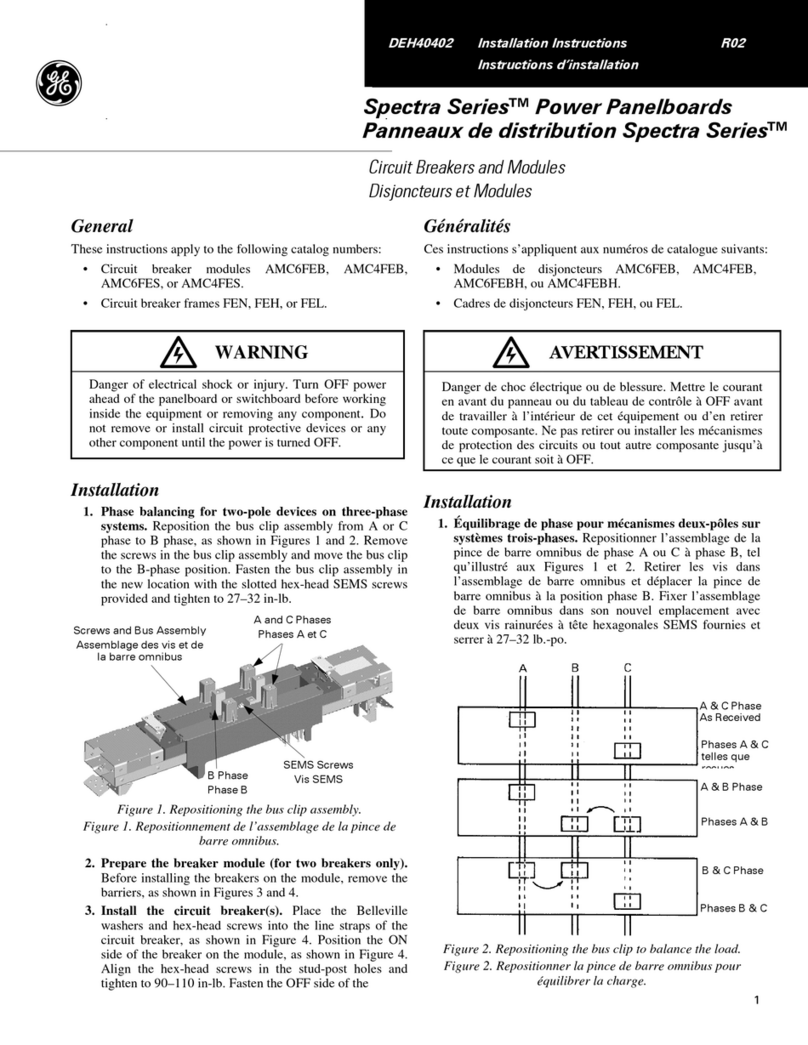
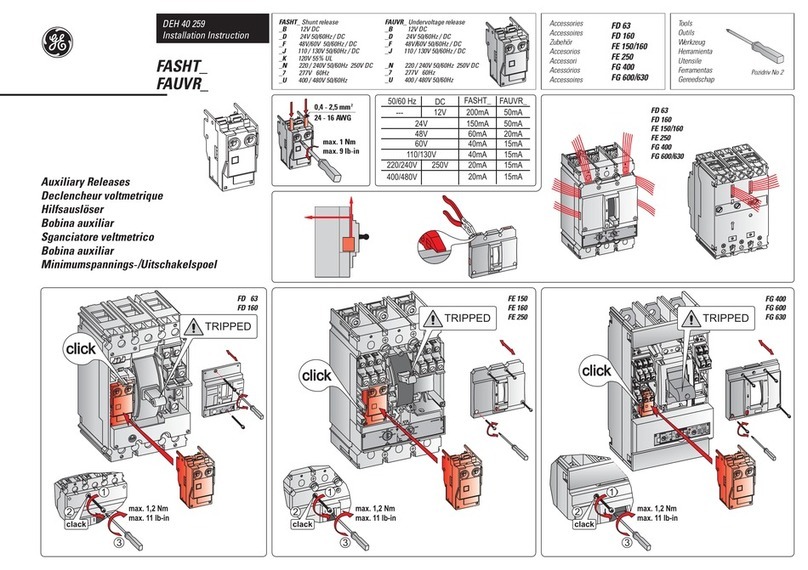
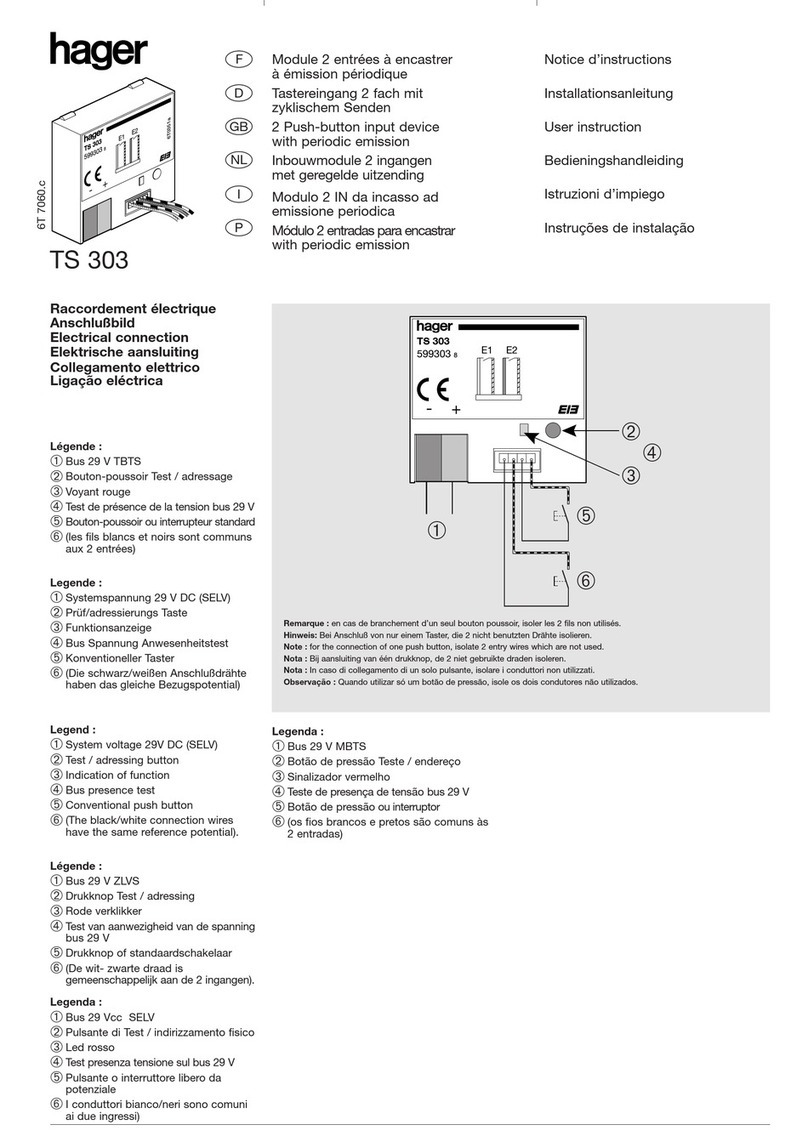
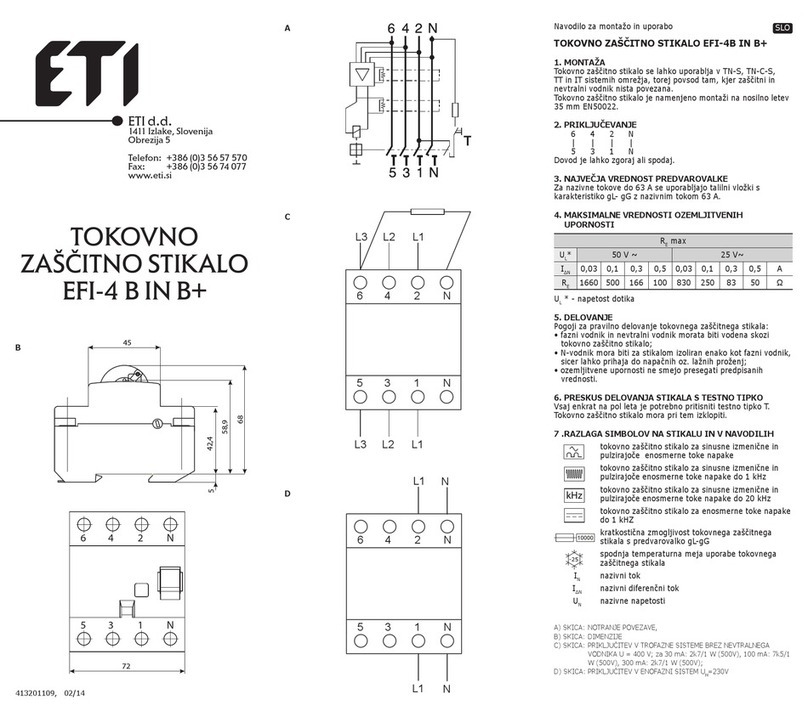
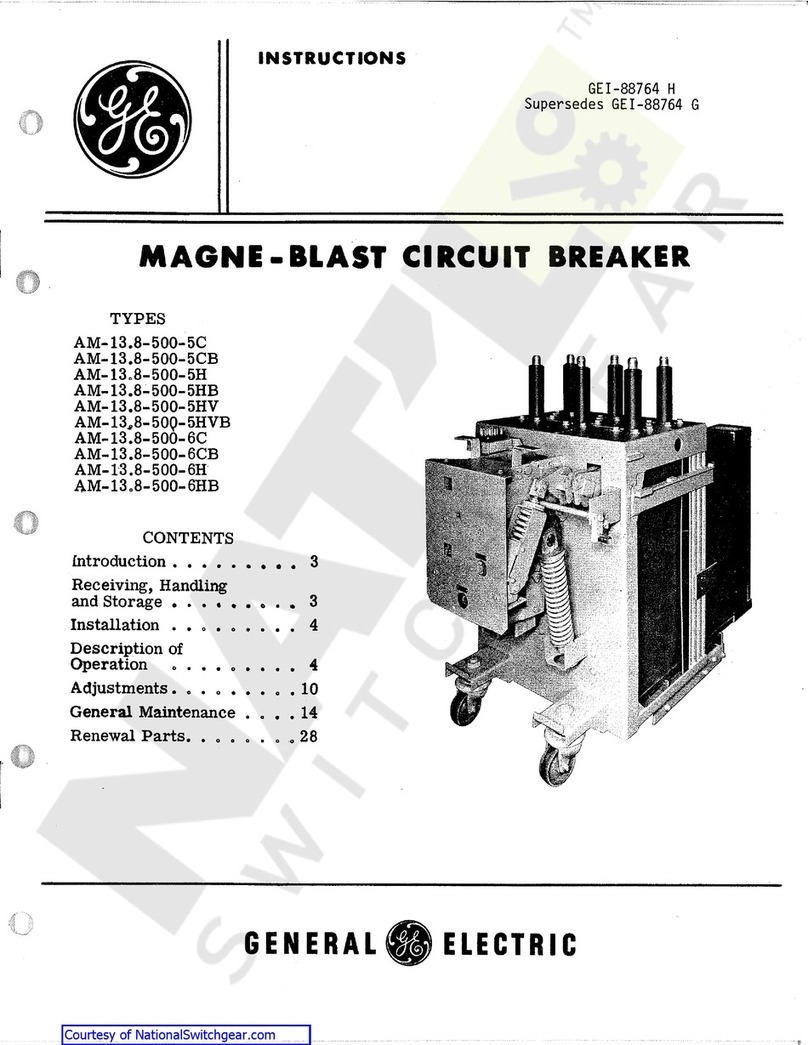
PowerVac®5kV Vertical Lift
Table of Contents
5
List of Figures
1. View of the 5kV ‘VL’ Breaker with Front Cover ............................................................................... 7
2. Hookinglifting eyes ........................................................................................................................... 8
3. ManualTrip & Close .......................................................................................................................... 9
4. PositiveInterlock ............................................................................................................................... 9
5. Rating Interference Bolt .................................................................................................................. 10
6. Positive Interlock system ................................................................................................................ 12
7. Manual charge handle ..................................................................................................................... 13
8. Primary Contact Insertion ............................................................................................................... 14
9. Primary contact penetration and wipe ........................................................................................... 15
10. MOCswitch ...................................................................................................................................... 16
11. Secondarydisconnect coupler........................................................................................................ 17
12. Front View of ML-19 Mechanism with Front Cover Removed ..................................................... 18
13. Charging & Trip system left side view ............................................................................................ 19
