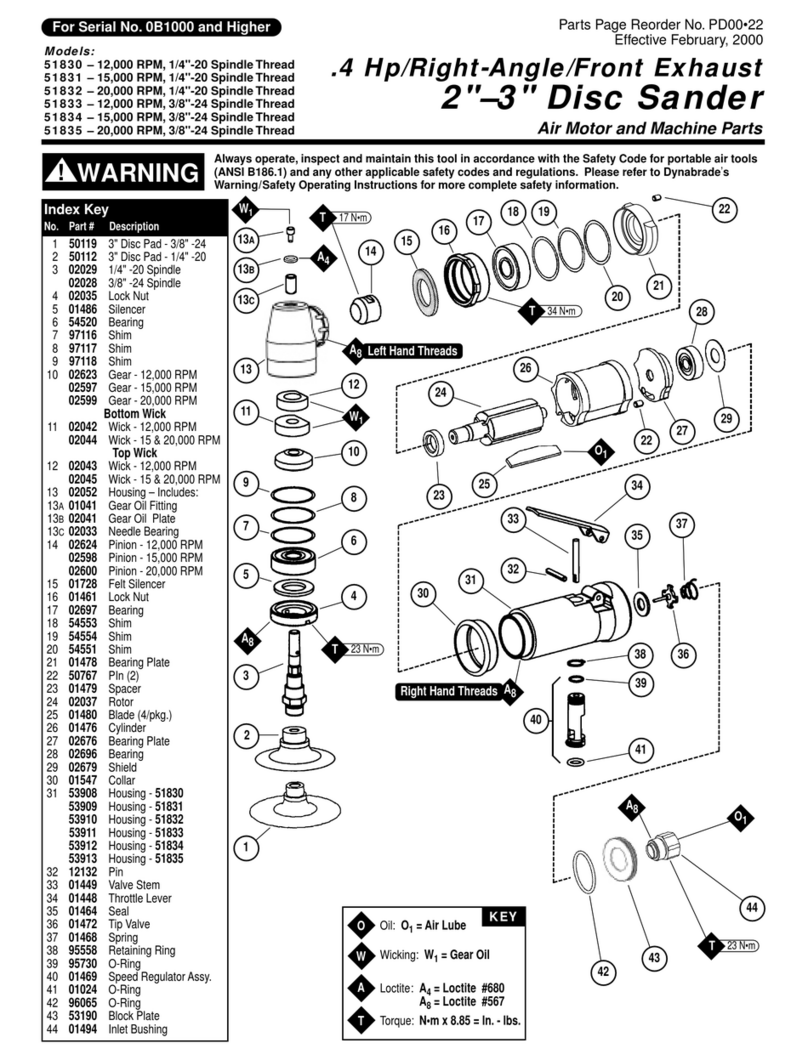
8Mirka® AIROS • 77 mm (3"), 125 mm (5") & 150 mm (6") • Electrical manual Mirka® AIROS • 77 mm (3"), 125 mm (5") & 150 mm (6") • Electrical manual 9
Input registers (F4)
Address Data type Name Description
30001 Uint16 Drop RPM count The number of times the speed has dropped from
set-point by more than 25%.
30002 Uint16 Warm tool count The number of times the tool temperature has
exceeded the “warm” limit, 79°C.
30003 Uint16 Warm motor drive count The number of times the motor drive temperature has
exceeded the “warm” limit, 73°C.
30004 Uint16 Hot tool count The number of times the tool temperature has
exceeded the “hot” limit, 134°C.
30005 Uint16 Hot motor drive count The number of times the motor drive temperature has
exceeded the “hot” limit, 117°C.
30006 Uint16 Stop tool count The number of times the tool temperature has
exceeded the “stop” limit, 142°C.
30007 Uint16 Stop motor drive count The number of times the motor drive temperature has
exceeded the “stop” limit, 123°C.
30008 Uint16 Voltage out of range count The number of times the input voltage has not been
within 44 to 52 VDC.
30009 Uint16 Over-current low count The number of times the current has exceeded 15.1 A.
30010 Uint16 Over-current medium count The number of times the current has exceeded 18.2 A.
30 011 Uint16 Usage count long The number of times the run time has been more than
60 seconds.
30012 Uint16 Usage count medium The number of times the run time has been between
20 and 60 seconds.
30013 Uint16 Usage count short The number of times the run time has been less than
20 seconds.
30014 Uint16 Usage time hours Hours part of usage time.
30015 Uint16 Usage time minutes Minutes part of usage time.
30016 Uint16 Usage time seconds Seconds part of usage time.
30017 Int16 Average current Average current in mA.
30018 Uint16 Average speed Average speed in RPM.
30019 Uint16 Tool temperature Tool temperature in °C.
30020 Uint16 Motor drive temperature Motor drive temperature in °C.
30021–30030 Char[20] Firmware version Firmware version and build date, e.g. “2.0 Jan 18 14:00”.
30031–30040 Char[20] Part version Part version and motor drive serial number, e.g. “AI1.3
123456”.
30041–30046 Char[12] Product serial number Product serial number, e.g. “749474379001”
30047 Uint16 Alarm status flag Alarm status flag can hold one of the following values
at any given time. This flag is automatically cleared
after 5 seconds if the cause of the alarm trigger is no
longer present.
0x0000 = Not triggered
0x0001 = Tool overheated
0x0002 = Motor drive overheated
0x0004 = Over-current
0x0008 = Under-voltage
0x0010 = Over-voltage
0x0020 = Self-test running
0x0040 = RPM drop
0x0080 = High current
0x0100 = Tool change in progress
0x0200 = Possible tool wiring fault
0x0400 = Factory reset mode