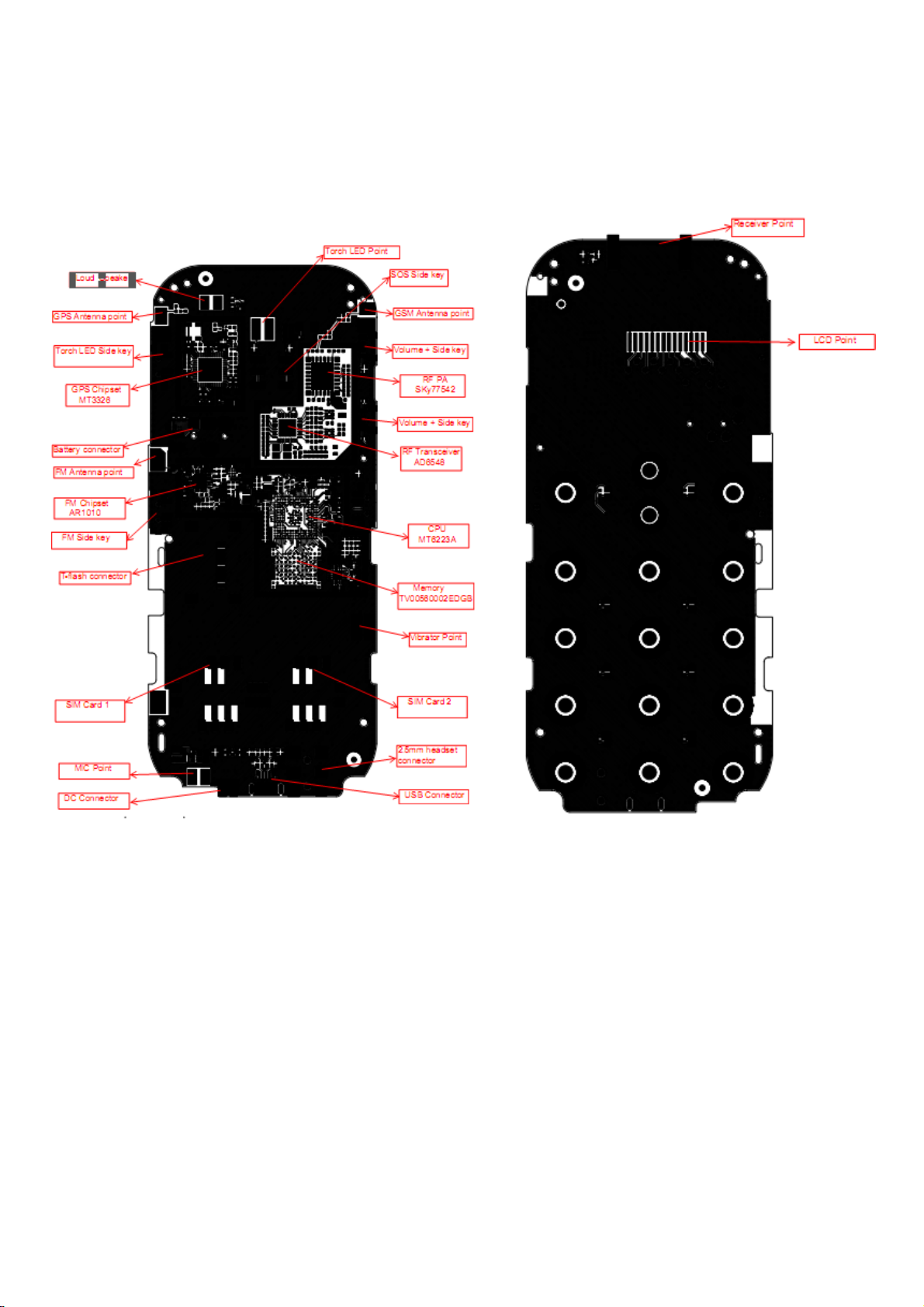
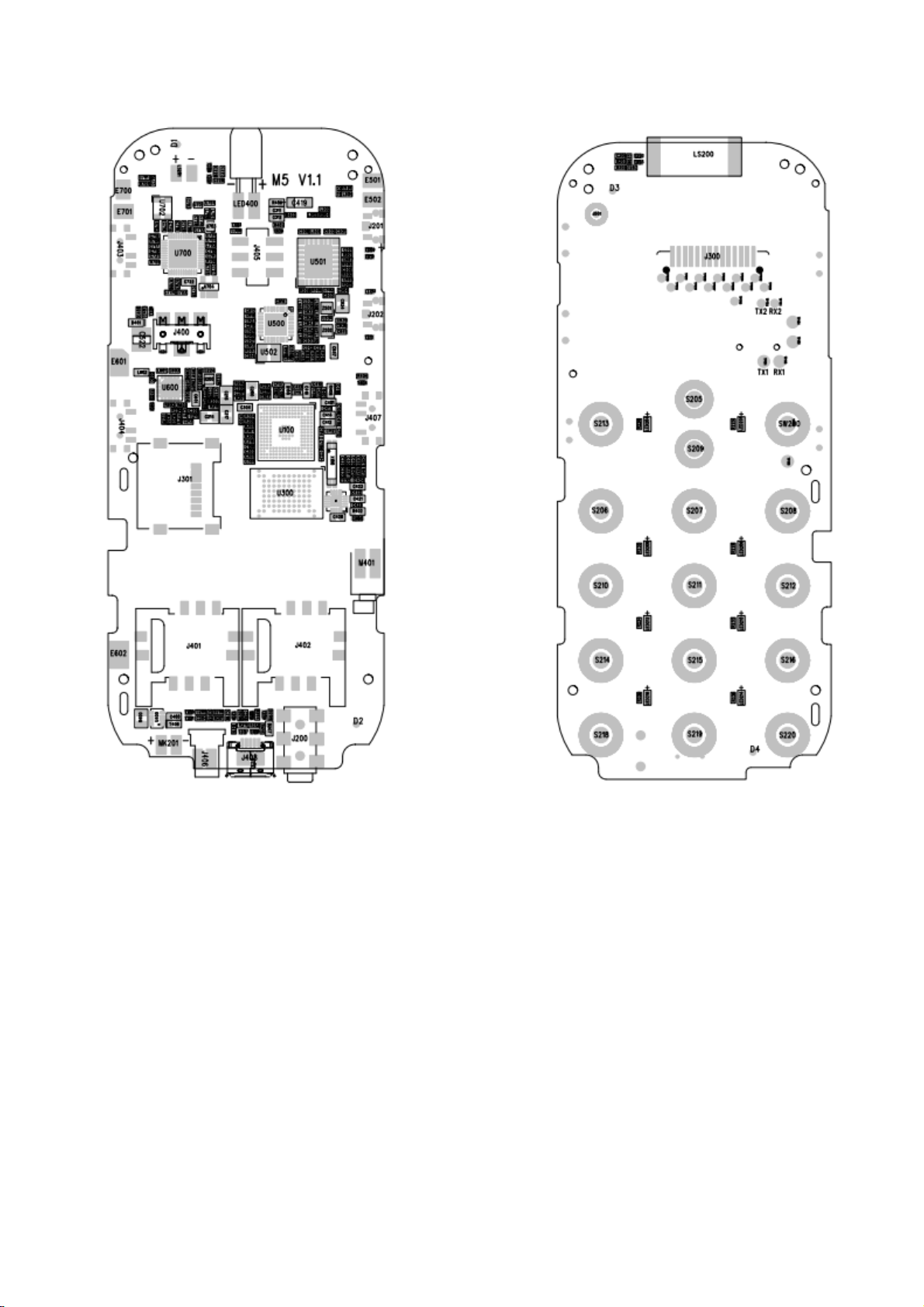
