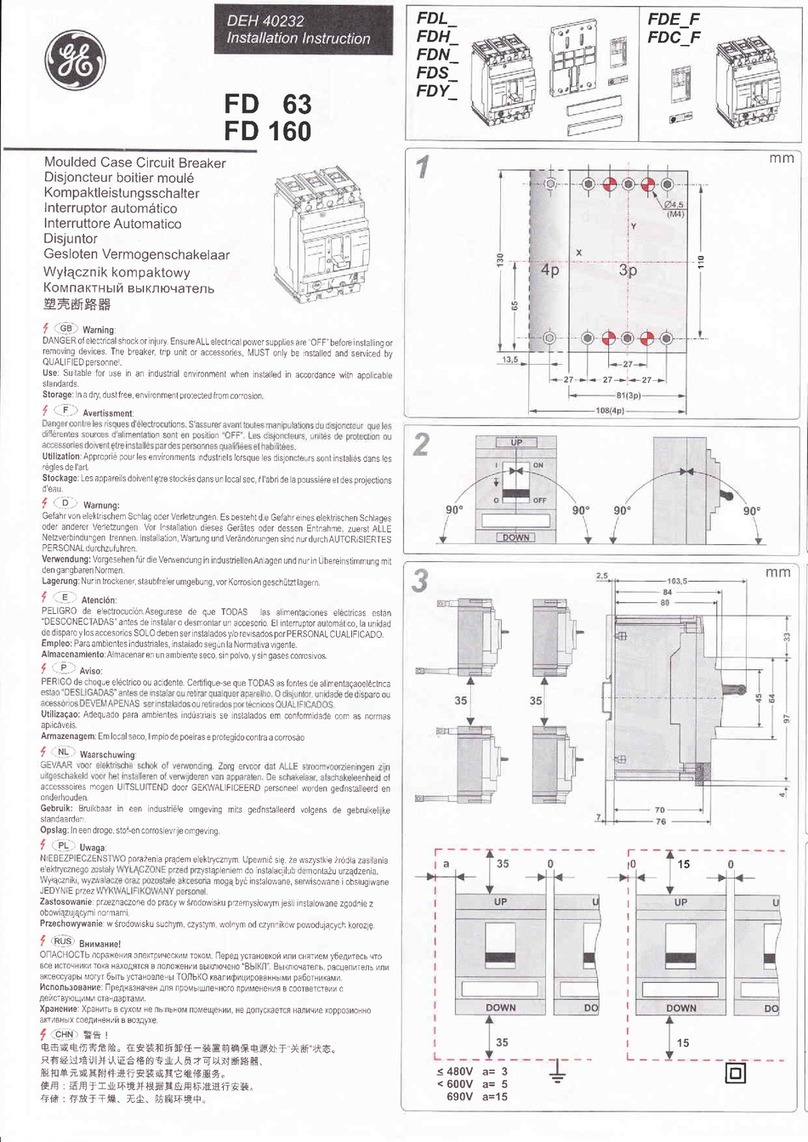
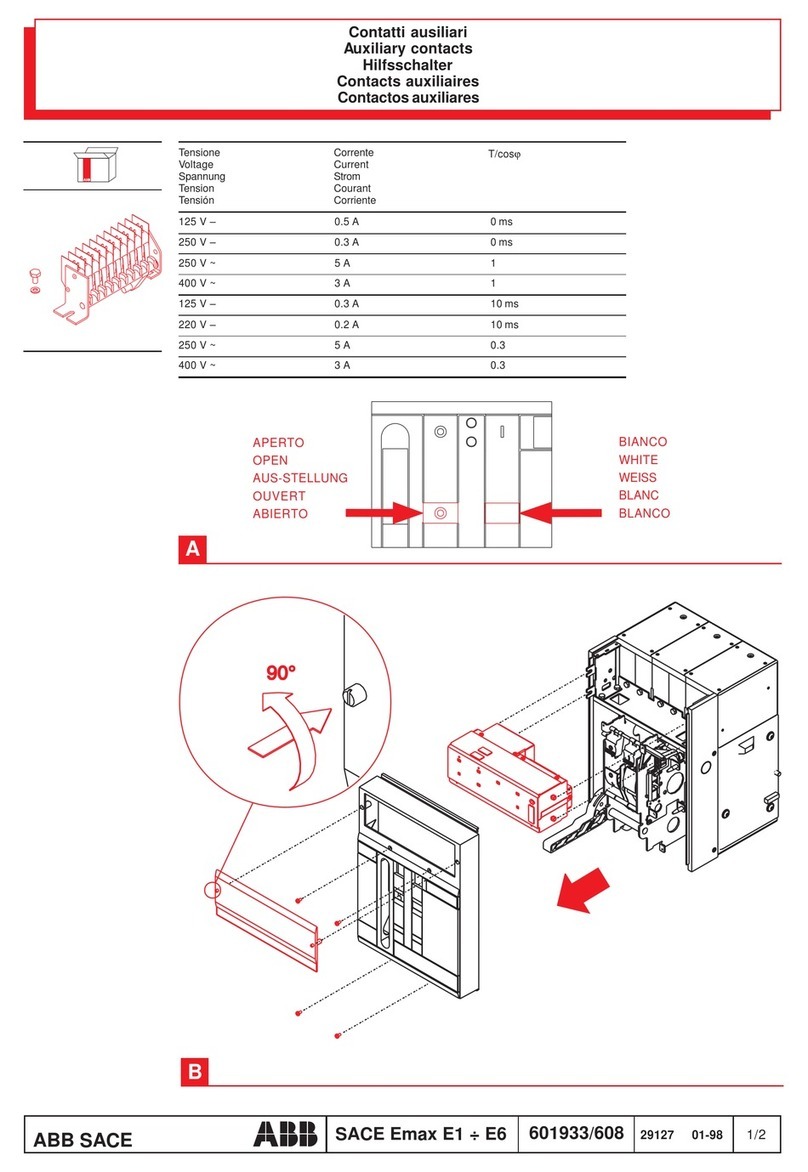
GE AK-50 Series Technical specifications
Other GE Circuit Breaker manuals

