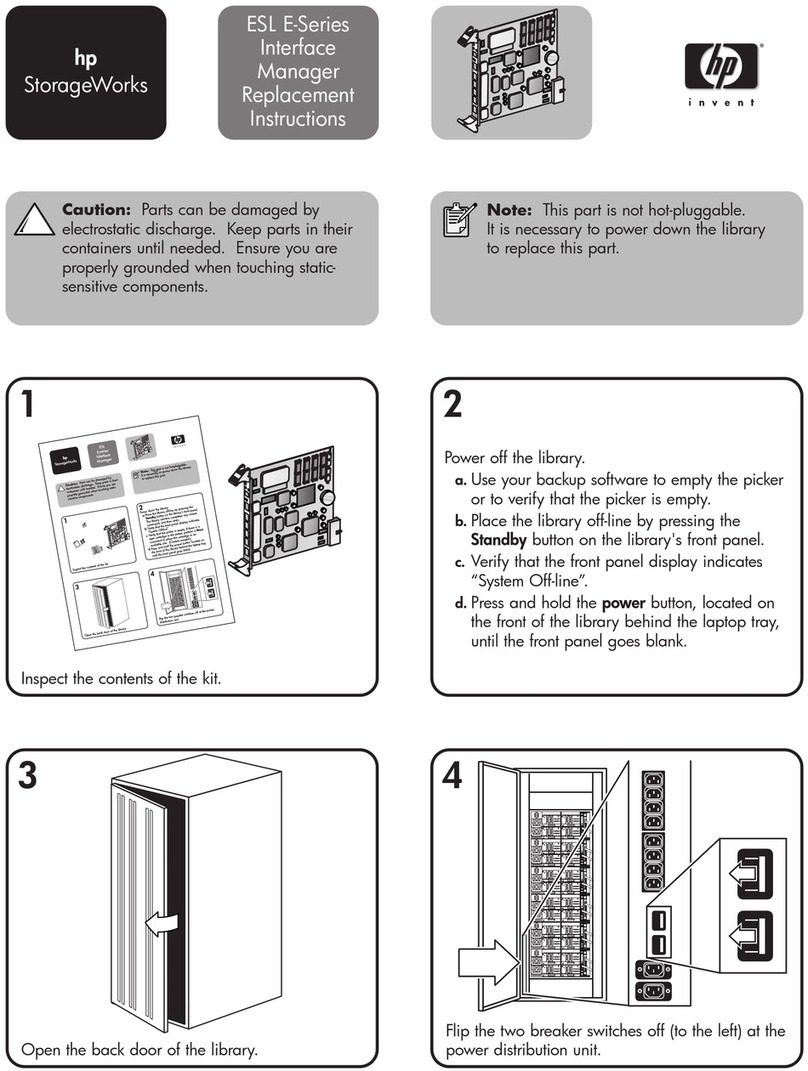
Figures
Figure 1. HP E2466C Preprocessor Interface 1–iii
Figure 2. Switches for State/Timing Mode and Clock Qualifier 1–6
Figure 3. Removing the S.E.C. Cartridge 1–7
Figure 4. Disassembling the S.E.C. Cartridge 1–8
Figure 5. Probe Connection Overview 1–9
Figure 6. Aligning the Probe End 1–10
Figure 7. Securing the Preprocessor Connection 1–11
Figure 8. Preprocessor Connector Numbers and Pin A1 Location 1–12
Figure 9. Configuration Menu with Timing Mode 1–19
Figure 10. Pin locations for APIC and JTAG signals 1–21
Figure 11. Logic Analyzer Format Specification 2–4
Figure 12. Logic Analyzer Listing Display 2–8
Figure 13. Logic Analyzer Waveform Display 2–9
Figure 14. Listing Display with Boundary Error Message 2–12
Figure 15. Listing Menu Showing End of Boundary 2–13
Figure 16. HP 16505A Pentium II Filter Dialog 2–15
Figure 17. HP 16505A Pentium II Preferences Dialog 2–17
Figure 18. HP 16505A Listing window for Software Analysis 2–18
Figure 19. Reset Configuration 2–20
Figure 20. Signal Line Loading 3–5
Figure 21. HP E2466C Block Diagram 3–8
Figure 22. HP E2466C Dimensions 3–21
Tables
Table 1. LED Indicators for Operating Mode 1–6
Table 2. Pin locations for APIC and JTAG signals (J5 and J6 are reserved)
1–21
Table 3. Signal/Label List 2–5
Table 4. Pentium II Processor Transaction Type Symbols 2–7
Table 5. Reset Configuration 2–20
Table 6. Operating Characteristics 3–3
Table 7. Product Regulations 3–4
Table 8. CMOS Inputs 3–5
Table 9. Pentium II Processor Signal List 3–10
Table 10. Replaceable Parts 3–23
Contents
viii Preprocessor Interface for the Pentium II Processor