7
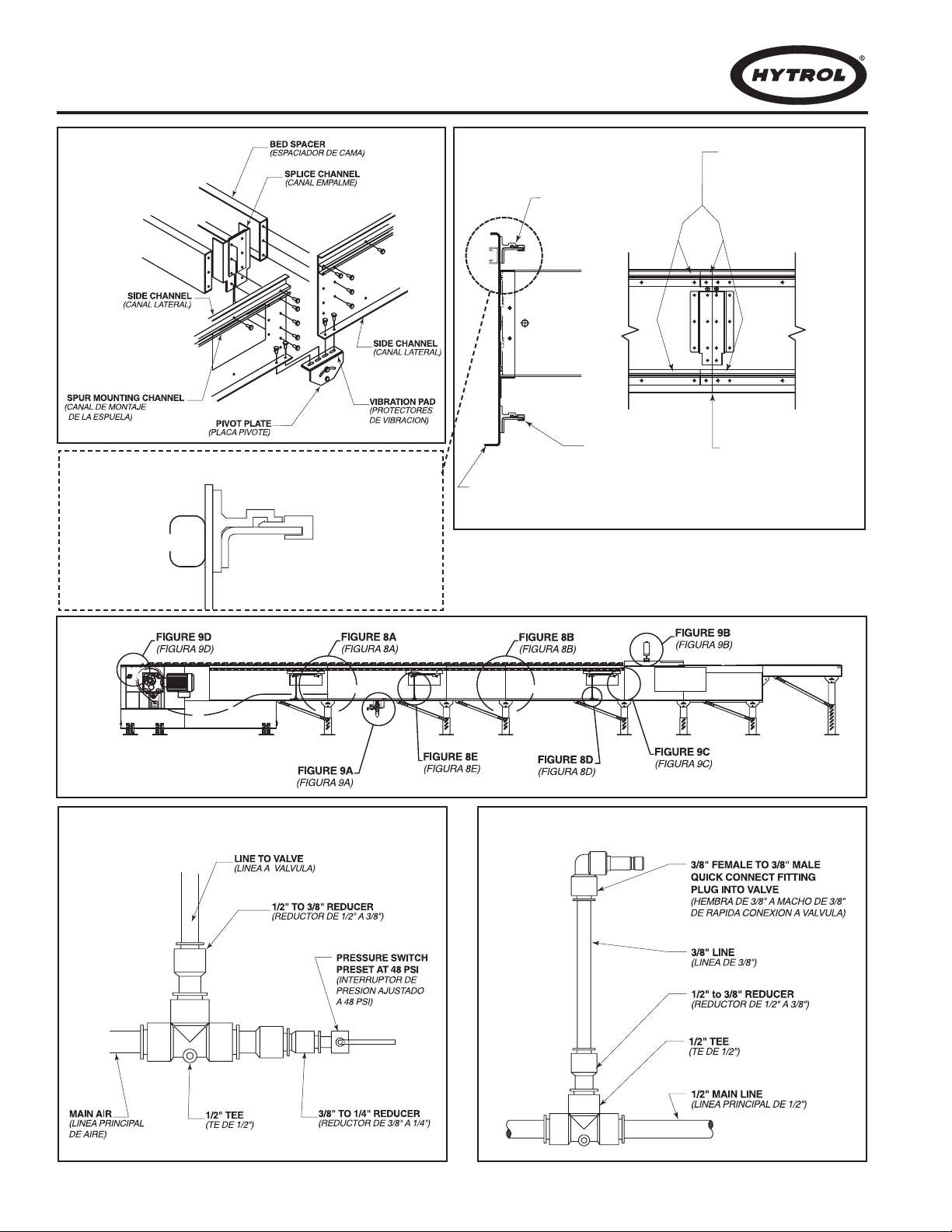
Mark a chalk line on floor to locate center of the conveyor.
Attach supports and vibration pads to all conveyor sections
shown in Figures 6A and 8A. Adjust elevation to required
height. Hand tighten bolts only at this time.
During installation, check to make sure each bed section is
square. Measure the diagonals from corner to corner of the
frame. If they are not equal the frame must be squared. Attach
a come-along or some other suitable pulling device across
longest corners and pull until the section is square.
Place the infeed (tail) section in position.
Install remaining sections, placing end without support on
extended pivot plate of previous section (Figure 6A).
Fasten sections together with splice plates and pivot plates.
(Figure 8A). Hand tighten bolts only at this time.
Check to see that conveyor is level across the width and length
of unit. Adjust supports as necessary.
After all sections have been squared and levelled, tighten all
splice channels and support mounting bolts and lag support to
the floor.
Check alignment of wearstrip at all section joints. Sand
wearstrip as necessary to provide a smooth wear surface
(Figure 8B).
