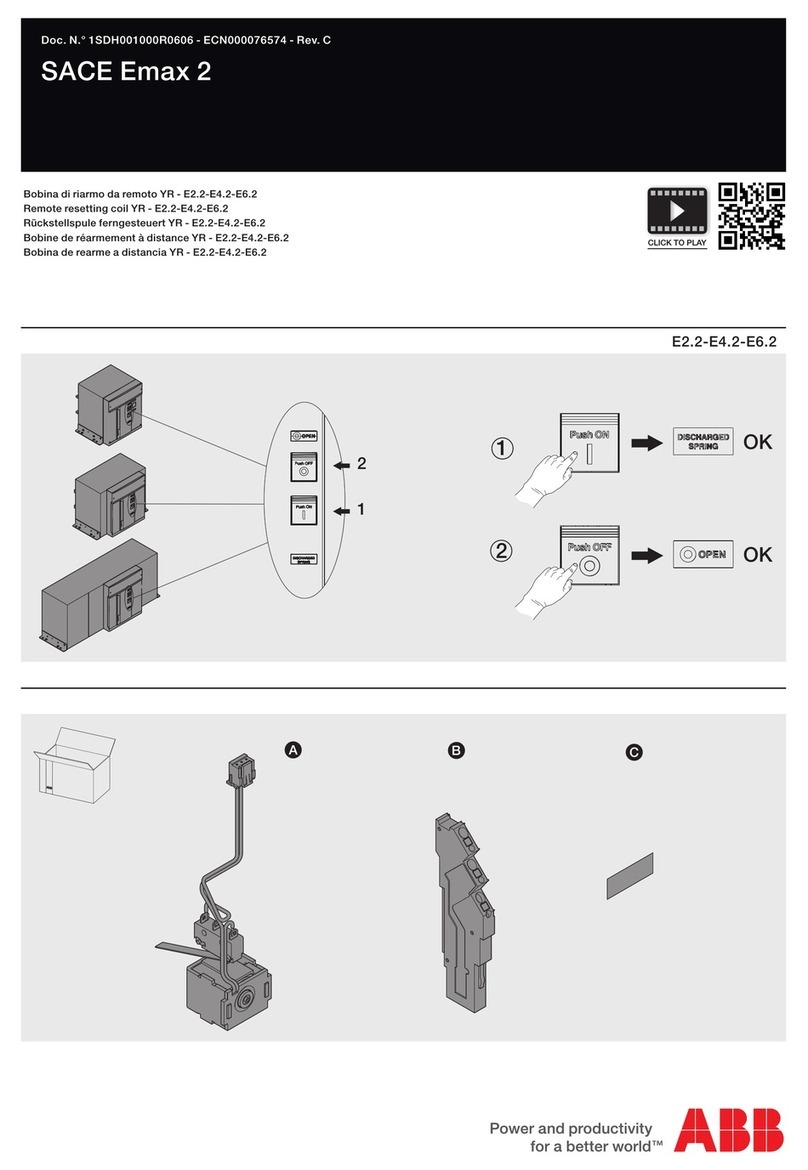
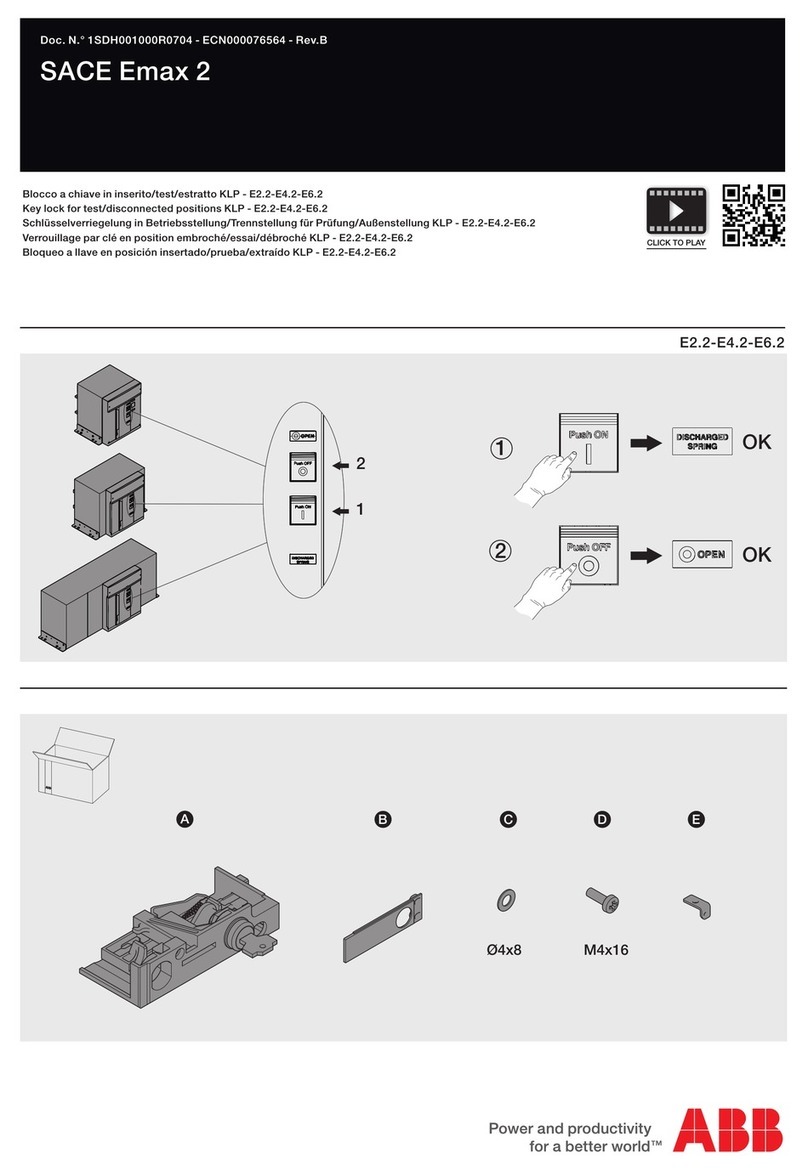
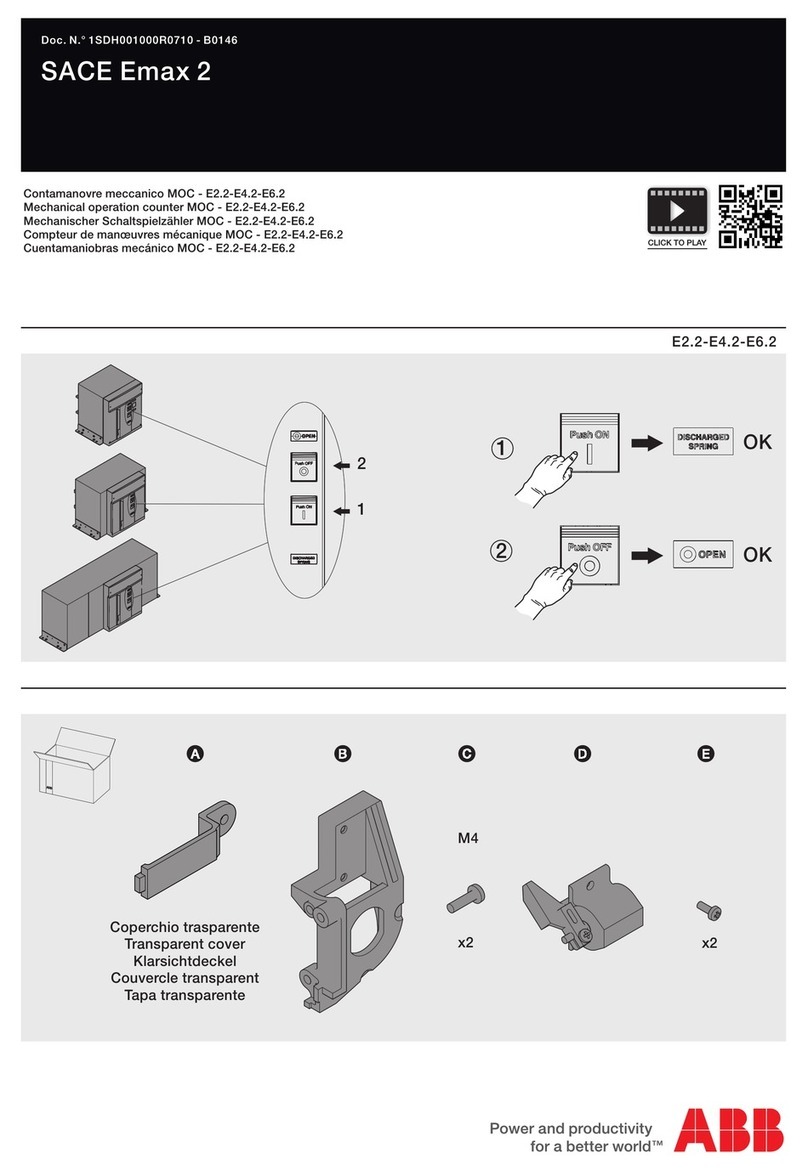
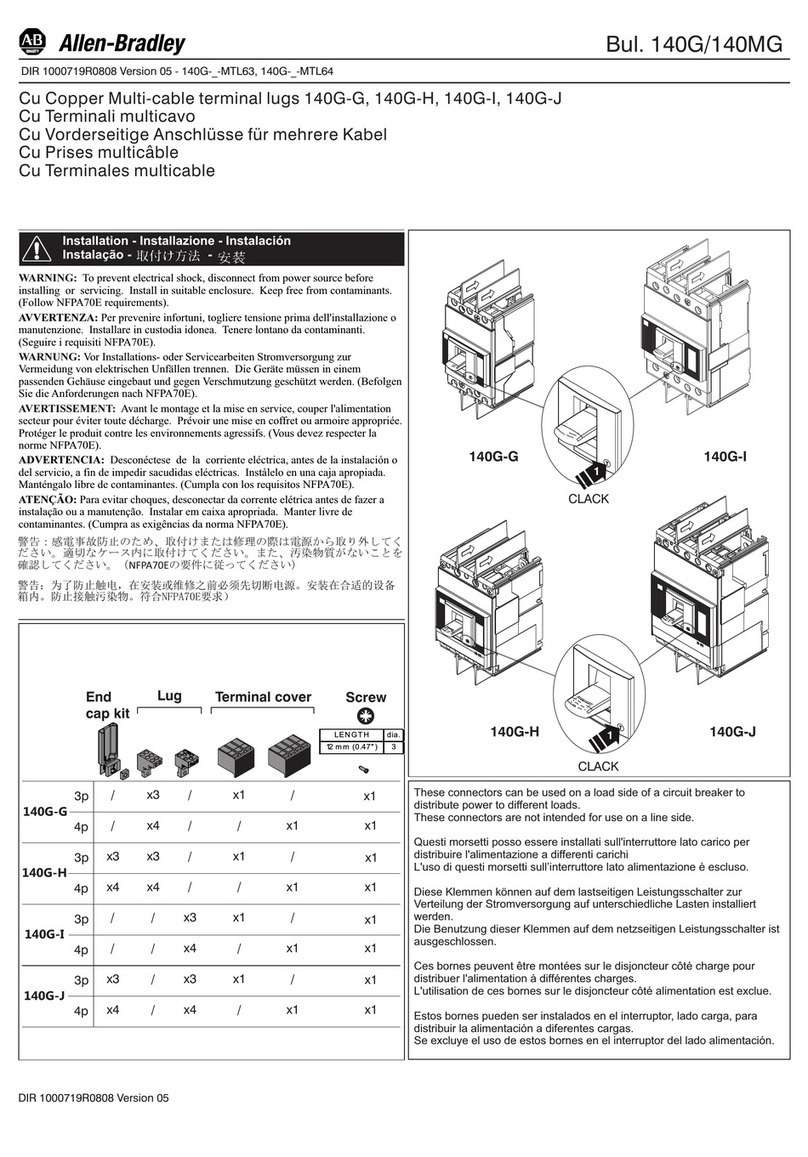
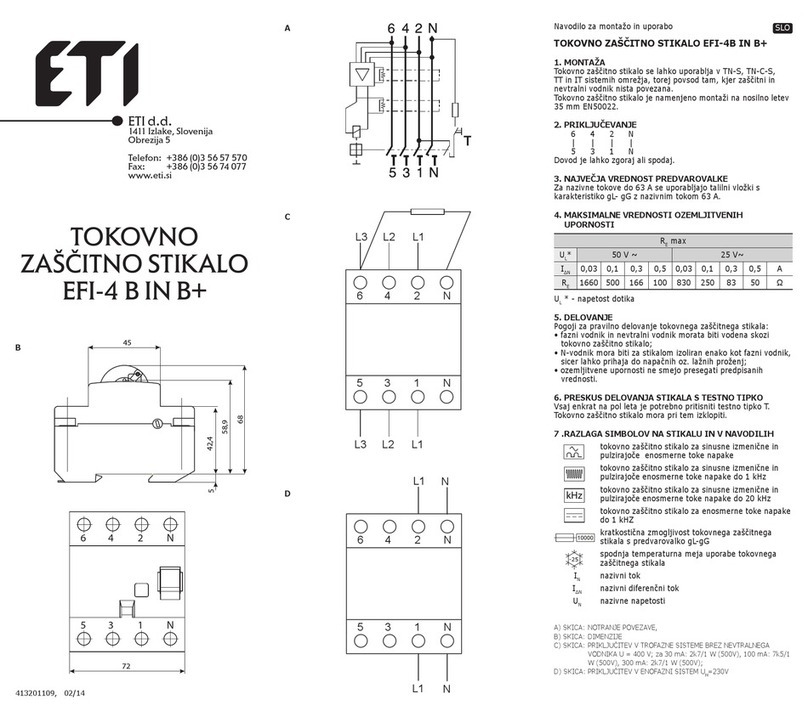
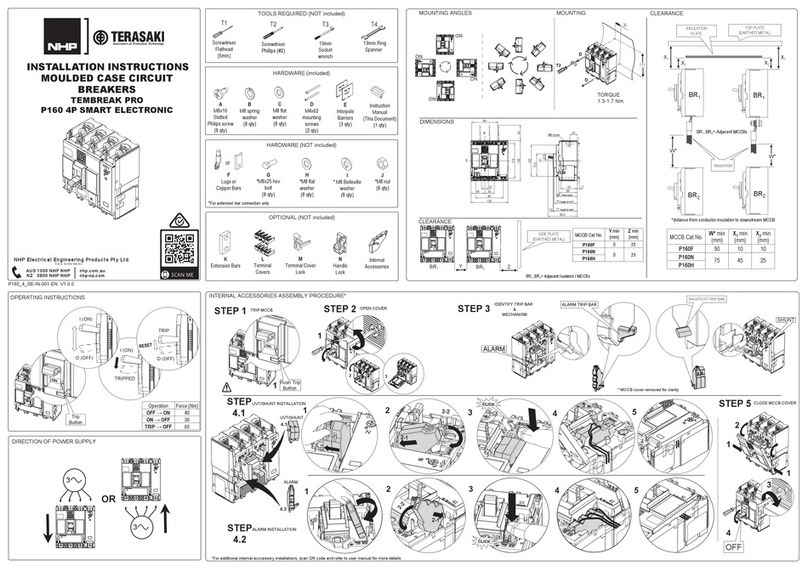
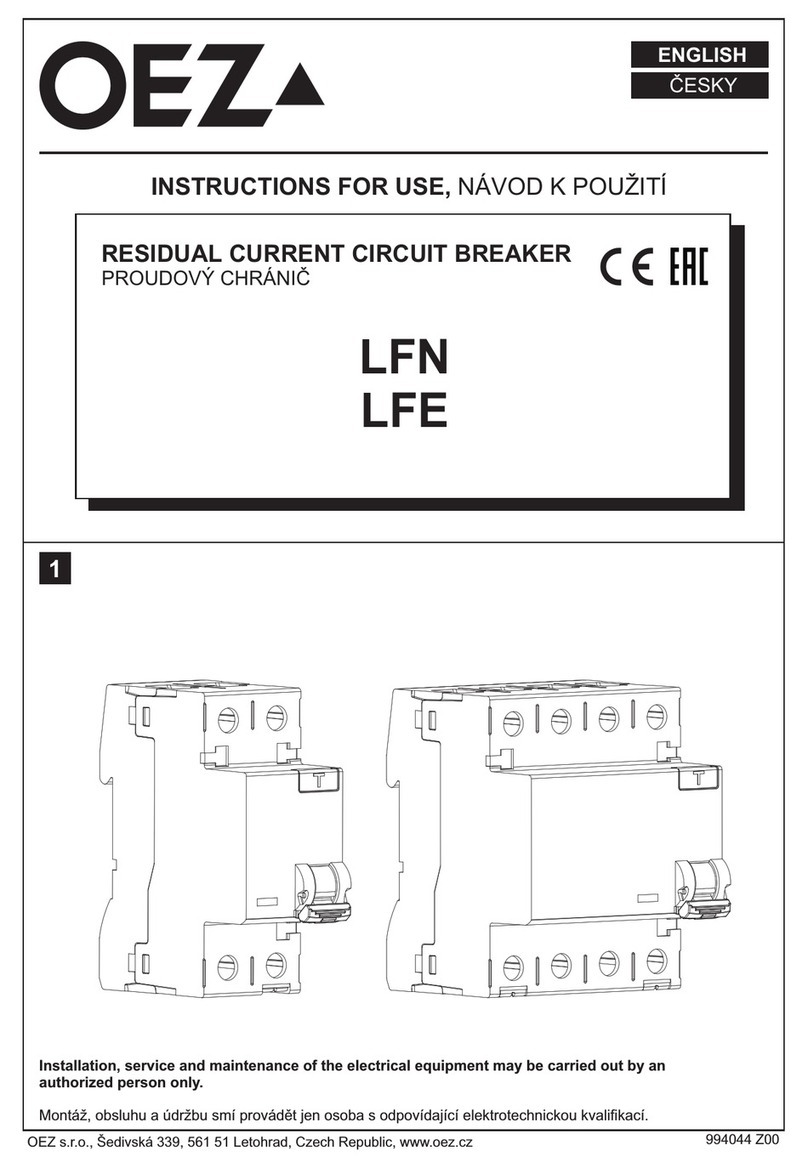
7 ABB IB 6.2.15.7-1C
RACKING:
ADVAC™ circuit breakers are designed with three positive racking positions. The Disconnect position allows only
manual operation of the breaker without control power and with the shutters closed. The Test Position allows manual
and electrical operation of the breaker with control power supplied through the secondary contacts with the shutters
closed. As the breaker approaches the Connected position, an increase in racking force is required to lift the shutters