GE
GE FK800 User manual

GE
GE Power Break II User manual
GE
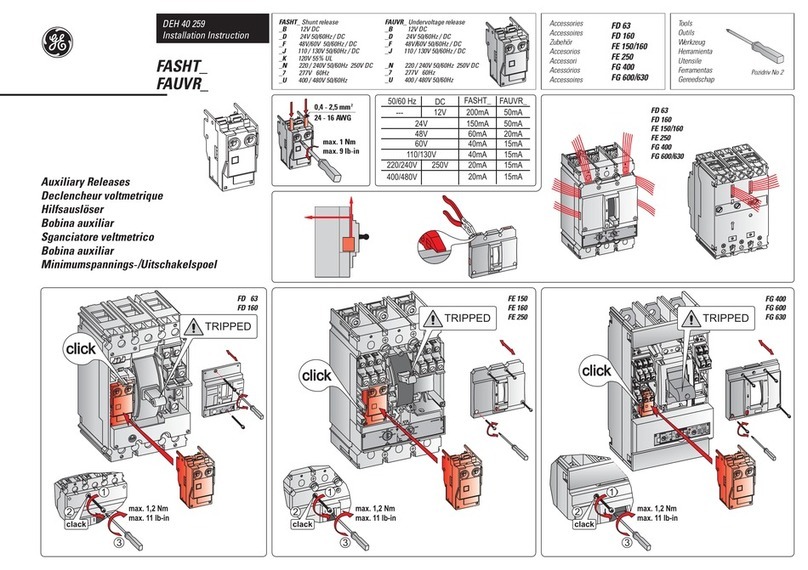
GE FASHT Series User manual