Starting on the infeed end, fasten bearing profile to wearstrip
guide using rubber mallet to force the profile edge under the
wearstrip (Figure 8B). Glue infeed end of profile to the support
angle with loctite # 401 or 454 adhesive.
Fasten 1/2” main air line to bottom of conveyor channel with
cable ties (Figures 8C & 9A). Connect 3/8”air lines at divert
switches as shown in Figures 8D & 8E.
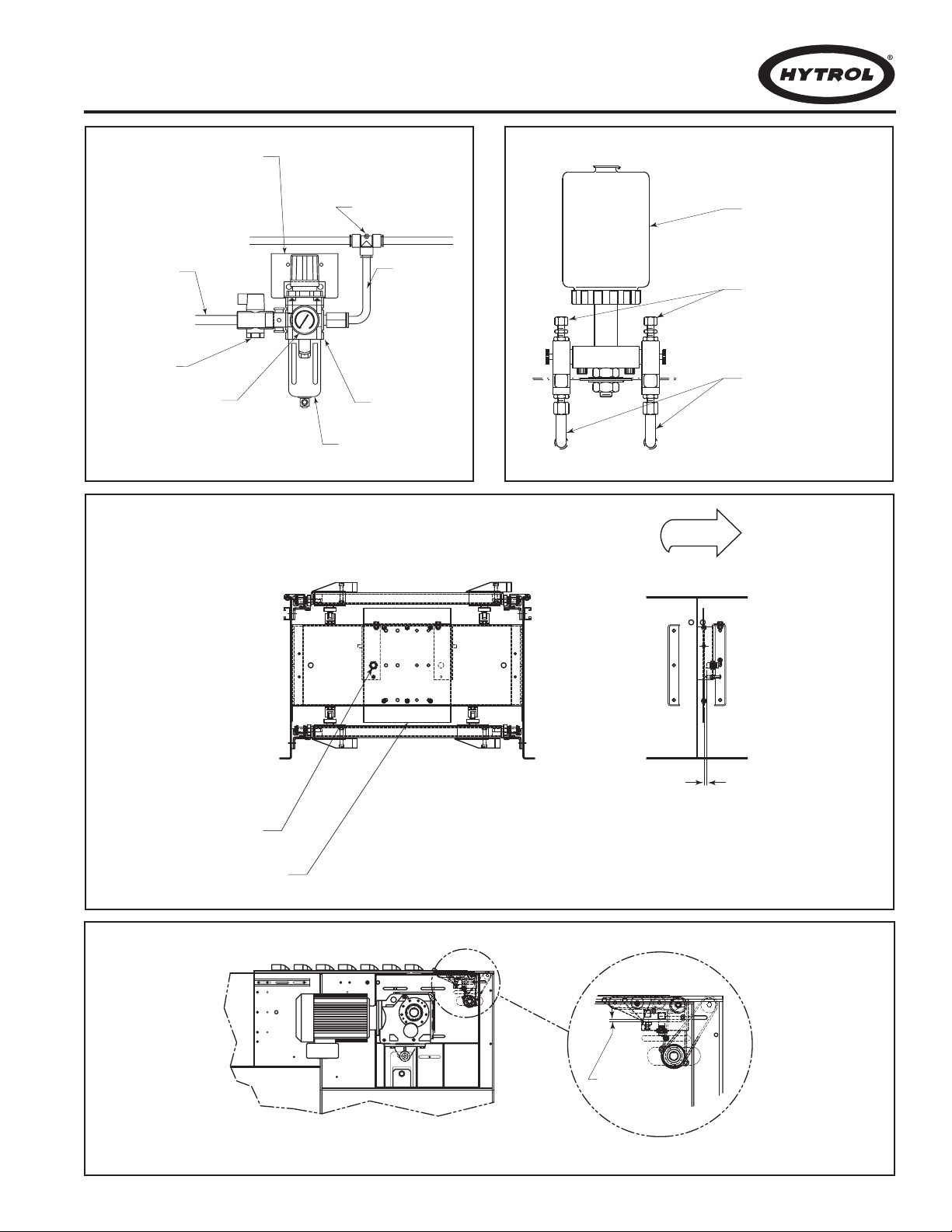
Connect main air line to the Filter/Regulator, (Figure 9A) Set
regulator to working pressure of 60 P.S.I. Install low pressure
switch, at farthest point from regulator (Figure 8D).
Install electrical controls and wire motor. Verify correct motor
rotation at this time. See Page 10 for electrical control
information.
Check each divert switch to see that it is operating properly.
This must be done before carrying chains are installed. See
instructions on Page 20.
Check proximity switch clearance at each internal safety switch
(Figure 9C). Adjust if necessary.
Install carrying chains per instructions on Page 22.