and to engage the primary contacts. In the Connected position, the primary disconnects are fully engaged with the
shutters open, electrical operation of the breaker through the secondary contacts remains enabled.
1. Engage Racking Handle onto Racking Screw (7)
2. Actuate Position Release Lever (9) to begin racking breaker.
a. CLOCKWISE (cw) rotation inserts the breaker towards the primary contacts.
b. COUNTER-CLOCKWISE (ccw) rotation withdraws the breaker away from the primary contacts.
TEST THROUGH CONNECT:
1. Perform visual inspection of the Circuit Breaker:
a. Verify Close/Open Indicator shows OPEN
b. Verify Charged/Discharged Indicator shows CHARGED
c. Verify switchgear door is CLOSED.
2. Actuate (push down) Position Release Lever (9) to begin racking from Test position:
a. Begin racking in the CLOCKWISE direction
b. Release Position Release Lever once racking has begun (after approx. 1/2 turn)
c. Approximately 21 revolutions (210mm) will move the breaker between the Test and Connect positions
•The Connect Position is indicated by a positive lock, preventing further racking shaft rotation.
•Closing of the breaker is prevented between Test and Connect positions
3. Once the Breaker is Fully in the connect position, and the positive lock position has been established, It is recom-
mended that the racking screw be turned in the counterclockwise direction to release the pressure on the locking
mechanism to insure positive engagement of the mechanical/electrical interlocks.