GE
GE GCCC024DR User manual
GE
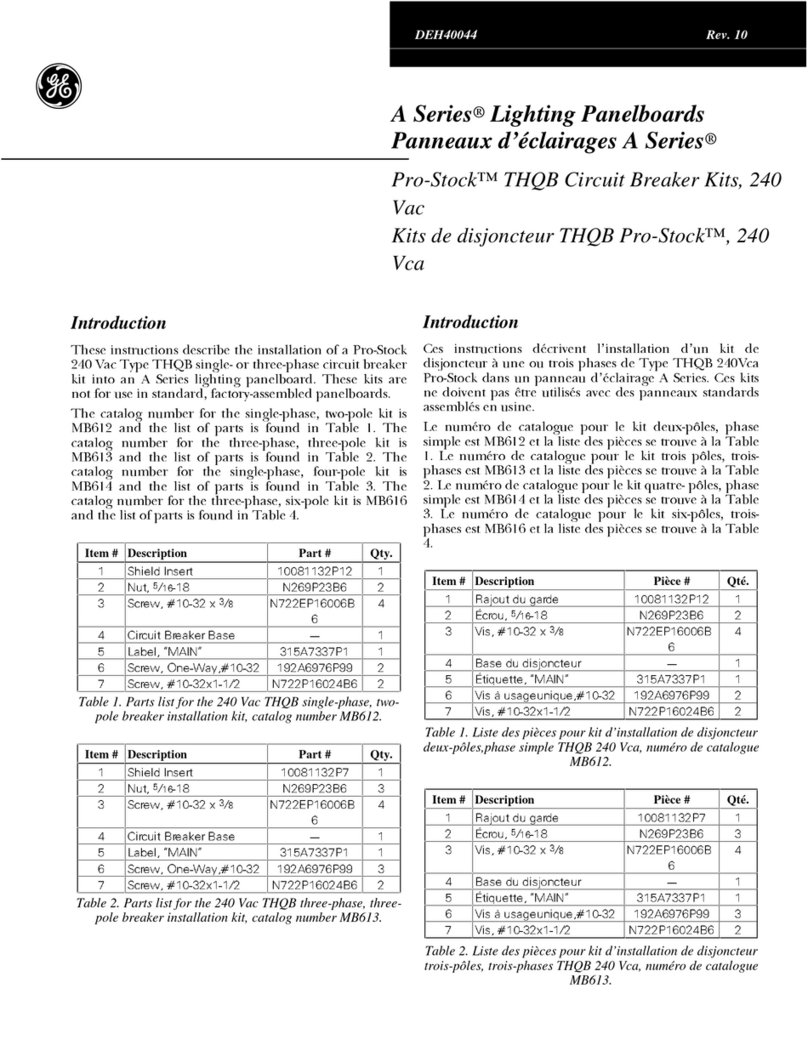
GE A Series Pro-Stock THQB User manual
GE
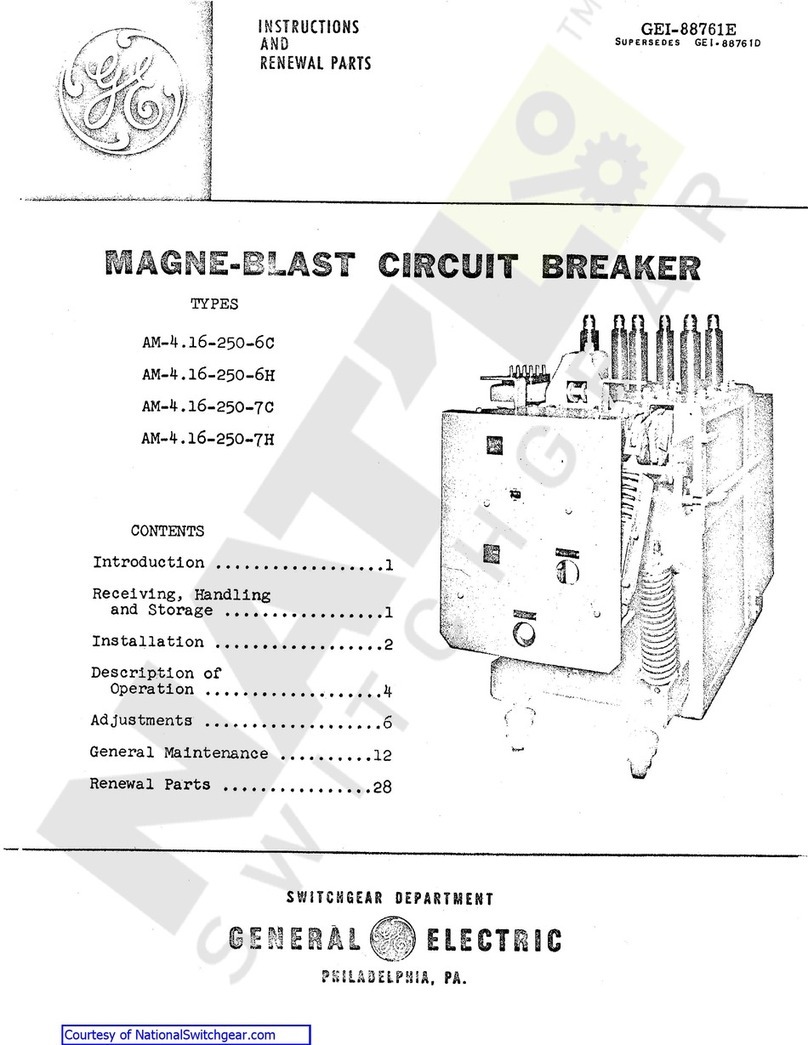
GE AM-4.16-250-6C User manual