Adjust pop-up roller assembly at discharge end to optimize
transition of packages from the ProSort to the take away
conveyor. Set pop-up roller proximity switch per Figure 9D.
Install chain oiler at infeed and connect to oil lines as shown in
Figure 9B. Refer to the Lubrication section, page 13 for type of
oil required. After mounting, the oiler will need to be adjusted
for proper oiling of mounting chains. Adjustment may be made
using a combination of solenoid activation time and flow
adjustment screws. (A good rule of thumb for solenoid
adjustment is to turn the oiler on for one complete chain
revolution for every 2 hours of sorter operation.) The chain on
the divert side will typically need slightly more oil which may be
accomplished using the flow adjustment screws. CAUTION:
Do not allow oil to drip on floor.
Locate spurs per instructions on Page 24.
1. . .
2. . .
3. . .
4. . .
5. . .
6. . .
7. . .
8. . .
9. . .
10. . .
11. . .
12. . .
13. . .
14. . .
15. . .
16. . .
17. . .
18. . .
19. . .
Marque con tiza una línea en el suelo para ubicar el centro del
transportador.
Una los soportes y los protectores de vibración a las secciones (Figuras 6A
y 8A).Ajústelos a la altura requerida.Apriete los tornillos manualmente.
Durante la instalación revise que cada sección de cama esté escuadrada.
Durante la instalación, revise que cada sección de transportador está
escuadrada. Mida las diagonales de esquina a esquina del marco y
escuadre si es necesario. Utilice un tirante de escuadre o algo similar para
escuadrar la sección.
Ponga la sección del extremo alimentador (cola) en posición.
Instale las secciones restantes poniendo el extremo sin soporte en la placa
pivote de la sección anterior (Fig. 6A).
Sujete las secciones con placas de unión y pivote (Fig 8A).Apriete los tornillos
manualmente.
Revise si el transportador esta nivelado a lo ancho y largo de la unidad.
Ajuste los soportes como sea necesario.
Después de que todas las secciones hayan sido escuadradas y niveladas
apriete los empalmes de extremo y los tornillos de montaje del soporte.
Ancle el soporte al suelo.
Revise la alineación de las guías de cadena en todas las uniones. Lije las
guías lo necesario para obtener una superficie suave (Fig. 8B).
Empezando desde el extremo alimentador asegure el perfil del rodamiento
a la guía de la cadena usando un martillo de hule para forzar el perfil
debajo de la guía (Fig.8B).Pegue el perfil del extremo alimentador al ángulo
de soporte con el adhesivo loctite # 401 o 454.
Sujete la línea principal de aire de 1/2” a la parte inferior del canal del
transportador con cables de unión (Fig. 8C). Conecte las líneas de aire de
3/8” a los en los interruptores desviadores (Fig. 8D & 8E).
Conecte la línea principal de aire al Filtro/Regulador (Fig. 9A ). Ajuste el
regulador a una presión de 60 PSI. Instale el interruptor de baja presión lo
más alejado posible del regulador (Fig. 8D).
Instale controles eléctricos y el cableado del motor. Verifique la correcta
rotación del motor.Ver Pag. 10 para información eléctrica.
Revise cada interruptor desviador asegurándose de que funcione
correctamente. Esto debe hacerse antes de instalar las cadenas.Ver Pág.20.
Revise que el interruptor de proximidad esté despejado en cada terminal
de seguridad (Fig 9C).Ajuste si es necesario.
Instale las cadenas; instrucciones en la Pag. 22.
Ajuste el ensamble pivote de los rodillos de transición en la zona de
descarga para optimizar la transición de paquetes del ProSort al
transportador saliente. Ajuste el interruptor de proximidad del ensamble
pivote (Fig. 9D).
Instale el lubricador de cadena en el extremo alimentador y conecte a las
líneas de aceite (Fig.9B).Refiérase a la sección de lubricación (Pág. 13) para
el tipo de aceite requerido. Después de instalado, el lubricador necesita ser
ajustado para la apropiada lubricación de las cadenas. Se puede ajustar
combinando el ciclo de activación del solenoide y los tornillos de ajuste del
flujo. (para un buen ajuste del solenoide, el lubricador debe activarse
durante una revolución completa de cadena cada 2 hrs de operación del
sorter). La cadena del lado desviador usualmente necesita más aceite que
puede suministrarse por medio de los tornillos de ajuste del flujo.
PRECAUCION: No permita que el aceite gotee en el piso.
Coloque las espuelas. Instrucciones en la página 24.
● Conveyor Set-Up ● Montaje
1. . .
2. . .
3. . .
4. . .
5. . .
6. . .
7. . .
8. . .
9. . .
10. . .
11. . .
12. . .
13. . .
14. . .
15. . .
16. . .
17. . .
18. . .
19. . .