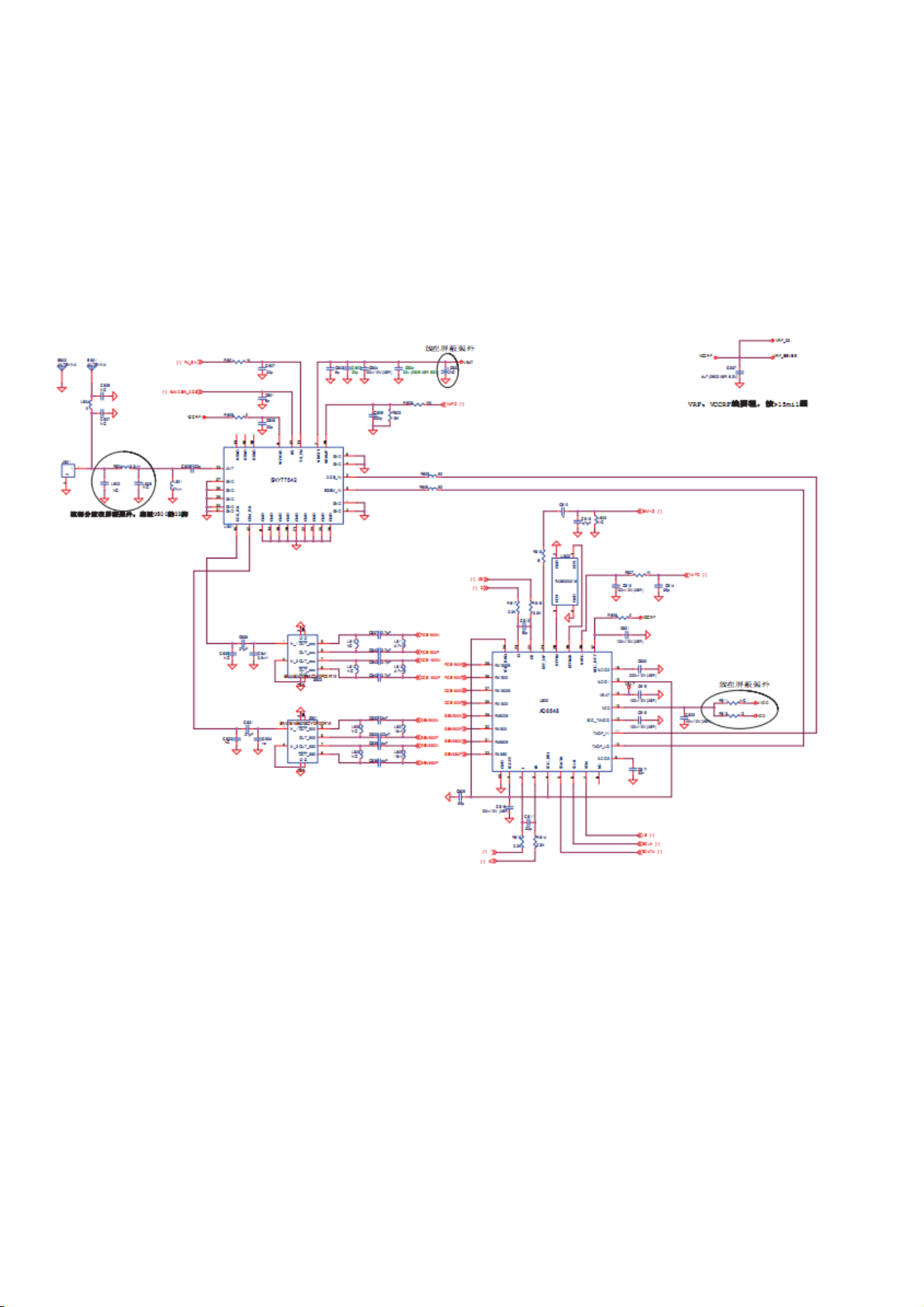