GE
GE Power Break II User manual

GE
GE MicroVersaTrip Plus User manual

GE
GE Power Break II User manual
GE
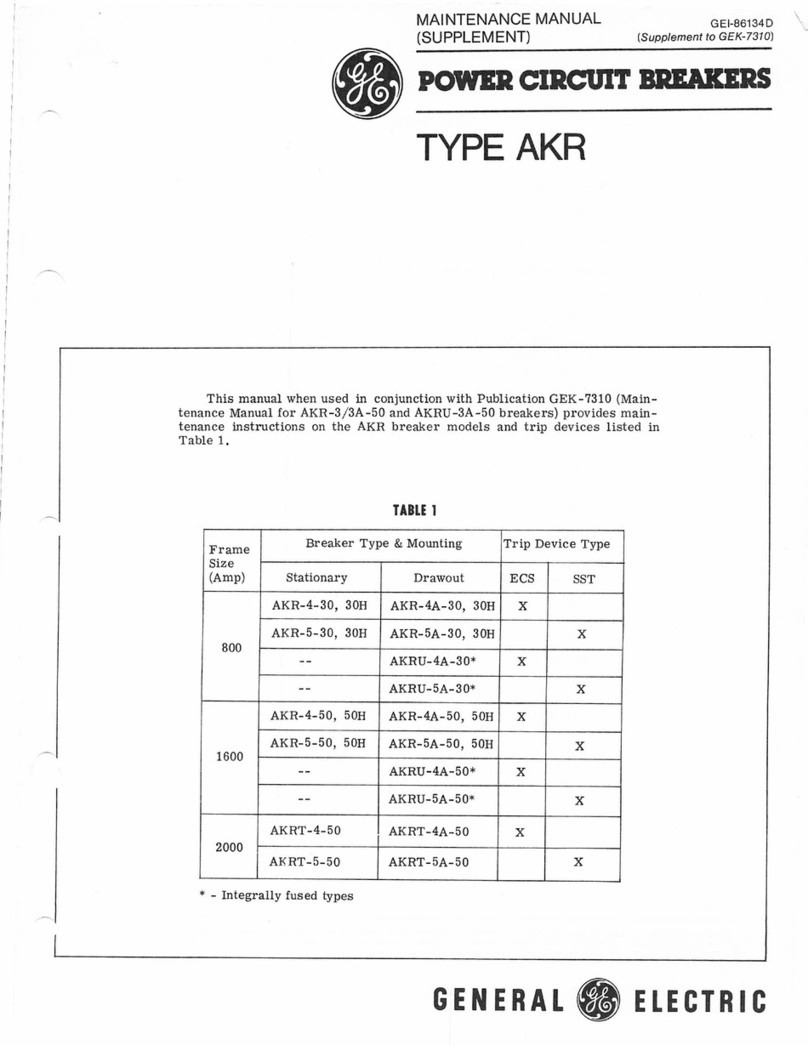
GE AKR Series Configuration guide
Popular Circuit Breaker manuals by other brands