DISCONNECT THROUGH TEST:
1. Perform visual inspection of the Circuit Breaker:
a. Verify Close/Open Indicator shows OPEN
b. Verify Charged/Discharged Indicator shows DISCHARGED
c. Breaker is prevented from closing by a mechanical interlock in the truck .
d. Verify switchgear door is CLOSED.
2. Actuate (push down) Position Release Lever (9) to begin racking from Disconnect position
a. Begin racking in the CLOCKWISE direction
b. Release Position Release Lever once racking has begun (after Approx. 1/2 turn)
c. Approximately four (4) revolutions (40mm) will move the breaker from the Disconnect to the Test position
•The Test Position is indicated by a positive lock, preventing further racking shaft rotation.
• Closing of the breaker is prevented between Disconnect and Test positions
• Control power is available in the Test Position; shutters remain closed.
CONNECT THROUGH TEST:
1. Perform visual inspection Circuit Breaker:
a. Verify Close/Open Indicator shows OPEN
b. Verify switchgear door is CLOSED.
2. Actuate (push down) Position Release Lever (9) to begin racking from Connect position:
a. Begin racking in the COUNTER-CLOCKWISE direction
b. Release Position Release Lever once racking has begun (after 1/2 turn)
c. Approximately 21 revolutions (210mm) will move the breaker between the Connect and Test positions
•The Test Position is indicated by a positive lock, further racking shaft rotation is prevented.
•Closing of the breaker is prevented between Connect and Test positions
INSERTION AND REMOVAL