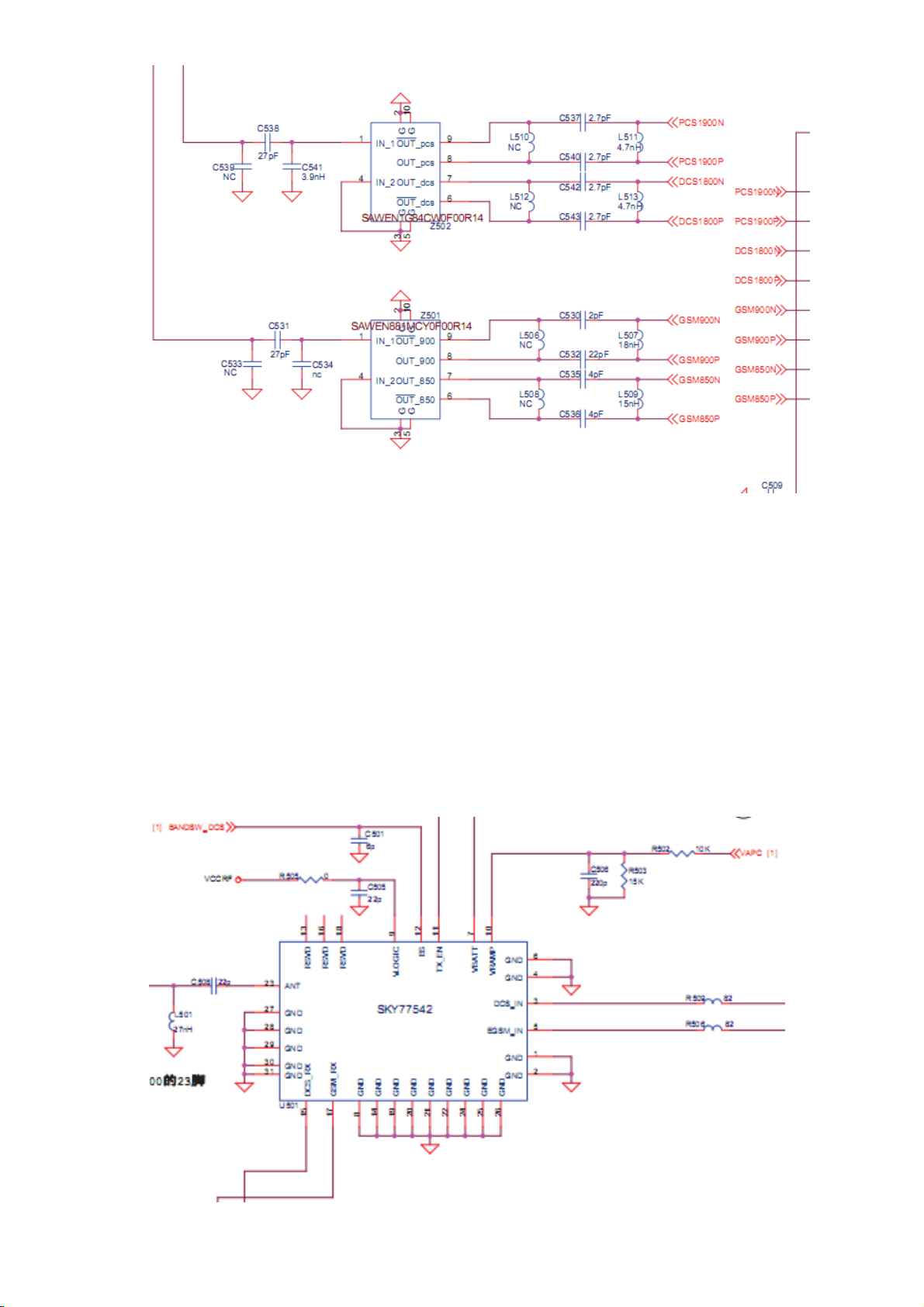
nal
he
Perfo ile phone!
mplifier,
nd the matching components between each other...
