datum 03.03.2010 Art.Nr. 84050 Änd. Stand 65/10 11
Fig. 14: Adjustment of the trimmpotentiometer
Trimmpotentiometer Po
10-turn-potentiomter
Trimmpotentiometer Pe
Fig. 16: Adjustment of trimmpotentiometer
10-turn-potentiomter
Trimmpotentiometer Pe
Fig. 15: Aligment
Current
Distance
20mA
4mA (Po)
(Pe)
0
6.2 Alignment of the instrument transformer
6.2.1 Instrument transformer R/I transformer
(MWI)
The unit comprises a resistance current converter.
The potentiometer's resistance is converted into a
current of 4...20mA (twin-core cable). The measu-
ring current is also used for feeding the instru-
ment transformer.
The instrument transformer is preset to standard
values 4mA for potentiometer's start position (Po)
and 20mA for end position (Pe).
Via two trimmpotentiometer's Po and Pe (see
fig. 14 these values can be adjusted to the
application's actual start and end position:
Adjustable:
Trimmpotentiometer's Po is used to adjust a
current of 4mA to potentiometer values of 0 to
15% of the total range.
Trimmpotentiometer's Pe is used to adjust a
current of 20mA to potentiometer values of 90
to 100% of the total range.
The smallest available potentiometer range, in
which 4 to 20mA are delivered, is hence 15% to
90% of the potentiometer's resistance range.
Alignment
Move axis to start position.
Turn left potentiometer (Po) until start value
(4mA) is measured.
Move axis to end position.
Turn right potentiometer (Pe) until end value
(20mA) is measured.
The steps 1 to 4 are to be repeated until the va-
lues are counterbalanced.
•
•
1.
2.
3.
4.
6.2.2 Instrument transformer R/U-transformer
(MWU)
If the device is equipped with a resistance-voltage
converter, tehen the potentiometer resistance is
converted into a voltage of 0 to 10VDC. Connec-
tion is via three-wire technology.
At the time of delivery, the instrument transformer
is preset to the standard value 0V output voltage
(Po) and the end value 10V output voltage (Pe).
The output of the instrument transformer should
be wired against GND with a resistor 2 to 10KΩ to
enable the initial value of 0V to be set. However,
the output current of 15mA won't be exceeded in
the end position (10V).
By means of the trimming potentiometer Pe
(see fig. 16), the final value can be adjusted to
the actual final position of the application.
Adjustable:
Trimmpotentiometer's Pe is used a adjust a voltage
of 10V to potentiometer value of 60 to 100% of
the total range.
Alignment
Move axis to end position.
Turn right potentiometer (Pe) until end value
(10V) is measured.
•
1.
2.

12 SGP/1 Datum 03.03.2010 Art.Nr. 84050 Änd. Stand 65/10
SIKO GmbH
Werk / Factory:
Weihermattenweg 2
79256 Buchenbach-Unteribental
Postanschrift / Postal address:
Postfach 1106
79195 Kirchzarten
Telefon/Phone +49 7661 394-0
Telefax/Fax +49 7661 394-388
E-Mail info@siko.de
Internet www.siko.de
Service [email protected]e
The steps 1 to 2 are to be repeated until the va-
lues are counterbalanced.
6.3 What to do if... (Instrument transformer)
...the counting direction is wrong?
You can:
exchange the device at SIKO company,
or by inverted interpretation of the 4 to 20mA
current (4mA would then correspond to the
end position; can be achieved via software
programming),
or by inverted interpretation of the 0 to 10V volta-
ge (0V would then correspond to the end position;
can be achieved via software programming).
... if the instrument transformer's start / end
value cannot be set to 4 / 20mA?
Then the adjustment range of the potentiometer
is probably too small (wiper moves within the
minimum range of 15...90% and sweeps a too
small resistance range).
check, whether you can do with a smaller current
range; otherwise adjust the gear's input ratio
accordingly (by ordering / changing the counting
direction at SIKO).
•
•
•
•
•
... if the instrument transformer's end value
cannot be set to 10V?
Then the adjustment range of the potentiometer
is probably too small (wiper moves below the
minimum range 60% and sweeps a too small
resistance range).
check, whether you can do with a smaller voltage
range; otherwise adjust the gear's input ratio
accordingly (by ordering / changing the counting
direction at SIKO).
7. Starting
Please ensure that the instructions given in chap-
ter 3 by 6 regarding mechanical and electrical
connection are followed. This will ensure correct
installation and the operating reliability of the
device.
Before starting check again:
correct polarity of the supply voltage
correct cable connection
correct mounting of the device
•
•
•
•
•
Other manuals for SGP/1
1
Table of contents
Languages:
Other Siko Measuring Instrument manuals
Popular Measuring Instrument manuals by other brands

Lasertec
Lasertec TruPulse L2 Quick reference field guide

Philips
Philips VoiceTracer DVT4110 user manual

AESSEAL
AESSEAL FLOWTRUE FTP-50-145 Installation, operation & maintenance manual

Satec
Satec PM290 reference guide

Xylem
Xylem sensus AutoRead user guide
Extech Instruments
Extech Instruments MA120 user guide