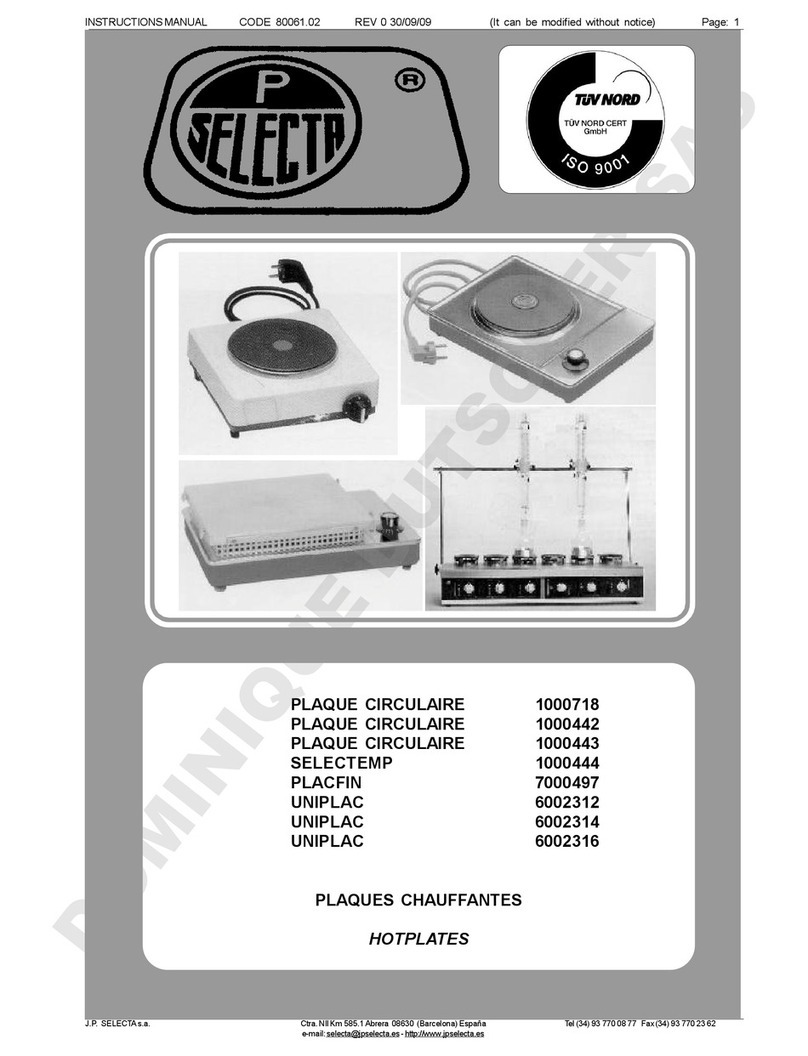
J.P.SELECTA, s.a.Ctra.NII Km585.1Abrera08630(Barcelona)EspañaTel 34937700877Fax 34937702362
e-mail: selecta@jpselecta.es -http://www.jpselecta.es
INSTRUCTIONMANUALCODE80137 REVB14/03/2008 (Can be modi ed withoutnotice)Pag.:3
2.-VOCABULARIO BÁSICO
CUBETA:
Contenedor devidriooplásticotransparente, deespesor
yprofundidad de nidos,parael análisis fotométricode
líquidos.Parala medición seintroduceenel portacubetas
delfotómetro.
FOTÓMETRO:
Aparatoelectrónicoquemide la atenuación de laintensi-
dadluminosaqueatraviesaellíquidocontenidoen lacu-
beta. Dichaatenuaciónesdebidaalaabsorcióndela luz
deunadeterminadalongitud deonda.La concentración
dela solución contenida enlacubetasemide mediantela
relación entre!aintensidad luminosaentranteysaliente.
LONGITUDDEONDA:
Laradiación luminosasepropaga enformade ondaspe-
riódicas. La longituddeondaesladistanciaentrepuntos
quetienenfasesigualesendosciclosconsecutivosde
unaonda periódica, segúnladireccióndepropagación
dela anda. Laluzvisibletiene una longitudde onda
comprendida entre380y780 nmque abarcatodoslos
coloresdel arcoirissiendo ¡osazulesen lasmáscortasy
e!rojoen lasondasmáslargas. Pordebajo de380 mm,
estamosen zonaultravioleta.
MUESTRA:
Pequeñascantidadesrepresentativas, extraídasdel
organismoodesusexcrecionespararealizar exámenes
bioquímicos, hematológicos, citológicosserológicoso
microbiológicos.
PLASMA:
Residuoacuosoprovenientede laseparación delos
componentescelularesde la sangrenocoagulada, por
ejemplo,por centrifugación.
SUERO:
Esel residuo acuosode la sangrecoagulada. Lasepara-
ción del coágulodelsueropuede hacersepor decanta-
ción ocentrifugación.
ENZIMAS:
Sonproteínasquecatalizan reaccionesbioquímicas
especí cas. Medimoslaactividadenzimáticaen condicio-
nesdereacción mantenidasconstantesyexactamente
de nidas. ElSustratodebetener unaconcentraciónalta,
elpH debe ser elóptimoparalareacciónylatempera-
turadebe ser pre jadaycontrolada estrictamente, los
enzimasmuestran una actividad mucho mayor a37 °C
quea30°C. Segúnel tipode enzimasidenti cadosen
los fluidospodemosdeducir eltipo decélula afectada.
2.-BASIC CONCEPTS
CELL:
Glassor transparentplasticcontainer, withathickness
anddepthpreciselyde ned, forthe fotometricanalysis
ofliquids. For themensuration it isintroducedintothe
photometer cell holder.
PHOTOMETER:
Electronicinstrument that measuresthelight intensity
acrosstheliquidthat isinthecell. This attenuation is
duetothe absorption of thelightat certainwavelength.
Theconcentrationof the solutioncontainedin the cellis
measured bymeansof thislight attenuation.
WAVELENGTH:
Thelightspreadsin formof periodicwaves. Thewave
lengthgivethe colour oftheligthand ismeassured in
nm(nano-meters). The visible light hasawavelength
among380and780nmthat itincludesallthe colorsof
therainbow beingyou bluein the shortestandandred in
thelongest waves. Below 380mm, weareinultraviolet
regionandover the780nmwearein the infra-red region.
SAMPLE:
Small representativequantities, extracted of theorganism
or of their excretionstocarryoutbiochemicalexams,
hematológicosor citológicos.
PLASMA:
Wateryresidualcomingfromtheseparationof thecellular
componentsof thenot coagulatedblood, forexample, for
centrifugación.
SERUM:
It isthe wateryresidualofthecoagulatedblood. The
separationofthe clot of the serumcan bemadeby
decantaciónor centrifugación.
ENZYMES:
Theyareproteinsthatcatalizanspeci cbiochemical
reactions. Wemeasurethe enzymaticactivity
under constant andexactlyde nedmaintained
reaction conditions.TheSustratoshouldhaveahigh
concentration, thepH it shouldbethegoodonefor
thereaction and thetemperatureshouldbepresetand
controlledstrictly, the enzymesshow amuchbigger
activityto37 °C that to30°C. Accordingtothetype of
enzymesidenti edinthe fluidswecan deducethe type
ofaffected cell.