14. Manual Charging system right side view .......................................................................................19
15. Electrical Charging system right side view .................................................................................... 20
16. Closing linkageleft side view.......................................................................................................... 20
17. Opening spring & auxiliary switch left side view ........................................................................... 21
18. Wipe Spring assembly left side view ............................................................................................. 21
19. Typical ML-19mechanisminternalwiring connections ................................................................ 22
20. Typical breaker wiring diagram (Replacement for breakers with MS mechanisms................... 23
21. Typical breaker wiring diagram (Replacement for breakers with ML mechanisms ................... 24
22. Closing spring withgagtool inserted ............................................................................................. 25
23. Contact ErosionIndicator ................................................................................................................ 26
24. Primary contact erosion measurement-rear view ........................................................................ 26
25. Wipe indicator check and wipe measurement-rear view ............................................................. 27
26. Sample Operating Speed Graphs .................................................................................................. 33
27. Opening SpeedAdjustment............................................................................................................ 33
28. Travel Transducer Installation (Part#0144D1235G00X)............................................................... 34
29. Wipe Insulator.................................................................................................................................. 35
30. Contact GapAdjustment—OpeningBuffer.................................................................................... 36
31. Contact Gap measurement, wipe indicator check and wipe measurement ................................ 36
32. Trip coil gapadjustment .................................................................................................................. 37
33. Tripcoil buttonwithgage ................................................................................................................ 37
34. Tripcoilassembly ............................................................................................................................ 37
35. Close coilassembly-frontview ....................................................................................................... 38
36. Close coil gapadjustment-front view ............................................................................................. 38
37. SM/LS & CHG switch adjustment-left side view............................................................................ 39
38. CL/MS andpositiveInterlock switchadjustment-right sideview ................................................. 39
39. Positive Interlock ............................................................................................................................. 40
40. Adjustment of MOCSwitch/PlungerInterlock................................................................................ 41
41. Toggle Linkage Positions ................................................................................................................. 42
41A ToggleLinkagePositions (ViewfromRight Side) .......................................................................... 42
42. Toggle Linkage Positions(Viewfrom Right Side) .......................................................................... 42
42A ToggleLinkagePositions (ViewfromRight Side) .......................................................................... 42
43. Pole Assembly ................................................................................................................................. 44
44. TripCoiland Linkage(ClosingSpring Removed) .......................................................................... 46
45. Front View of ML-19 Breaker Mechanism (Lower)....................................................................... 48
46. Front View of ML-19 Breaker Mechanism (Upper) ....................................................................... 49
47. Motor Cutoff Switch ........................................................................................................................ 50
48. ClosingSpringGag .......................................................................................................................... 50
49. Front View of ML-19 Mechanism with Front Cover Removed ..................................................... 51
50. Schematic of ML-19 Mechanism .................................................................................................... 52
51. Typical stationary structure wiring ................................................................................................. 56
52. Electrical schematic diagram for vertical lift elevating mechanism ............................................ 57
53. Positive interlock M-26 units ........................................................................................................... 59
Appendix A .............................................................................................................................................. 63
List of Tables
1. Measurements .................................................................................................... 43
2. Adjustments........................................................................................................ 43
3. ML-19 Control Devices and Voltages................................................................ 47
4. Elevating Motor Troubleshooting...................................................................... 57
Trouble Reporting Form.......................................................................................... 66-67
Courtesy of NationalSwitchgear.com