Siemens
Siemens Sentron 3VA9157-0PK1 Series operating instructions
hager
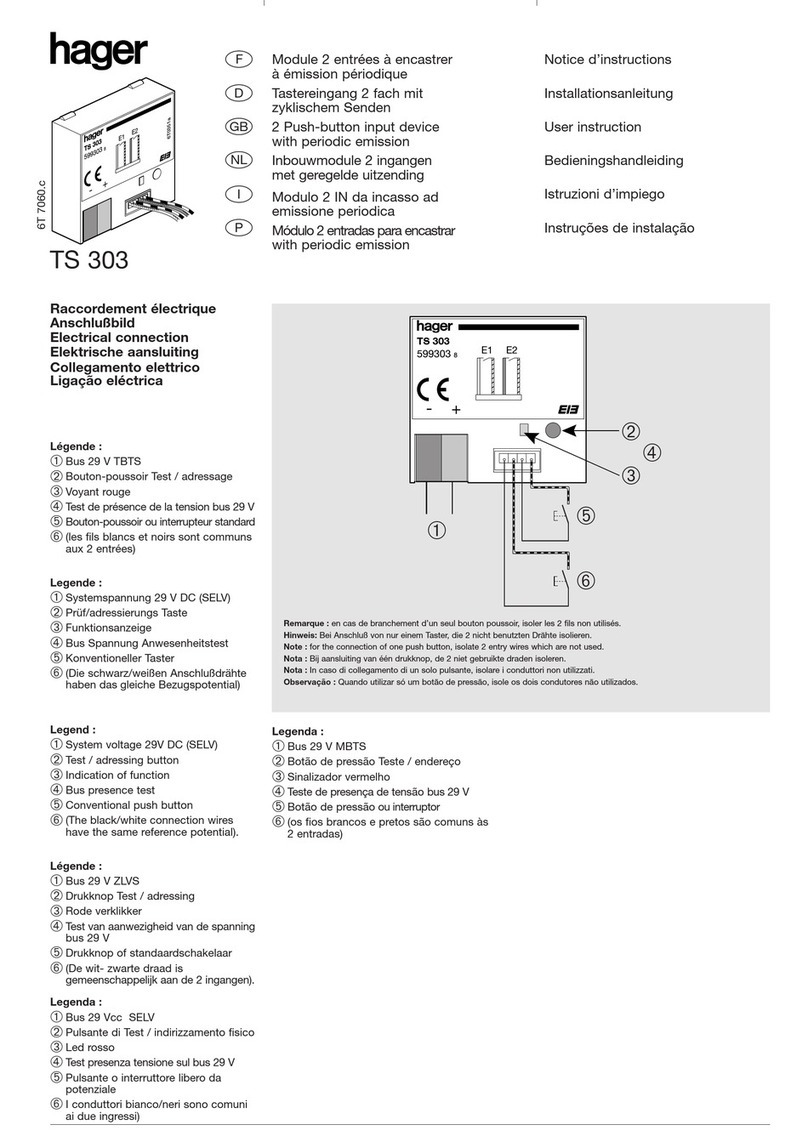
hager TS 303 User instruction
ETI
ETI EFI-4B Instructions for mounting

nader
nader NDM3EU-225 operating instructions
TERASAKI
TERASAKI NHP TemBreak PRO P160 Series installation instructions

Gladiator
Gladiator GCB150 Installation instruction