ion Receiver
n Baseband Amplifiers
–Th receive path
RF Circuit deals with the RX and TX of wireless signal, with responsibility for the bidirectio
Transmission of speech and data between the MS and BS through the air interface. In detail RX part
Accomplishes the AGC amplifying, mix and demodulation of RF weak signal received from BS, The
Final signal output from RX part is the analog baseband I/Q signal. The final RX I/Q will be sent to
Baseband Circuit for later disposal. On the other hand TX part deals with the signal modulation,
Up-conversion mix and power amplifying of analog I/Q signal received from baseband, generating
Burst which meets the GSM specification. And then the bursts are transmitted to Base station through
The antenna. The signal interface between RF Circuit and Baseband is analog baseband I/Q signal. T
rmance of RF Circuit can directly affects the signal transmission quality of the mob
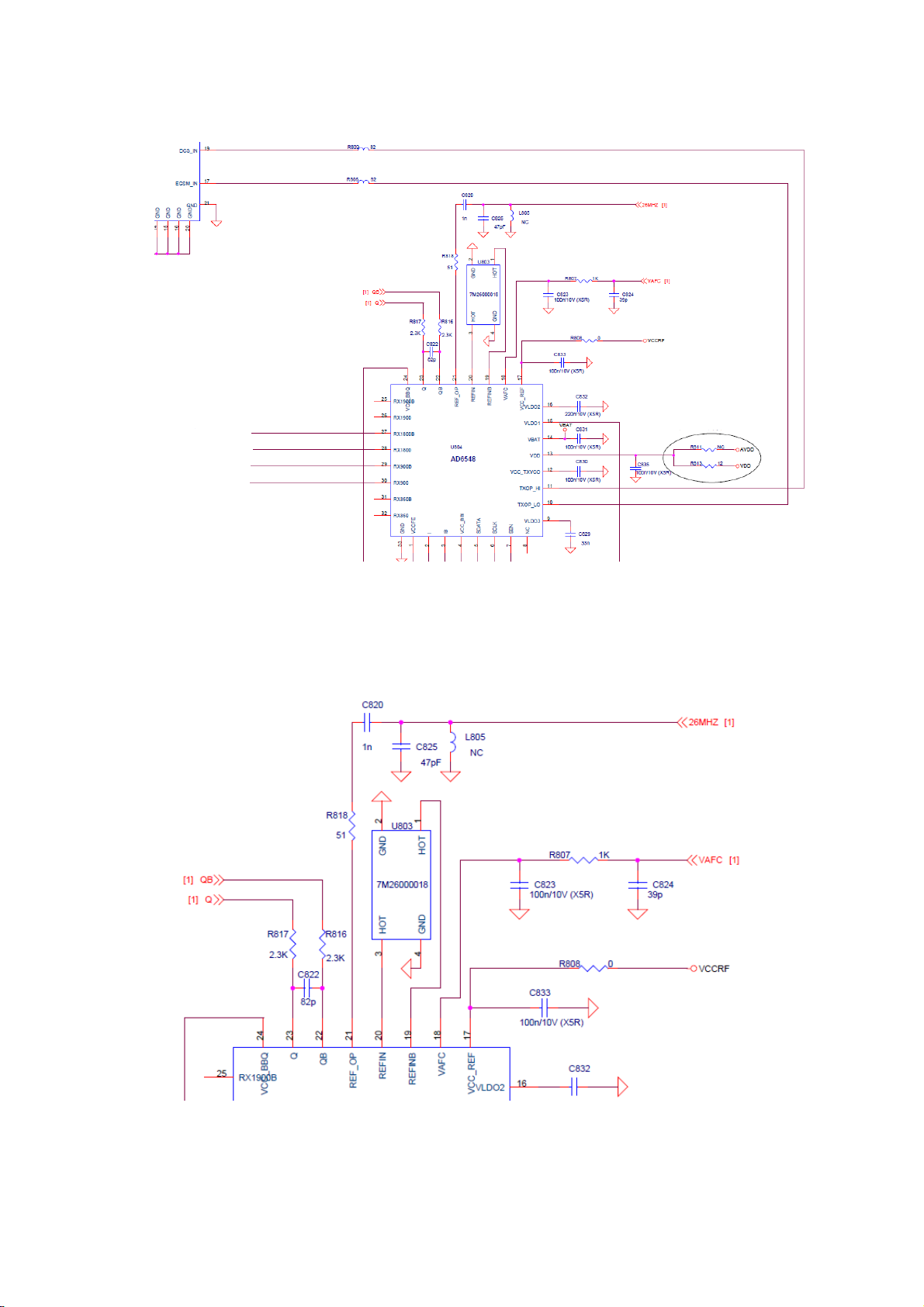
The schematic of RF block for MTK GSM Dual-band RF solution is show below:
From the chart we can see that the RF part is mainly composed of a highly integrated CMOS
Transceiver chip (AD6548), some RX Saw filters, reference crystal oscillator, power a
Antenna switch module, antenna a
3.1.2 Direct Convers
–Differential LNA RX Channel Select Filters–Integrated Active
–Programmable Gai
e